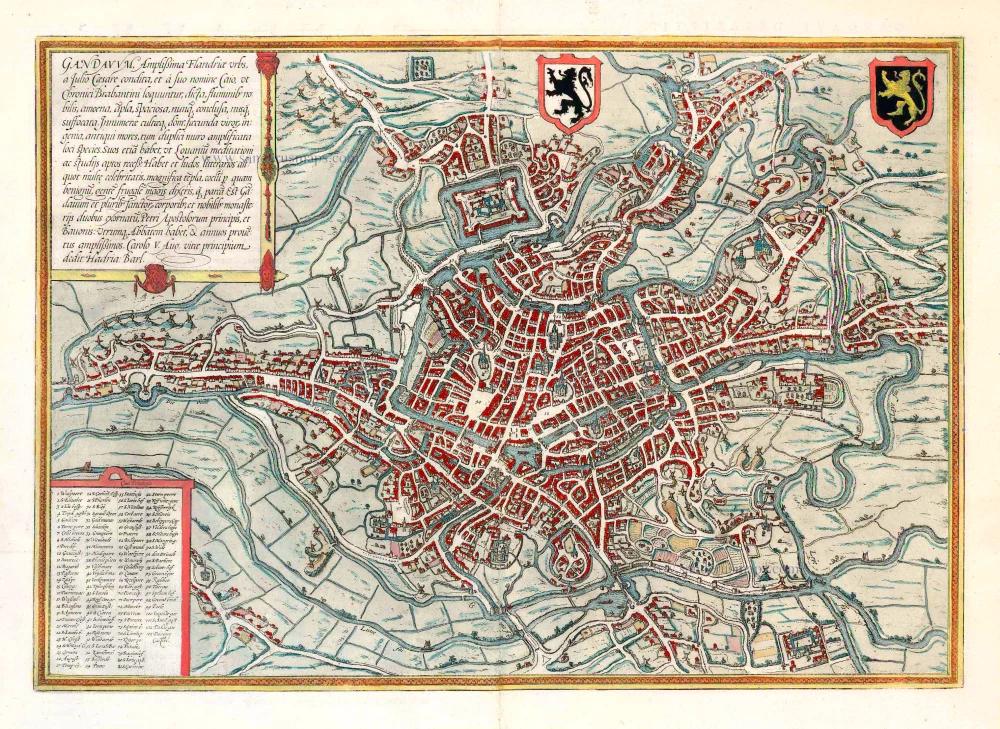
Old antique plan of Gent by Johannes Janssonius 1657
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Ghent, the most splendid city in Flanders, was founded by Julius Caesar and called Gaius after his forename, as the Brabant chroniclers relate. The city is distinguished by its rivers, altogether delightful, magnificent, spacious, never confined, nowhere stifling. The houses are innumerable and well-kept, the men richly talented, the customs venerable. A double wall amplifies the beautiful appearance of the place, which - like Louvain - also has quiet corners for reflection and study. Ghent also possesses famous schools and magnificent churches; the climate is excellent. The people, it can be said, are more frugal than parsimonious. Ghent is embellished by the relics of several saints and two famous monasteries dedicated to St Peter, Prince of the Apostles, and St Bavo; each has an abbot and a sizeable annual rental income.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "Ghent has a circumference of three German miles, possesses 20 islands, which lie in the surrounding lakes and rivers and are also inhabited, 98 bridges, including three that have more than two spans and beneath which even the biggest ships can pass. There are 100 windmills that can grind even the largest produce. In this city alone there are seven parish churches, five abbeys, two collegiate churches, 25 monasteries and seven general hospices. On the site where the new castle now stands, lay in olden times the village of Ganden, from which the city also took its name, and a magnificent Benedictine monastery of St Bavo, which was constructed from an old fortress and which in 1540 was enlarged by Emperor Charles V into an even bigger palace."
The view of Ghent shows the city from the northwest in plan view from a great height. The historical core of the city occupies the peninsula between the two Rivers Schelde and Leie. The cathedral of Sint-Baafs (51) is almost at the very centre of the map: it houses the famous Ghent Altarpiece painted by Hubert and Jan van Eyck. Together with the Gothic church of Sint-Niklaas (57) lower down and the nearby Sint-Jacobskerk (43), Sint-Baafs serves as one of the three main orientation points inside the city centre. Within this triangle stands the 14th-century belfry (55), 118 m high, which forms part of the cloth hall. The former Sint-Baafs monastery lies somewhat outside the city centre and is surrounded by fortifications and moats (103). Ghent, which is situated to the northwest of Brussels, derives its name from the Celtic ganda , meaning "confluence". As a leading centre of cloth production, in the High Middle Ages, Ghent rose to become a major power with a flourishing economy and together with Bruges was the most important centre of commerce in Flanders. From the 13th to the middle of the 14th century Ghent was the second-largest city in northern Europe after Paris, with some 60,000 inhabitants, but in the second half of the 14th century these numbers began to decline. Flemish-speaking Ghent is today the third-largest city in Belgium, with a population of around 230,000. (Taschen)
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
Item Number: 26172 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Belgium - Cities
Old, antique map - bird's-eye view plan of Ghent by J. Janssonius
Date of the first edition: 1572
Date of this map: 1657
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 34 x 48.5cm (13.3 x 18.9 inches)
Verso text: Latin
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+
References: Van der Krogt 4, 1503 State 2;.
