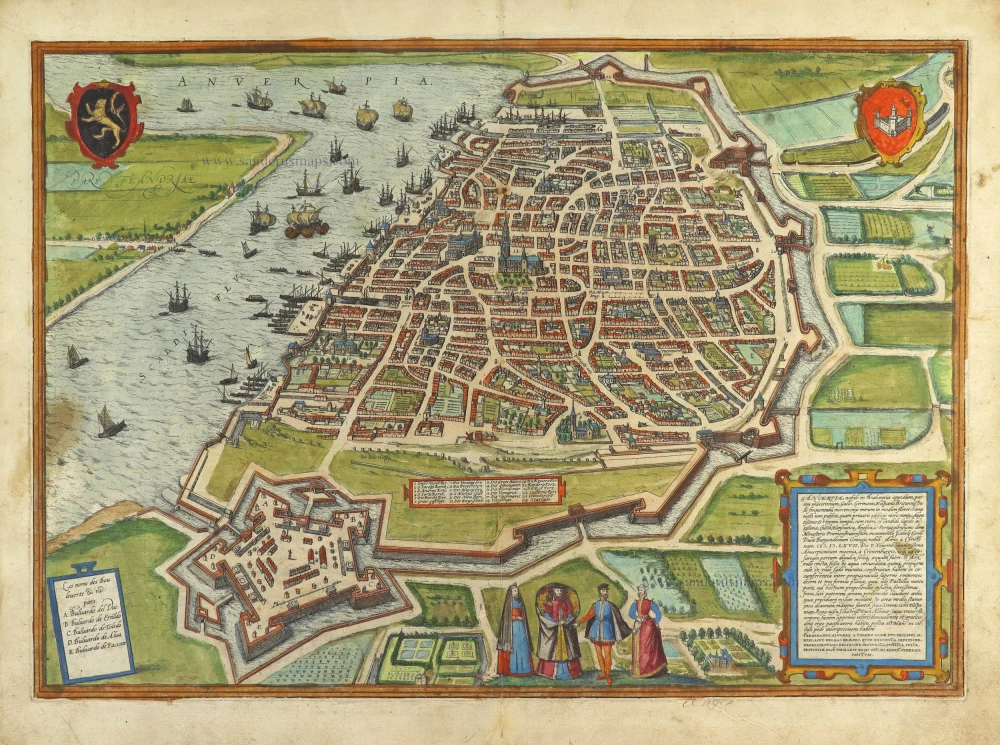
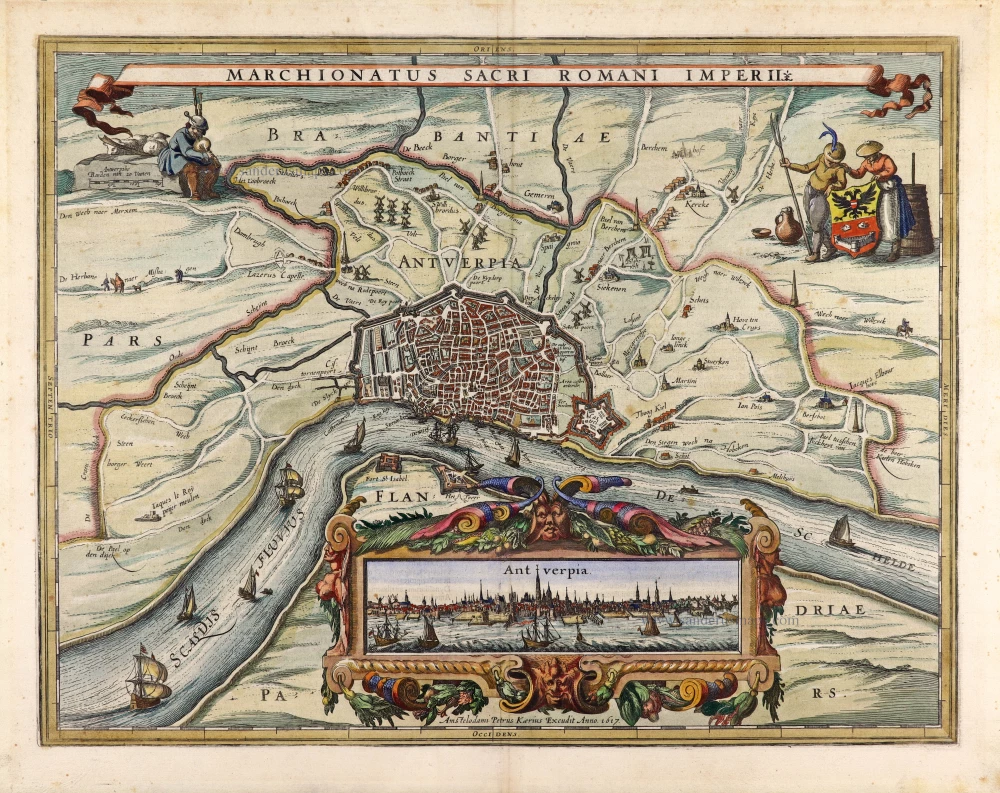
Antwerp, by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg. 1574
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Antwerp is a well-built and noted trade city in Brabant, which attracts many Germans, French, Italians, Spaniards, English and other nations. This city has beautiful, monumental churches and houses, particularly the church of Our Lady with a tall stone tower and a splendid town hall. The venerable Hansa, the English and the Portuguese also own public buildings where the merchants have residences. In the church of St Michael is a magnificent monument and tomb for Isabella's husband, Charles, Duke of Burgundy. On 5 November 1567, the massive city wall was built with imposing blockhouses and bulwarks and surrounded by a large moat. Inside, comfortable houses inhabited by the occupying troops surround a broad square. In the middle stands a statue of the famous Duke of Alba made of gilt metal, cast at great expense on the orders of the King of Spain and erected in memory of Ferdinand Alvarez of Toledo, Duke of Alba, Philip II of Spain's commander-in-chief in the Spanish Netherlands, as the King's most faithful servant because after quelling the uprising and crushing the insurgents, he upheld the faith, law and peace of the province.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The city of Antwerp possesses all the vital necessities of life in abundance, as is also observed with wonder by the foreign merchants; here we find Spanish, French and Rhenish wines, a huge fish market with a great number of fresh sea and river fish, and also salted fish. Among the public buildings, the splendid town hall must be mentioned first. It was built in four years at