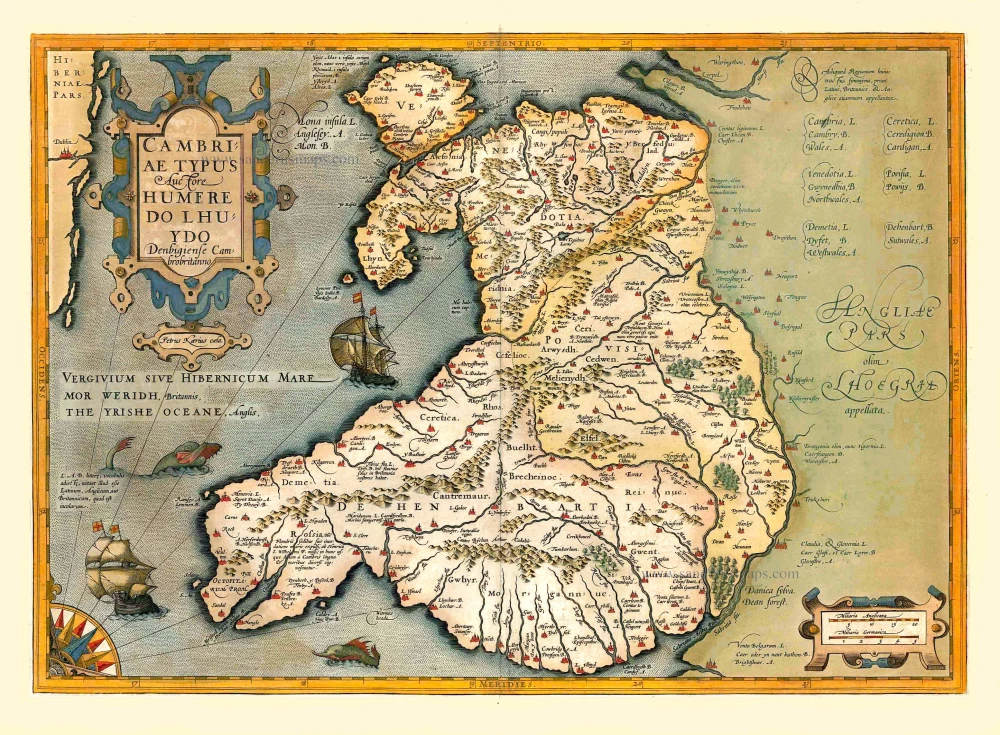
Wales, by Jodocus Hondius. 1623
The Hondius Family
Jodocus Hondius the Elder (1563-1612)
Joost d’Hondt was born at Wakken (Flanders) in 1563. Two years later, his family settled in Ghent, where young Joost displayed an excellent gift for drawing and calligraphy. Through study and lessons, he developed his talents and became an engraver with a good reputation.
Due to the circumstances of the war, he moved to London in 1584, where he settled down as an engraver, instrument-maker, and map-maker. In 1587, he married Coletta van den Keere, sister of the well-known engraver Pieter van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius); some years earlier, his sister, Jacomina, had married Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus). Joost, who had Latinized his name to Jodocus Hondius, closely co-operated with his two brothers-in-law.
The political situation in the Northern Netherlands in 1593 was such that Jodocus seemed justified in establishing himself in Amsterdam, where many Antwerp printers, publishers, and engravers had gone. In this new centre of cartography, Jodocus Hondius set up his business “In de Wackere Hondt” (in the vigilant dog), this name being an allusion to his birthplace and name. He engraved many maps and published atlases and many other works, such as his continuation of Gerard Mercator’s Atlas.
He suddenly passed away in February 1612. The publishing firm of Jodocus Hondius was continued by his widow, later on, by his two sons, Jodocus Jr. and Henricus, and by his son-in-law, J. Janssonius.
Jodocus Hondius II (1594-1629) & Henricus Hondius (1597-1651)
After the father’s death, the widow and her seven children continued publishing the atlases under the name of Jodocus Hondius till 1620. The firm was reinforced by the very welcome help of Joannes Janssonius (1588-1664), who married 24-year-old Elisabeth Hondius in 1612. After 1619, Mercator’s Atlas was published under the name of Henricus Hondius.
One of the most dramatic events in the early history of commercial cartography in Amsterdam was the sale of Jodocus Hondius Jr.’s copper plates to Willem Jansz. Blaeu in 1629, the year of his death. At least 34 plates, from which Jodocus II had printed single-sheet maps for his benefit, passed into the hands of his great competitor. Immediately after that, his brother, Henricus, and Joannes Janssonius ordered the engraving of identical plates.
Henricus devoted all his energy to publishing the Atlas for an extended period. He saw its growth up to and including the fourth part in 1646; after that, his name no longer figures on the title pages. After 1638, the title of the Atlas was changed to Atlas Novus; Joannes Janssonius mainly carried it on.
