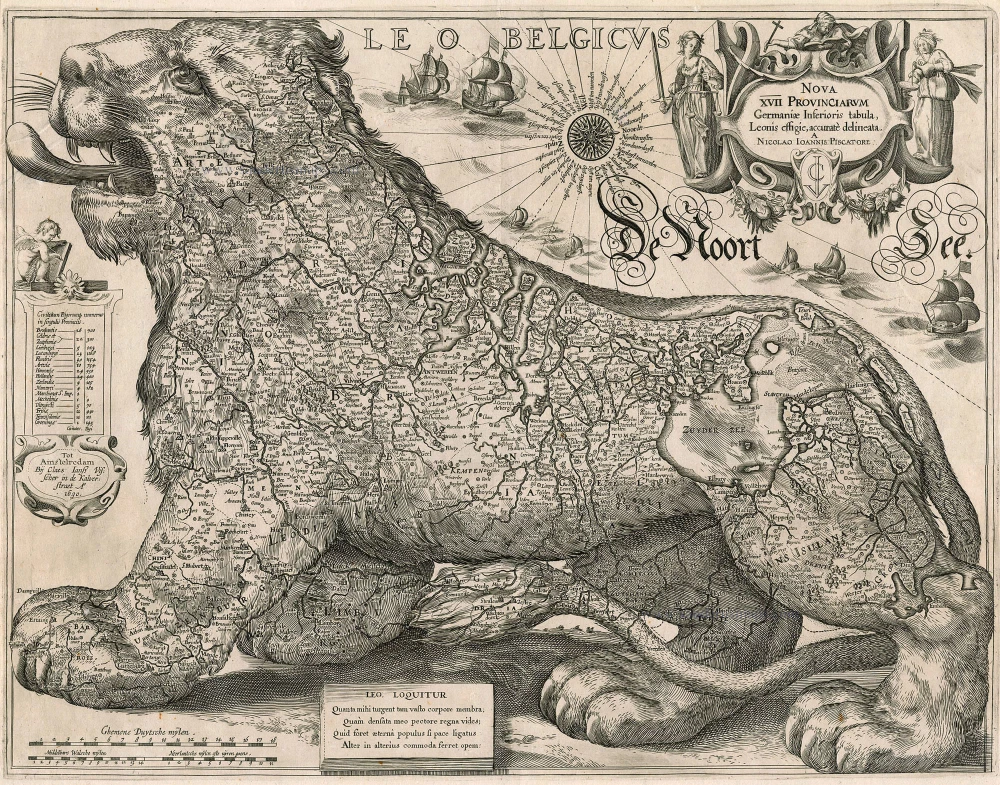
Antique map of Leo Belgicus by Visscher C.J. - Gerritsz 1630
The Visscher Family
For nearly a century, the members of the Visscher family were essential art dealers and map publishers in Amsterdam.
Claes Jansz. Visscher, or N.J. Piscator (1587-1652)
Claes Jansz. Vischer bought a house in Amsterdam, 'de gulden Bors', on the crucial Kalverstraat and changed the name into "In de Visscher"; under this title, the shop was to flourish for many years.
He was famous for his engravings and etchings of Dutch landscapes and 'historical scenes', such as sieges, battles, etc. These 'historical scenes' were considered contemporary illustrated news items, especially e.g. that of 'the Eighty Years' War'.
For the publication of his first atlas, he bought copperplates of the atlas Germania Inferior by Pieter van den Keere (1623).
In 1649, he published an atlas entitled Tabularum Geographicarum Contractarum, containing the same maps as Langenes' Caert Thresoor, for which Visscher had only new title pages engraved.
Claes Jansz. Visscher died in 1652. His wife, Neeltjen Florisdr., had already died in 1640. They had seven children, four of whom were still alive at Claes Jansz.'s death. One was Nicolaes Visscher I, who was to continue his father's business.