a considerable cost and with great skill. It is made of striking marble from far-off lands. ... In the city's heart lies a square marketplace with a colonnade where merchants can conduct business. There is also a magnificent church here, dedicated to Our Lady, with an extremely tall tower of white marble."
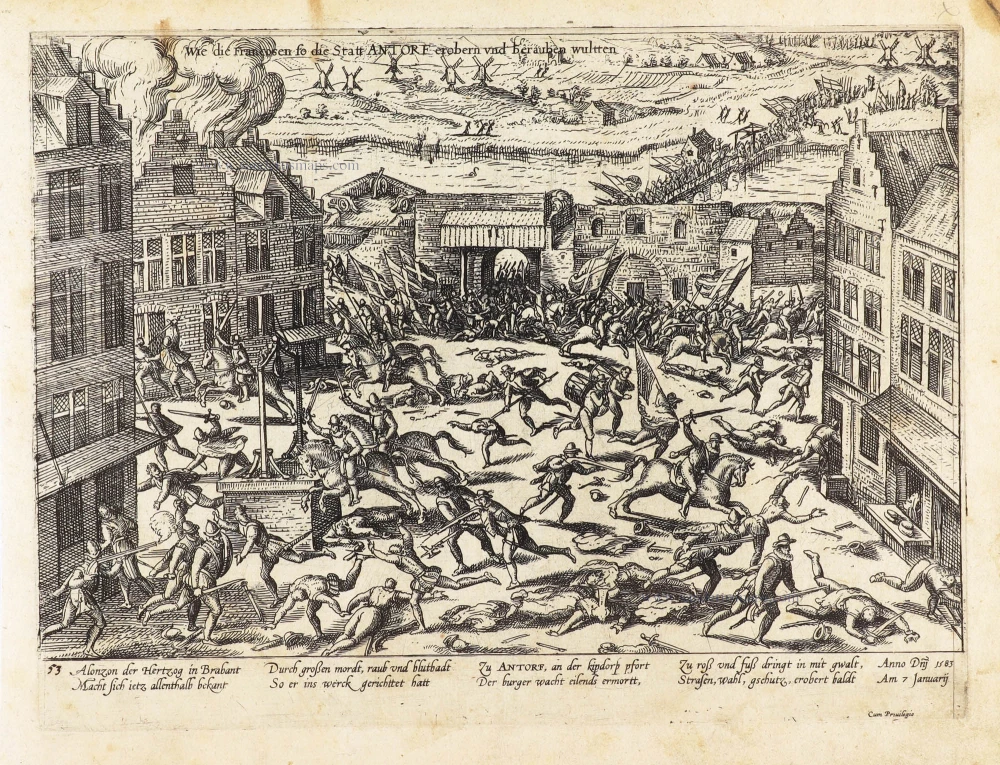
The two plan views (the second appeared in the 6th volume) show the Belgian port on the River Schelde from a birds-eye perspective. The eye is struck by the star-shaped citadel built by the Duke of Alba on Antwerp's southern side, the defensive moat and the harbour serving the prosperous centre of commerce. The city centre is recognisable with the Onze-Lieve-Vrouwe cathedral (1), its town hall (24) behind it overlooking the Grote Markt and the fish market (17). The north tower of the Gothic cathedral is the city landmark. First mentioned in records in AD 726, Antwerp was granted its charter in 1291 and, in 1315, became a Hansa town. The merchants' guilds relocated here, and between 1347 and 1496, Antwerp's population grew from 5,000 to 50,000; by 1565, this figure is estimated to have reached 95,000. In the 16th century, Antwerp was also an important centre of the arts and home to the leading printer and publisher north of the Alps, Christoffel Plantin. The prosperous metropolis attracted numerous artists (including Jan Brueghel the Elder, Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck). But Antwerp, too, became embroiled in the Wars of Religion, and in 1585, the city was taken by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. Countless Protestant merchants and artisans were subsequently driven out of the town, whose importance declined sharply. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.
