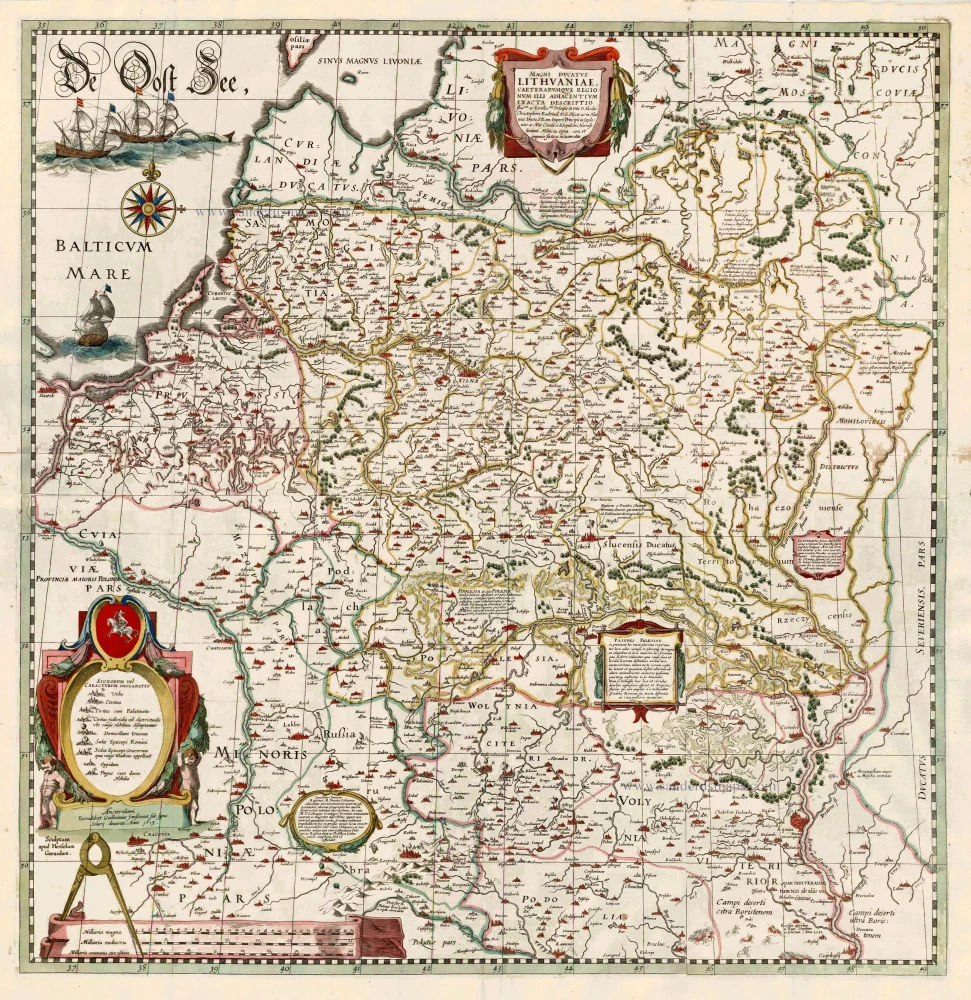
Lithuania by Willem Blaeu 1643
The original of this map was made during the last decade of the sixteenth century by the efforts of prince Nikolaj Krzystof Radziwill (Radvillas 1549-1616) and was a collaborative effort. Only the name of the draughtsman, Tomasz Makowski, is known. Alexandrowicz (1989) assumes that a first (now lost) printed state existed before 1604, of which the printing plate is no longer extant. The second plate of the map was engraved by Hessel Gerritsz and published by Blaeu. Blaeu changed the arrangement of the map sheets; he separated the map of the river Dniepr from the map of Lithuania. The first atlas edition (1631) has printed Latin text on the back; from 1634, the map was included in the atlas without text on the back.
The Blaeus: Willem Janszoon, Cornelis & Joan
Willem Jansz. Blaeu and his son Joan Blaeu are the seventeenth century's most widely known cartographic publishers.
Willem Jansz. (also written Guilielmus Janssonius) = Willem Janszoon Blaeu was born in Uitgeest (Netherlands), near Alkmaar, in 1571. He studied mathematics under Tycho Brahe and learned the theory and practice of astronomical observations and the art of instrument- and globe-making.
In 1596, he came to Amsterdam, where he settled down as a globe-, instrument- and map-maker. He published his first cartographic work (a globe) in 1599 and probably published his first printed map (a map of the Netherlands) in 1604. He specialised in maritime cartography, published the first edition of the pilot guide Het Licht der Zeevaert in 1608, and was appointed Hydrographer of the V.O.C. (United East India Company) in 1633. After publishing books, wall maps, globes, charts and pilot guides for thirty years, he brought out his first atlas, Atlas Appendix (1630). This was the beginning of the great tradition of atlas-making by the Blaeus.