Nicolaes Visscher I (1618-1679)
Nicolaes Visscher I partnered with his father, continued the business, and stayed on the Kalverstraat 'in de Visscher' till his death.
In about 1657, the first edition of his Atlas Contractus Orbis Terrarum appeared.
Between 1664 and 1677, several editions of his Atlas Contractus appeared without a printed index, for these atlases had no fixed contents but were composed according to the buyer's financial leaping pole.
In May 1664, Nicolaes Visscher was admitted as a member of the Booksellers' Guild of his town. In July 1677, he was granted a patent of the States of Holland and West-Friesland for printing and publishing maps and atlases for 15 years.
After this, he again published an Atlas Contractus with a printed index. At about the same time, he also brought out an Atlas Minor.
Nicolaes Visscher II (1649-1702)
Nicolaes Visscher II inherited the 'shop' from his father. To obtain a new privilege, he applied to the States of Holland and West-Friesland in 1682 for a patent for printing and publishing maps. This patent was granted to him the same year. He moved the firm to the Dam, but it kept the same signboard: "In de Visscher".
Around 1683, he published his first Atlas Minor with a printed index of 91 maps. In 1684, an atlas Germania Inferior appeared. Till 1697, he published another number of atlases. He used his grandfather's (Claes Jansz.) maps less often now and relied more and more on his own.
The wars waged at this time initiated the compilation of maps of the countries where the armies operated. Many war maps were included in the various editions of his Atlas Minor.
After Nicolaes's death, his wife, Elizabeth Verseyl, published all the war maps as an atlas under the title De Stoel des Oorlogs in de Wereld (The seat of war in the world).
The widow of Nicolaes Visscher II (?-1726)
His widow continued the business energetically, and by her hand, under the name of her deceased husband, numerous atlases appeared, e.g., several editions of the Atlas Minor, an Atlas Maior and De Stoel des Oorlogs. The shop enjoyed a high reputation due to the assortment's incredible variety. Not only 'Visscher' maps but also maps of other publishers were obtainable. With the death of Elizabeth Verseyl in 1726, the last descendant died of a great map- and atlas-publishing firm in Amsterdam.
Hessel Gerritsz. (1580/81 – 1632)
Hessel Gerritsz. was one of the seventeenth century's most influential and innovative map makers. He was born in Assum in North Holland and attended Alkmaar school. He must have known Willem Jansz. (= Willem Blaeu) who stayed in Alkmaar for several years. Later, he moved to Amsterdam for his further education.
After the closing of the Scheldt River, Amsterdam’s competitor was cut off so Amsterdam could take over the world trade centre's function. Flourishing Amsterdam offered plenty of work and was an excellent attraction for artisans from the Southern Netherlands. The two dominating publishers in the cartographical field were Cornelis Claesz. and Jodocus Hondius, both from the Southern Netherlands. Hessel Gerritsz. was trained in the graphic trade by David Vingboons, a painter and artist from the Southern Netherlands.
After his apprenticeship with David Vingboons, Hessel Gerritsz. continued his schooling in the publishing house of Willem Jansz. (Blaeu). There, he could perfect his etching style, was given the mathematical skills that would be useful to him later, and learned the trade of mapmaking. With the engraver Josua van den Ende, he was responsible for engraving the superb wall map of the Seventeen Provinces (1608). Van den Ende engraved the map image while Hessel Gerritsz. took care of the decorative borders and the decorations on the main map.
During his activities for Willem Jansz. Hessel Gerritsz. not only perfected his etching and engraving style but also received the geographical and mathematical education that would stand him in good stead in later years. He could not wish for a better cartographical school. Blaeu’s workshop was a repository where geographical information from all parts of the world came together.
Hessel Gerritsz. married in 1607 to Geertje Gijsbertdr. One of his children, Gerrit, born in 1609, was to follow in his father’s footsteps. Shortly after his marriage, he established himself as an independent engraver, mapmaker and printer.