Anverpia, nobile in Brabantia oppidum, ...
Item Number: 29496 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Belgium - Cities
Old, antique bird’s-eye view plan of Antwerp, by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg.
Title: Anverpia, nobile in Brabantia oppidum, ...
Date of the first edition: 1572.
Date of this map: 1574.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 340 x 475mm (13.39 x 18.7 inches).
Sheet size: 410 x 535mm (16.14 x 21.06 inches).
Verso: German text.
Condition: Original coloured, lower centrefold split reinforced, some staining, some marginal soiling.
Condition Rating: B.
From: Beschreibung und Contrafactur der Vornembster Stät der Welt. Köln, Heinrich von Ach, 1574. (Van der Krogt 4, 41:2.1)
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Antwerp is a well-built and noted trade city in Brabant, which attracts many Germans, French, Italians, Spaniards, English and other nations. This city has beautiful, monumental churches and houses, particularly the church of Our Lady with a tall stone tower and a splendid town hall. The venerable Hansa, the English and the Portuguese also own public buildings where the merchants have residences. In the church of St Michael is a magnificent monument and tomb for Isabella's husband, Charles, Duke of Burgundy. On 5 November 1567, the massive city wall was built with imposing blockhouses and bulwarks and surrounded by a large moat. Inside, comfortable houses inhabited by the occupying troops surround a broad square. In the middle stands a statue of the famous Duke of Alba made of gilt metal, cast at great expense on the orders of the King of Spain and erected in memory of Ferdinand Alvarez of Toledo, Duke of Alba, Philip II of Spain's commander-in-chief in the Spanish Netherlands, as the King's most faithful servant because after quelling the uprising and crushing the insurgents, he upheld the faith, law and peace of the province.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The city of Antwerp possesses all the vital necessities of life in abundance, as is also observed with wonder by the foreign merchants; here we find Spanish, French and Rhenish wines, a huge fish market with a great number of fresh sea and river fish, and also salted fish. Among the public buildings, the splendid town hall must be mentioned first. It was built in four years at a considerable cost and with great skill. It is made of striking marble from far-off lands. ... In the city's heart lies a square marketplace with a colonnade where merchants can conduct business. There is also a magnificent church here, dedicated to Our Lady, with an extremely tall tower of white marble."
The two plan views (the second appeared in the 6th volume) show the Belgian port on the River Schelde from a birds-eye perspective. The eye is struck by the star-shaped citadel built by the Duke of Alba on Antwerp's southern side, the defensive moat and the harbour serving the prosperous centre of commerce. The city centre is recognisable with the Onze-Lieve-Vrouwe cathedral (1), its town hall (24) behind it overlooking the Grote Markt and the fish market (17). The north tower of the Gothic cathedral is the city landmark. First mentioned in records in AD 726, Antwerp was granted its charter in 1291 and, in 1315, became a Hansa town. The merchants' guilds relocated here, and between 1347 and 1496, Antwerp's population grew from 5,000 to 50,000; by 1565, this figure is estimated to have reached 95,000. In the 16th century, Antwerp was also an important centre of the arts and home to the leading printer and publisher north of the Alps, Christoffel Plantin. The prosperous metropolis attracted numerous artists (including Jan Brueghel the Elder, Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck). But Antwerp, too, became embroiled in the Wars of Religion, and in 1585, the city was taken by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. Countless Protestant merchants and artisans were subsequently driven out of the town, whose importance declined sharply. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.