In 1618, another mapmaker, bookseller and publisher, Johannes Janssonius, established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu's shop. No wonder these two neighbours began accusing each other of copying and stealing their information and became fierce competitors who did not have a good word to say about each other. In about 1621 Willem Jansz. decided to end the confusion between his name and his competitor's and assumed his grandfather's nickname, 'blauwe Willem' ('blue Willem'), as the family name; after that, he called himself Willem Jansz. Blaeu.
Willem Janszoon Blaeu died in 1638, leaving his prospering business to his sons, Cornelis and Joan. We only know that Cornelis's name occurs in the prefaces of books and atlases until c. 1645.
Joan Blaeu, born in Amsterdam in 1596, became a partner in his father’s book trade and printing business. 1638, he was appointed his father’s successor in the Hydrographic Office of the V.O.C. His efforts culminated in the magnificent Atlas Major and the town books of the Netherlands and Italy – works unsurpassed in history and modern times, giving eternal fame to the name of the Blaeu's.
On February 23, 1672, a fire ruined the business. One year later, Dr Joan Blaeu died. The fire of 1672 and the passing away of the director gave rise to a complete sale of the stock of the Blaeu House. Five public auctions dispersed the remaining books, atlases, copperplates, globes, etc., among many other map dealers and publishers in Amsterdam. The majority was acquired by several booksellers acting in partnership.
In the succeeding years, the remaining printing department was left in the hands of the Blaeu family until 1695, when the printing house's inventory was sold at a public auction. That meant the end of the Blaeu's as a printing house of world renown.
Hessel Gerritsz. (1580/81 – 1632)
Hessel Gerritsz. was one of the seventeenth century's most influential and innovative map makers. He was born in Assum in North Holland and attended Alkmaar school. He must have known Willem Jansz. (= Willem Blaeu) who stayed in Alkmaar for several years. Later, he moved to Amsterdam for his further education.
After the closing of the Scheldt River, Amsterdam’s competitor was cut off so Amsterdam could take over the world trade centre's function. Flourishing Amsterdam offered plenty of work and was an excellent attraction for artisans from the Southern Netherlands. The two dominating publishers in the cartographical field were Cornelis Claesz. and Jodocus Hondius, both from the Southern Netherlands. Hessel Gerritsz. was trained in the graphic trade by David Vingboons, a painter and artist from the Southern Netherlands.
After his apprenticeship with David Vingboons, Hessel Gerritsz. continued his schooling in the publishing house of Willem Jansz. (Blaeu). There, he could perfect his etching style, was given the mathematical skills that would be useful to him later, and learned the trade of mapmaking. With the engraver Josua van den Ende, he was responsible for engraving the superb wall map of the Seventeen Provinces (1608). Van den Ende engraved the map image while Hessel Gerritsz. took care of the decorative borders and the decorations on the main map.
During his activities for Willem Jansz. Hessel Gerritsz. not only perfected his etching and engraving style but also received the geographical and mathematical education that would stand him in good stead in later years. He could not wish for a better cartographical school. Blaeu’s workshop was a repository where geographical information from all parts of the world came together.
Hessel Gerritsz. married in 1607 to Geertje Gijsbertdr. One of his children, Gerrit, born in 1609, was to follow in his father’s footsteps. Shortly after his marriage, he established himself as an independent engraver, mapmaker and printer.
Hessel Gerritsz. regularly worked with Claes Jansz. Visscher, as well. They cooperated for a long time.
His artistic talent comes to the fore in his map of the Leo Belgicus, depicting the Seventeen Provinces in the shape of a lion. This was seen as a symbol of the courage and persistence of the Dutch provinces in their resistance against Spanish tyranny.
In 1612-13, Hessel Gerritsz. was intensively busy with publications about Russia. In 1612, he published the influential booklet Beschryvinghe vander Samoyeden Landt. The two chapters about Siberia were provided by Isaac Massa, who had lived in Moscow for nine years. With the aid of original Russian material, Gerrritsz. produced a series of three maps in folio format: a map of Russia and Moscow and the Kremlin town plans. He also made an essential new wall map of Lithuania and engraved it on four plates for Willem Blaeu. In the meantime, he also made a wall map and a folio map of Spain.
Next to these works undertaken on his initiative, Hessel Gerritsz. also accepted engraving and publishing tasks for third parties.
In 1617, Hessel Gerritsz. published a large wall map of Italy in six sheets. He gave his wall map an extra cachet by extending the map image with town views and costumed figures. The map was copied shortly after publication by Willem Blaeu. To protect himself against such plagiarism in the future, he requested a patent from the States-General. In January 1618, they granted him a general license in which, amongst other things, it was forbidden in any way to reproduce, copy or distribute his maps, both written or printed.
