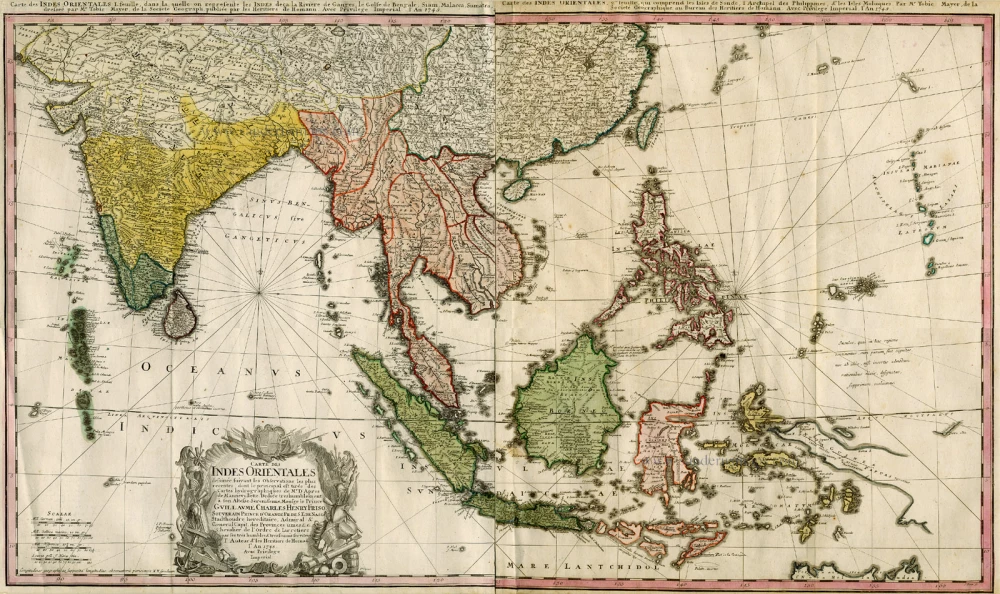
Southern Asia, by Homann Heirs. c. 1759
The Homann Family: Masters of German Cartography and Publishing
The Homann family stands as one of the most significant names in the history of German cartography and publishing. Their maps, atlases, and geographic works not only shaped contemporary understanding of the world during the 18th century but also left an enduring legacy in the fields of geography, engraving, and scholarly publishing.
The family's prominence began with Johann Baptist Homann (1664–1724), a native of Oberkammlach in Bavaria. Initially trained in law and theology, Johann Baptist later turned to engraving and cartography — a field that was flourishing amid the Age of Discovery and the growing demand for precise geographic knowledge.
In 1702, he founded his own publishing house in Nürnberg, a city then renowned for its vibrant intellectual, artistic, and scientific community. Nuremberg’s rich tradition of printmaking and map production provided fertile ground for Homann's enterprise.
Johann Baptist Homann quickly rose to prominence as one of Germany’s leading cartographers and publishers. His works combined technical accuracy, artistic merit, and rich ornamentation, often embellished with elaborate cartouches, mythological scenes, and heraldic symbols.
In 1715, Homann was appointed Imperial Geographer to the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI. He obtained the "Imperial Privilege" (Privilegium Imperialis). This prestigious title solidified his status and bestowed upon his publishing house both credibility and influence. His most famous works include:
- Atlas Novus Terrarum Orbis (1707) — an early and ambitious atlas project.
- Grosser Atlas über die ganze Welt (1716) — one of the most crucial German world atlases of the early 18th century.
Homann’s maps covered both European and global territories, including the Americas, Asia, and Africa, reflecting contemporary geographical knowledge and political boundaries.
The Homann Heirs (Homannische Erben)
After Johann Baptist Homann died in 1724, his son Johann Christoph Homann (1703–1730) briefly took over the business. However, Johann Christoph died at a young age, and the enterprise was then continued under the name Homännische Erben ("Homann Heirs"), a partnership of family members and associates.
Despite the loss of its founder, the firm remained highly productive and influential for several decades. The Homann Heirs continued to publish atlases, wall maps, city views, and geographical treatises well into the late 18th century. Their catalogue included works by noted cartographers such as Johann Matthias Hase, Leonhard Euler, and Tobias Conrad Lotter.