The competition with the Blaeu's dates from 1630. In 1630, Willem Janszoon (=Blaeu) first attacked with his Atlantis Appendix. In 1635, Blaeu completed his Theatrum Orbis Terrarum in two volumes with French, Latin, Dutch, and German texts, prompting Henricus Hondius to speed up the enlargement of his Atlas.
Pieter Van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius) (1571-c.1650)
Pieter van den Keere was born in Ghent in 1571 as the son of the type-founder, Hendrik van den Keere. In 1584, he moved with his family to London for religious reasons. There, Van den Keere received training as an engraver from Jodocus Hondius, his brother-in-law. Not only the companionship with Jodocus Hondius but also the acquaintanceship with Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus), author of the text of the Germania Inferior, originates from the years of refuge in London.
Upon their settlement in Amsterdam in 1593, both Keere and Hondius embarked on a monumental project. Their collaboration resulted in the creation of a large wall map of Europe, a masterpiece that still stands as a testament to their skill and vision, dated 1595: Nova totius Europae descriptio.
In 1610, he set up a workshop in the Kalverstraat that he called ‘In den onseeckeren tijd’ (In the uncertain time). During this period, he made numerous copperplates, including maps for his Atlas of the Netherlands and the Atlas Minor published by Jodocus Hondius.
The Germania Inferior (1617) is the first original atlas of the Netherlands published in folio size. The text for the atlas, both in Dutch and in French, was written by Petrus Montanus. After 1623, Claes Jansz. Visscher bought the plates and substituted his name for Kaerius’s. In 1634, Visscher included many of these maps in his Germana Inferior.
Kaerius's fame is not only based on his atlas of the Netherlands. He is even better known as an engraver of many loose-leaf maps and as a collaborator of book publishers. His maps are found, i.e., in the Caert thresoor (Barent Langenes, 1598), Licht der Zeevaert (Blaeu, 1608), Atlas Minor (Hondius, 1628), and Caertboeck vande Midellandsche Zee (Barents, 1595).
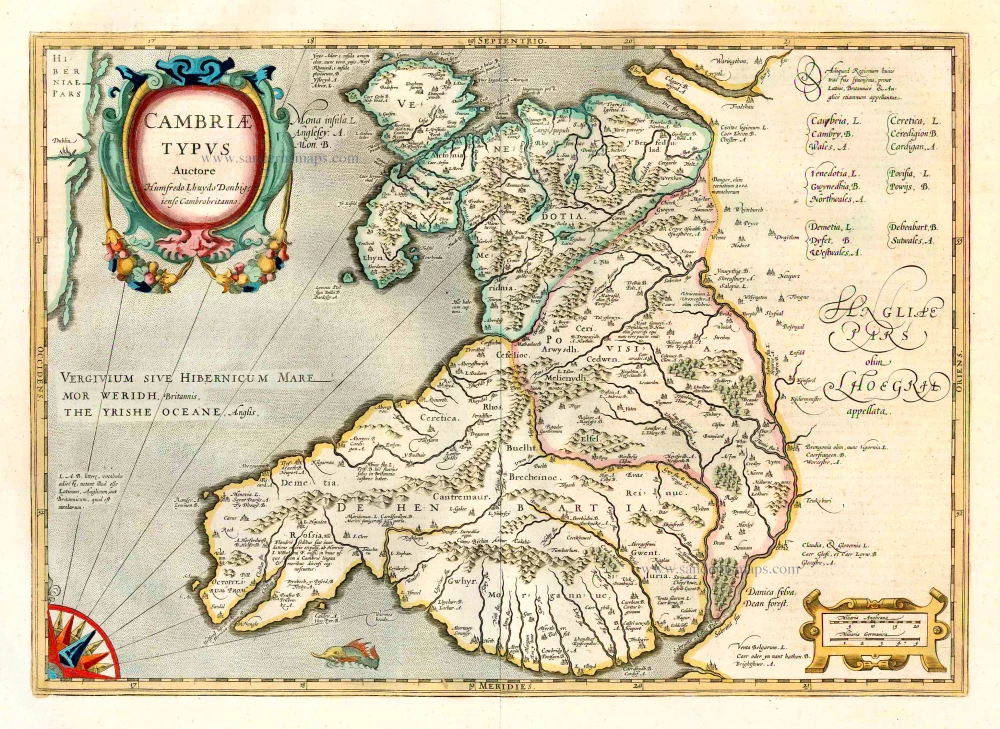
Cambriae Typus.
Currently not available
Item Number: 27762 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > British Isles
Wales, by Jodocus Hondius.
Title: Cambriae Typus.
Auctore Humfredo Lhuydo Denbigiense Cambrobritanno.
Petrus Kaerius cela.
Cartographer: Humphrey Loyd.