Hessel Gerritsz. regularly worked with Claes Jansz. Visscher, as well. They cooperated for a long time.
His artistic talent comes to the fore in his map of the Leo Belgicus, depicting the Seventeen Provinces in the shape of a lion. This was seen as a symbol of the courage and persistence of the Dutch provinces in their resistance against Spanish tyranny.
In 1612-13, Hessel Gerritsz. was intensively busy with publications about Russia. In 1612, he published the influential booklet Beschryvinghe vander Samoyeden Landt. The two chapters about Siberia were provided by Isaac Massa, who had lived in Moscow for nine years. With the aid of original Russian material, Gerrritsz. produced a series of three maps in folio format: a map of Russia and Moscow and the Kremlin town plans. He also made an essential new wall map of Lithuania and engraved it on four plates for Willem Blaeu. In the meantime, he also made a wall map and a folio map of Spain.
Next to these works undertaken on his initiative, Hessel Gerritsz. also accepted engraving and publishing tasks for third parties.
In 1617, Hessel Gerritsz. published a large wall map of Italy in six sheets. He gave his wall map an extra cachet by extending the map image with town views and costumed figures. The map was copied shortly after publication by Willem Blaeu. To protect himself against such plagiarism in the future, he requested a patent from the States-General. In January 1618, they granted him a general license in which, amongst other things, it was forbidden in any way to reproduce, copy or distribute his maps, both written or printed.
Hessel Gerritsz. was so highly regarded in 1617 that he received such an extraordinary privilege. He was appointed as a geography instructor for the Councillors of the Admiralty at Amsterdam and as a mapmaker for the Chamber Amsterdam of the VOC. With both appointments, his old employer, Willem Blaeu, was passed over. In his function as VOC's mapmaker, he improved and expanded the charts for navigation to and from the Indies. The chart maker, of course, did not draw the charts needed for the VOC ships himself. He manufactured specific prototypes, the so-called leggers (master charts), which served as models for copying work by his assistants in his house.
At the beginning of September 1632, Hessel Gerritsz. died at the age of 52. He must be considered one of the most comprehensive map makers of his time. “He was multi-disciplined in his working method, integrating graphical technique and artistic expression in his scientific approach. Because of his mathematical talent, he could solve nautical problems and make proposals about them. His exceptional network – the interviews with pilots from diverse companies and his correspondence with persons at home and abroad – supplied him with a huge amount of geographical and nautical information that he used most efficiently. His good contacts with the families of the great merchants, ship owners, and the influential regents' representatives opened doors for him. He was, without doubt, the most informed person in geographical matters in Amsterdam of his time.” (Schilder)
Nova XVII Provinciarum Germaniae Inferioris tabula, Leonis effigie, accurate delineata. A Nicolao Ioannis Piscatore
Item Number: 19186 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Curiosities
Copper engraving.
Size: 44 x 56.5cm (17.2 x 22 inches)
Verso: Blank
Condition: Two small printercreases in the upper left corner retouched, else perfect.
References: Schilder 7, 15.15 4th state; Van der Heijden (Leo Belg), 16.4;.
From: Belgium sive Germania Inferior Amsterdam, C.J. Visscher, 1634. (Koeman, Vis 1 - 3)
Superb copy of this magnificent and very rare Leo Belgicus. There is no known exemplar of the first state, one of the second and one of the third.
Schilder quotes seven loose copies of this fourth state + some inserted in Visschers very rare atlas Belgium sive Germania Inferior, 1634-45 (Less than 10 known copies of this atlas).
There are two types of this Leo Belgicus: the "lion rampant facing right" engraved by Hendrik Floris van Langren; and the "lion passant facing left", which was introduced by the engraver Hessel Gerritsz, who masterfully engraved it in copper. The publication history of the latter is complicated, however, and was only unraveled in the course of Van der Heijden's research. What complicates the story is that Hessel Gerritz engraved two almost identical copperplates in the same period, each of which was subsequently published by a series of publishing houses in Amsterdam.