The Homann publishing house played a crucial role in disseminating geographic and scientific knowledge during the Enlightenment. Their maps combined artistry with empirical detail and were sought after by scholars, navigators, governments, and collectors.
Several of their works are now prized as valuable historical artefacts, housed in museums, libraries, and private collections around the world. The Homann Heirs' firm gradually declined by the end of the 18th century, overtaken by newer publishing houses and changing technologies, but their contribution to the cartographic tradition remains significant.
The Homann family’s name is indelibly linked to the golden age of German cartography. Through meticulous craftsmanship and a keen sense of visual storytelling, they charted the known world of their time, leaving a remarkable record of early modern geography. Today, their maps not only inform historians of cartography but also captivate collectors and enthusiasts for their aesthetic beauty and historical value.
Carte des Indes Orientales ...
Item Number: 994 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Asia > Southeast Asia
Antique map of Southern Asia by Homann Heirs.
Title: Carte des Indes Orientales ...
Date: c. 1759.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 517 x 874mm (20.35 x 34.41 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Old coloured.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Atlas Geographicus Maior. Nürnberg, 1759.
The Homann Family: Masters of German Cartography and Publishing
The Homann family stands as one of the most significant names in the history of German cartography and publishing. Their maps, atlases, and geographic works not only shaped contemporary understanding of the world during the 18th century but also left an enduring legacy in the fields of geography, engraving, and scholarly publishing.
The family's prominence began with Johann Baptist Homann (1664–1724), a native of Oberkammlach in Bavaria. Initially trained in law and theology, Johann Baptist later turned to engraving and cartography — a field that was flourishing amid the Age of Discovery and the growing demand for precise geographic knowledge.
In 1702, he founded his own publishing house in Nürnberg, a city then renowned for its vibrant intellectual, artistic, and scientific community. Nuremberg’s rich tradition of printmaking and map production provided fertile ground for Homann's enterprise.
Johann Baptist Homann quickly rose to prominence as one of Germany’s leading cartographers and publishers. His works combined technical accuracy, artistic merit, and rich ornamentation, often embellished with elaborate cartouches, mythological scenes, and heraldic symbols.
In 1715, Homann was appointed Imperial Geographer to the Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI. He obtained the "Imperial Privilege" (Privilegium Imperialis). This prestigious title solidified his status and bestowed upon his publishing house both credibility and influence. His most famous works include:
- Atlas Novus Terrarum Orbis (1707) — an early and ambitious atlas project.
- Grosser Atlas über die ganze Welt (1716) — one of the most crucial German world atlases of the early 18th century.
Homann’s maps covered both European and global territories, including the Americas, Asia, and Africa, reflecting contemporary geographical knowledge and political boundaries.
The Homann Heirs (Homannische Erben)
After Johann Baptist Homann died in 1724, his son Johann Christoph Homann (1703–1730) briefly took over the business. However, Johann Christoph died at a young age, and the enterprise was then continued under the name Homännische Erben ("Homann Heirs"), a partnership of family members and associates.
Despite the loss of its founder, the firm remained highly productive and influential for several decades. The Homann Heirs continued to publish atlases, wall maps, city views, and geographical treatises well into the late 18th century. Their catalogue included works by noted cartographers such as Johann Matthias Hase, Leonhard Euler, and Tobias Conrad Lotter.
The Homann publishing house played a crucial role in disseminating geographic and scientific knowledge during the Enlightenment. Their maps combined artistry with empirical detail and were sought after by scholars, navigators, governments, and collectors.
Several of their works are now prized as valuable historical artefacts, housed in museums, libraries, and private collections around the world. The Homann Heirs' firm gradually declined by the end of the 18th century, overtaken by newer publishing houses and changing technologies, but their contribution to the cartographic tradition remains significant.
The Homann family’s name is indelibly linked to the golden age of German cartography. Through meticulous craftsmanship and a keen sense of visual storytelling, they charted the known world of their time, leaving a remarkable record of early modern geography. Today, their maps not only inform historians of cartography but also captivate collectors and enthusiasts for their aesthetic beauty and historical value.