Hessel Gerritsz. was so highly regarded in 1617 that he received such an extraordinary privilege. He was appointed as a geography instructor for the Councillors of the Admiralty at Amsterdam and as a mapmaker for the Chamber Amsterdam of the VOC. With both appointments, his old employer, Willem Blaeu, was passed over. In his function as VOC's mapmaker, he improved and expanded the charts for navigation to and from the Indies. The chart maker, of course, did not draw the charts needed for the VOC ships himself. He manufactured specific prototypes, the so-called leggers (master charts), which served as models for copying work by his assistants in his house.
At the beginning of September 1632, Hessel Gerritsz. died at the age of 52. He must be considered one of the most comprehensive map makers of his time. “He was multi-disciplined in his working method, integrating graphical technique and artistic expression in his scientific approach. Because of his mathematical talent, he could solve nautical problems and make proposals about them. His exceptional network – the interviews with pilots from diverse companies and his correspondence with persons at home and abroad – supplied him with a huge amount of geographical and nautical information that he used most efficiently. His good contacts with the families of the great merchants, ship owners, and the influential regents' representatives opened doors for him. He was, without doubt, the most informed person in geographical matters in Amsterdam of his time.” (Schilder)
Magni Ducatus Lithuaniae Caeterarumque Regionum illi Adiacentium Exacta Descriptio.
Item Number: 27324 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Eastern Europe
Old, antique map of Lithuania, by Willem Blaeu.
Cartographer: Nikolaj Krzysztof Radziwill
Engraver: Hessel Gerritsz.
Date of the first edition: 1613
Date of the first atlas edition: 1631
Date of this map: 1643
Date on map: 1613
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 76 x 74cm (29.6 x 28.9 inches)
Verso: Blank
Condition: Original coloured, some small creases flattened, good copy.
Condition Rating: A
References: Van der Krogt 2, 1730 I:2A; Schilder 4, 29.5; Schilder 9, #7.14
From: Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.. J. Blaeu, 1634-49. (Van der Krogt 2, 2:202)
Printed from two plates and two half plates, joined.
The original of this map was made during the last decade of the sixteenth century by the efforts of prince Nikolaj Krzystof Radziwill (Radvillas 1549-1616) and was a collaborative effort. Only the name of the draughtsman, Tomasz Makowski, is known. Alexandrowicz (1989) assumes that a first (now lost) printed state existed before 1604, of which the printing plate is no longer extant. The second plate of the map was engraved by Hessel Gerritsz and published by Blaeu. Blaeu changed the arrangement of the map sheets; he separated the map of the river Dniepr from the map of Lithuania. The first atlas edition (1631) has printed Latin text on the back; from 1634, the map was included in the atlas without text on the back.
The Blaeus: Willem Janszoon, Cornelis & Joan
Willem Jansz. Blaeu and his son Joan Blaeu are the seventeenth century's most widely known cartographic publishers.
Willem Jansz. (also written Guilielmus Janssonius) = Willem Janszoon Blaeu was born in Uitgeest (Netherlands), near Alkmaar, in 1571. He studied mathematics under Tycho Brahe and learned the theory and practice of astronomical observations and the art of instrument- and globe-making.
In 1596, he came to Amsterdam, where he settled down as a globe-, instrument- and map-maker. He published his first cartographic work (a globe) in 1599 and probably published his first printed map (a map of the Netherlands) in 1604. He specialised in maritime cartography, published the first edition of the pilot guide Het Licht der Zeevaert in 1608, and was appointed Hydrographer of the V.O.C. (United East India Company) in 1633. After publishing books, wall maps, globes, charts and pilot guides for thirty years, he brought out his first atlas, Atlas Appendix (1630). This was the beginning of the great tradition of atlas-making by the Blaeus.
In 1618, another mapmaker, bookseller and publisher, Johannes Janssonius, established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu's shop. No wonder these two neighbours began accusing each other of copying and stealing their information and became fierce competitors who did not have a good word to say about each other. In about 1621 Willem Jansz. decided to end the confusion between his name and his competitor's and assumed his grandfather's nickname, 'blauwe Willem' ('blue Willem'), as the family name; after that, he called himself Willem Jansz. Blaeu.
Willem Janszoon Blaeu died in 1638, leaving his prospering business to his sons, Cornelis and Joan. We only know that Cornelis's name occurs in the prefaces of books and atlases until c. 1645.
Joan Blaeu, born in Amsterdam in 1596, became a partner in his father’s book trade and printing business. 1638, he was appointed his father’s successor in the Hydrographic Office of the V.O.C. His efforts culminated in the magnificent Atlas Major and the town books of the Netherlands and Italy – works unsurpassed in history and modern times, giving eternal fame to the name of the Blaeu's.