From: Theatrum Urbium Celebriorum totius Belgii sive Germaniae Inferioris.Amsterdam, 1657. (Koeman, Ja 12)
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Ghent, the most splendid city in Flanders, was founded by Julius Caesar and called Gaius after his forename, as the Brabant chroniclers relate. The city is distinguished by its rivers, altogether delightful, magnificent, spacious, never confined, nowhere stifling. The houses are innumerable and well-kept, the men richly talented, the customs venerable. A double wall amplifies the beautiful appearance of the place, which - like Louvain - also has quiet corners for reflection and study. Ghent also possesses famous schools and magnificent churches; the climate is excellent. The people, it can be said, are more frugal than parsimonious. Ghent is embellished by the relics of several saints and two famous monasteries dedicated to St Peter, Prince of the Apostles, and St Bavo; each has an abbot and a sizeable annual rental income.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "Ghent has a circumference of three German miles, possesses 20 islands, which lie in the surrounding lakes and rivers and are also inhabited, 98 bridges, including three that have more than two spans and beneath which even the biggest ships can pass. There are 100 windmills that can grind even the largest produce. In this city alone there are seven parish churches, five abbeys, two collegiate churches, 25 monasteries and seven general hospices. On the site where the new castle now stands, lay in olden times the village of Ganden, from which the city also took its name, and a magnificent Benedictine monastery of St Bavo, which was constructed from an old fortress and which in 1540 was enlarged by Emperor Charles V into an even bigger palace."
The view of Ghent shows the city from the northwest in plan view from a great height. The historical core of the city occupies the peninsula between the two Rivers Schelde and Leie. The cathedral of Sint-Baafs (51) is almost at the very centre of the map: it houses the famous Ghent Altarpiece painted by Hubert and Jan van Eyck. Together with the Gothic church of Sint-Niklaas (57) lower down and the nearby Sint-Jacobskerk (43), Sint-Baafs serves as one of the three main orientation points inside the city centre. Within this triangle stands the 14th-century belfry (55), 118 m high, which forms part of the cloth hall. The former Sint-Baafs monastery lies somewhat outside the city centre and is surrounded by fortifications and moats (103). Ghent, which is situated to the northwest of Brussels, derives its name from the Celtic ganda , meaning "confluence". As a leading centre of cloth production, in the High Middle Ages, Ghent rose to become a major power with a flourishing economy and together with Bruges was the most important centre of commerce in Flanders. From the 13th to the middle of the 14th century Ghent was the second-largest city in northern Europe after Paris, with some 60,000 inhabitants, but in the second half of the 14th century these numbers began to decline. Flemish-speaking Ghent is today the third-largest city in Belgium, with a population of around 230,000. (Taschen)
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Ghent, the most splendid city in Flanders, was founded by Julius Caesar and called Gaius after his forename, as the Brabant chroniclers relate. The city is distinguished by its rivers, altogether delightful, magnificent, spacious, never confined, nowhere stifling. The houses are innumerable and well-kept, the men richly talented, the customs venerable. A double wall amplifies the beautiful appearance of the place, which - like Louvain - also has quiet corners for reflection and study. Ghent also possesses famous schools and magnificent churches; the climate is excellent. The people, it can be said, are more frugal than parsimonious. Ghent is embellished by the relics of several saints and two famous monasteries dedicated to St Peter, Prince of the Apostles, and St Bavo; each has an abbot and a sizeable annual rental income.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "Ghent has a circumference of three German miles, possesses 20 islands, which lie in the surrounding lakes and rivers and are also inhabited, 98 bridges, including three that have more than two spans and beneath which even the biggest ships can pass. There are 100 windmills that can grind even the largest produce. In this city alone there are seven parish churches, five abbeys, two collegiate churches, 25 monasteries and seven general hospices. On the site where the new castle now stands, lay in olden times the village of Ganden, from which the city also took its name, and a magnificent Benedictine monastery of St Bavo, which was constructed from an old fortress and which in 1540 was enlarged by Emperor Charles V into an even bigger palace."
The view of Ghent shows the city from the northwest in plan view from a great height. The historical core of the city occupies the peninsula between the two Rivers Schelde and Leie. The cathedral of Sint-Baafs (51) is almost at the very centre of the map: it houses the famous Ghent Altarpiece painted by Hubert and Jan van Eyck. Together with the Gothic church of Sint-Niklaas (57) lower down and the nearby Sint-Jacobskerk (43), Sint-Baafs serves as one of the three main orientation points inside the city centre. Within this triangle stands the 14th-century belfry (55), 118 m high, which forms part of the cloth hall. The former Sint-Baafs monastery lies somewhat outside the city centre and is surrounded by fortifications and moats (103). Ghent, which is situated to the northwest of Brussels, derives its name from the Celtic ganda , meaning "confluence". As a leading centre of cloth production, in the High Middle Ages, Ghent rose to become a major power with a flourishing economy and together with Bruges was the most important centre of commerce in Flanders. From the 13th to the middle of the 14th century Ghent was the second-largest city in northern Europe after Paris, with some 60,000 inhabitants, but in the second half of the 14th century these numbers began to decline. Flemish-speaking Ghent is today the third-largest city in Belgium, with a population of around 230,000. (Taschen)
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.