The Visscher Family
For nearly a century, the members of the Visscher family were essential art dealers and map publishers in Amsterdam.
Claes Jansz. Visscher, or N.J. Piscator (1587-1652)
Claes Jansz. Vischer bought a house in Amsterdam, 'de gulden Bors', on the crucial Kalverstraat and changed the name into "In de Visscher"; under this title, the shop was to flourish for many years.
He was famous for his engravings and etchings of Dutch landscapes and 'historical scenes', such as sieges, battles, etc. These 'historical scenes' were considered contemporary illustrated news items, especially e.g. that of 'the Eighty Years' War'.
For the publication of his first atlas, he bought copperplates of the atlas Germania Inferior by Pieter van den Keere (1623).
In 1649, he published an atlas entitled Tabularum Geographicarum Contractarum, containing the same maps as Langenes' Caert Thresoor, for which Visscher had only new title pages engraved.
Claes Jansz. Visscher died in 1652. His wife, Neeltjen Florisdr., had already died in 1640. They had seven children, four of whom were still alive at Claes Jansz.'s death. One was Nicolaes Visscher I, who was to continue his father's business.
Nicolaes Visscher I (1618-1679)
Nicolaes Visscher I partnered with his father, continued the business, and stayed on the Kalverstraat 'in de Visscher' till his death.
In about 1657, the first edition of his Atlas Contractus Orbis Terrarum appeared.
Between 1664 and 1677, several editions of his Atlas Contractus appeared without a printed index, for these atlases had no fixed contents but were composed according to the buyer's financial leaping pole.
In May 1664, Nicolaes Visscher was admitted as a member of the Booksellers' Guild of his town. In July 1677, he was granted a patent of the States of Holland and West-Friesland for printing and publishing maps and atlases for 15 years.
After this, he again published an Atlas Contractus with a printed index. At about the same time, he also brought out an Atlas Minor.
Nicolaes Visscher II (1649-1702)
Nicolaes Visscher II inherited the 'shop' from his father. To obtain a new privilege, he applied to the States of Holland and West-Friesland in 1682 for a patent for printing and publishing maps. This patent was granted to him the same year. He moved the firm to the Dam, but it kept the same signboard: "In de Visscher".
Around 1683, he published his first Atlas Minor with a printed index of 91 maps. In 1684, an atlas Germania Inferior appeared. Till 1697, he published another number of atlases. He used his grandfather's (Claes Jansz.) maps less often now and relied more and more on his own.
The wars waged at this time initiated the compilation of maps of the countries where the armies operated. Many war maps were included in the various editions of his Atlas Minor.
After Nicolaes's death, his wife, Elizabeth Verseyl, published all the war maps as an atlas under the title De Stoel des Oorlogs in de Wereld (The seat of war in the world).
The widow of Nicolaes Visscher II (?-1726)
His widow continued the business energetically, and by her hand, under the name of her deceased husband, numerous atlases appeared, e.g., several editions of the Atlas Minor, an Atlas Maior and De Stoel des Oorlogs. The shop enjoyed a high reputation due to the assortment's incredible variety. Not only 'Visscher' maps but also maps of other publishers were obtainable. With the death of Elizabeth Verseyl in 1726, the last descendant died of a great map- and atlas-publishing firm in Amsterdam.
Hessel Gerritsz. (1580/81 – 1632)
Hessel Gerritsz. was one of the seventeenth century's most influential and innovative map makers. He was born in Assum in North Holland and attended Alkmaar school. He must have known Willem Jansz. (= Willem Blaeu) who stayed in Alkmaar for several years. Later, he moved to Amsterdam for his further education.