On February 23, 1672, a fire ruined the business. One year later, Dr Joan Blaeu died. The fire of 1672 and the passing away of the director gave rise to a complete sale of the stock of the Blaeu House. Five public auctions dispersed the remaining books, atlases, copperplates, globes, etc., among many other map dealers and publishers in Amsterdam. The majority was acquired by several booksellers acting in partnership.
In the succeeding years, the remaining printing department was left in the hands of the Blaeu family until 1695, when the printing house's inventory was sold at a public auction. That meant the end of the Blaeu's as a printing house of world renown.
Hessel Gerritsz. (1580/81 – 1632)
Hessel Gerritsz. was one of the seventeenth century's most influential and innovative map makers. He was born in Assum in North Holland and attended Alkmaar school. He must have known Willem Jansz. (= Willem Blaeu) who stayed in Alkmaar for several years. Later, he moved to Amsterdam for his further education.
After the closing of the Scheldt River, Amsterdam’s competitor was cut off so Amsterdam could take over the world trade centre's function. Flourishing Amsterdam offered plenty of work and was an excellent attraction for artisans from the Southern Netherlands. The two dominating publishers in the cartographical field were Cornelis Claesz. and Jodocus Hondius, both from the Southern Netherlands. Hessel Gerritsz. was trained in the graphic trade by David Vingboons, a painter and artist from the Southern Netherlands.
After his apprenticeship with David Vingboons, Hessel Gerritsz. continued his schooling in the publishing house of Willem Jansz. (Blaeu). There, he could perfect his etching style, was given the mathematical skills that would be useful to him later, and learned the trade of mapmaking. With the engraver Josua van den Ende, he was responsible for engraving the superb wall map of the Seventeen Provinces (1608). Van den Ende engraved the map image while Hessel Gerritsz. took care of the decorative borders and the decorations on the main map.
During his activities for Willem Jansz. Hessel Gerritsz. not only perfected his etching and engraving style but also received the geographical and mathematical education that would stand him in good stead in later years. He could not wish for a better cartographical school. Blaeu’s workshop was a repository where geographical information from all parts of the world came together.
Hessel Gerritsz. married in 1607 to Geertje Gijsbertdr. One of his children, Gerrit, born in 1609, was to follow in his father’s footsteps. Shortly after his marriage, he established himself as an independent engraver, mapmaker and printer.
Hessel Gerritsz. regularly worked with Claes Jansz. Visscher, as well. They cooperated for a long time.
His artistic talent comes to the fore in his map of the Leo Belgicus, depicting the Seventeen Provinces in the shape of a lion. This was seen as a symbol of the courage and persistence of the Dutch provinces in their resistance against Spanish tyranny.
In 1612-13, Hessel Gerritsz. was intensively busy with publications about Russia. In 1612, he published the influential booklet Beschryvinghe vander Samoyeden Landt. The two chapters about Siberia were provided by Isaac Massa, who had lived in Moscow for nine years. With the aid of original Russian material, Gerrritsz. produced a series of three maps in folio format: a map of Russia and Moscow and the Kremlin town plans. He also made an essential new wall map of Lithuania and engraved it on four plates for Willem Blaeu. In the meantime, he also made a wall map and a folio map of Spain.
Next to these works undertaken on his initiative, Hessel Gerritsz. also accepted engraving and publishing tasks for third parties.
In 1617, Hessel Gerritsz. published a large wall map of Italy in six sheets. He gave his wall map an extra cachet by extending the map image with town views and costumed figures. The map was copied shortly after publication by Willem Blaeu. To protect himself against such plagiarism in the future, he requested a patent from the States-General. In January 1618, they granted him a general license in which, amongst other things, it was forbidden in any way to reproduce, copy or distribute his maps, both written or printed.
Hessel Gerritsz. was so highly regarded in 1617 that he received such an extraordinary privilege. He was appointed as a geography instructor for the Councillors of the Admiralty at Amsterdam and as a mapmaker for the Chamber Amsterdam of the VOC. With both appointments, his old employer, Willem Blaeu, was passed over. In his function as VOC's mapmaker, he improved and expanded the charts for navigation to and from the Indies. The chart maker, of course, did not draw the charts needed for the VOC ships himself. He manufactured specific prototypes, the so-called leggers (master charts), which served as models for copying work by his assistants in his house.
At the beginning of September 1632, Hessel Gerritsz. died at the age of 52. He must be considered one of the most comprehensive map makers of his time. “He was multi-disciplined in his working method, integrating graphical technique and artistic expression in his scientific approach. Because of his mathematical talent, he could solve nautical problems and make proposals about them. His exceptional network – the interviews with pilots from diverse companies and his correspondence with persons at home and abroad – supplied him with a huge amount of geographical and nautical information that he used most efficiently. His good contacts with the families of the great merchants, ship owners, and the influential regents' representatives opened doors for him. He was, without doubt, the most informed person in geographical matters in Amsterdam of his time.” (Schilder)