Engraver: Petrus Kaerius (Pieter Van den Keere).
Date of the first edition: 1607.
Date of this map: 1623.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 350 x 490mm (13.78 x 19.29 inches).
Verso: Latin text.
Condition: Original coloured, some offsetting.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Gerardi Mercatoris - Atlas sive Cosmographicae Meditationes de Fabrica Mundi et Fabricati Figura. Denuo auctus Editio Quinta. Henricus Hondius. 1623. (Van der Krogt 1, 105)
The Hondius Family
Jodocus Hondius the Elder (1563-1612)
Joost d’Hondt was born at Wakken (Flanders) in 1563. Two years later, his family settled in Ghent, where young Joost displayed an excellent gift for drawing and calligraphy. Through study and lessons, he developed his talents and became an engraver with a good reputation.
Due to the circumstances of the war, he moved to London in 1584, where he settled down as an engraver, instrument-maker, and map-maker. In 1587, he married Coletta van den Keere, sister of the well-known engraver Pieter van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius); some years earlier, his sister, Jacomina, had married Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus). Joost, who had Latinized his name to Jodocus Hondius, closely co-operated with his two brothers-in-law.
The political situation in the Northern Netherlands in 1593 was such that Jodocus seemed justified in establishing himself in Amsterdam, where many Antwerp printers, publishers, and engravers had gone. In this new centre of cartography, Jodocus Hondius set up his business “In de Wackere Hondt” (in the vigilant dog), this name being an allusion to his birthplace and name. He engraved many maps and published atlases and many other works, such as his continuation of Gerard Mercator’s Atlas.
He suddenly passed away in February 1612. The publishing firm of Jodocus Hondius was continued by his widow, later on, by his two sons, Jodocus Jr. and Henricus, and by his son-in-law, J. Janssonius.
Jodocus Hondius II (1594-1629) & Henricus Hondius (1597-1651)
After the father’s death, the widow and her seven children continued publishing the atlases under the name of Jodocus Hondius till 1620. The firm was reinforced by the very welcome help of Joannes Janssonius (1588-1664), who married 24-year-old Elisabeth Hondius in 1612. After 1619, Mercator’s Atlas was published under the name of Henricus Hondius.
One of the most dramatic events in the early history of commercial cartography in Amsterdam was the sale of Jodocus Hondius Jr.’s copper plates to Willem Jansz. Blaeu in 1629, the year of his death. At least 34 plates, from which Jodocus II had printed single-sheet maps for his benefit, passed into the hands of his great competitor. Immediately after that, his brother, Henricus, and Joannes Janssonius ordered the engraving of identical plates.
Henricus devoted all his energy to publishing the Atlas for an extended period. He saw its growth up to and including the fourth part in 1646; after that, his name no longer figures on the title pages. After 1638, the title of the Atlas was changed to Atlas Novus; Joannes Janssonius mainly carried it on.
The competition with the Blaeu's dates from 1630. In 1630, Willem Janszoon (=Blaeu) first attacked with his Atlantis Appendix. In 1635, Blaeu completed his Theatrum Orbis Terrarum in two volumes with French, Latin, Dutch, and German texts, prompting Henricus Hondius to speed up the enlargement of his Atlas.
Pieter Van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius) (1571-c.1650)
Pieter van den Keere was born in Ghent in 1571 as the son of the type-founder, Hendrik van den Keere. In 1584, he moved with his family to London for religious reasons. There, Van den Keere received training as an engraver from Jodocus Hondius, his brother-in-law. Not only the companionship with Jodocus Hondius but also the acquaintanceship with Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus), author of the text of the Germania Inferior, originates from the years of refuge in London.
Upon their settlement in Amsterdam in 1593, both Keere and Hondius embarked on a monumental project. Their collaboration resulted in the creation of a large wall map of Europe, a masterpiece that still stands as a testament to their skill and vision, dated 1595: Nova totius Europae descriptio.
In 1610, he set up a workshop in the Kalverstraat that he called ‘In den onseeckeren tijd’ (In the uncertain time). During this period, he made numerous copperplates, including maps for his Atlas of the Netherlands and the Atlas Minor published by Jodocus Hondius.
The Germania Inferior (1617) is the first original atlas of the Netherlands published in folio size. The text for the atlas, both in Dutch and in French, was written by Petrus Montanus. After 1623, Claes Jansz. Visscher bought the plates and substituted his name for Kaerius’s. In 1634, Visscher included many of these maps in his Germana Inferior.
Kaerius's fame is not only based on his atlas of the Netherlands. He is even better known as an engraver of many loose-leaf maps and as a collaborator of book publishers. His maps are found, i.e., in the Caert thresoor (Barent Langenes, 1598), Licht der Zeevaert (Blaeu, 1608), Atlas Minor (Hondius, 1628), and Caertboeck vande Midellandsche Zee (Barents, 1595).