After the closing of the Scheldt River, Amsterdam’s competitor was cut off so Amsterdam could take over the world trade centre's function. Flourishing Amsterdam offered plenty of work and was an excellent attraction for artisans from the Southern Netherlands. The two dominating publishers in the cartographical field were Cornelis Claesz. and Jodocus Hondius, both from the Southern Netherlands. Hessel Gerritsz. was trained in the graphic trade by David Vingboons, a painter and artist from the Southern Netherlands.
After his apprenticeship with David Vingboons, Hessel Gerritsz. continued his schooling in the publishing house of Willem Jansz. (Blaeu). There, he could perfect his etching style, was given the mathematical skills that would be useful to him later, and learned the trade of mapmaking. With the engraver Josua van den Ende, he was responsible for engraving the superb wall map of the Seventeen Provinces (1608). Van den Ende engraved the map image while Hessel Gerritsz. took care of the decorative borders and the decorations on the main map.
During his activities for Willem Jansz. Hessel Gerritsz. not only perfected his etching and engraving style but also received the geographical and mathematical education that would stand him in good stead in later years. He could not wish for a better cartographical school. Blaeu’s workshop was a repository where geographical information from all parts of the world came together.
Hessel Gerritsz. married in 1607 to Geertje Gijsbertdr. One of his children, Gerrit, born in 1609, was to follow in his father’s footsteps. Shortly after his marriage, he established himself as an independent engraver, mapmaker and printer.
Hessel Gerritsz. regularly worked with Claes Jansz. Visscher, as well. They cooperated for a long time.
His artistic talent comes to the fore in his map of the Leo Belgicus, depicting the Seventeen Provinces in the shape of a lion. This was seen as a symbol of the courage and persistence of the Dutch provinces in their resistance against Spanish tyranny.
In 1612-13, Hessel Gerritsz. was intensively busy with publications about Russia. In 1612, he published the influential booklet Beschryvinghe vander Samoyeden Landt. The two chapters about Siberia were provided by Isaac Massa, who had lived in Moscow for nine years. With the aid of original Russian material, Gerrritsz. produced a series of three maps in folio format: a map of Russia and Moscow and the Kremlin town plans. He also made an essential new wall map of Lithuania and engraved it on four plates for Willem Blaeu. In the meantime, he also made a wall map and a folio map of Spain.
Next to these works undertaken on his initiative, Hessel Gerritsz. also accepted engraving and publishing tasks for third parties.
In 1617, Hessel Gerritsz. published a large wall map of Italy in six sheets. He gave his wall map an extra cachet by extending the map image with town views and costumed figures. The map was copied shortly after publication by Willem Blaeu. To protect himself against such plagiarism in the future, he requested a patent from the States-General. In January 1618, they granted him a general license in which, amongst other things, it was forbidden in any way to reproduce, copy or distribute his maps, both written or printed.
Hessel Gerritsz. was so highly regarded in 1617 that he received such an extraordinary privilege. He was appointed as a geography instructor for the Councillors of the Admiralty at Amsterdam and as a mapmaker for the Chamber Amsterdam of the VOC. With both appointments, his old employer, Willem Blaeu, was passed over. In his function as VOC's mapmaker, he improved and expanded the charts for navigation to and from the Indies. The chart maker, of course, did not draw the charts needed for the VOC ships himself. He manufactured specific prototypes, the so-called leggers (master charts), which served as models for copying work by his assistants in his house.
At the beginning of September 1632, Hessel Gerritsz. died at the age of 52. He must be considered one of the most comprehensive map makers of his time. “He was multi-disciplined in his working method, integrating graphical technique and artistic expression in his scientific approach. Because of his mathematical talent, he could solve nautical problems and make proposals about them. His exceptional network – the interviews with pilots from diverse companies and his correspondence with persons at home and abroad – supplied him with a huge amount of geographical and nautical information that he used most efficiently. His good contacts with the families of the great merchants, ship owners, and the influential regents' representatives opened doors for him. He was, without doubt, the most informed person in geographical matters in Amsterdam of his time.” (Schilder)