Moscow, by Georg Braun & Frans Hogenberg. 1576
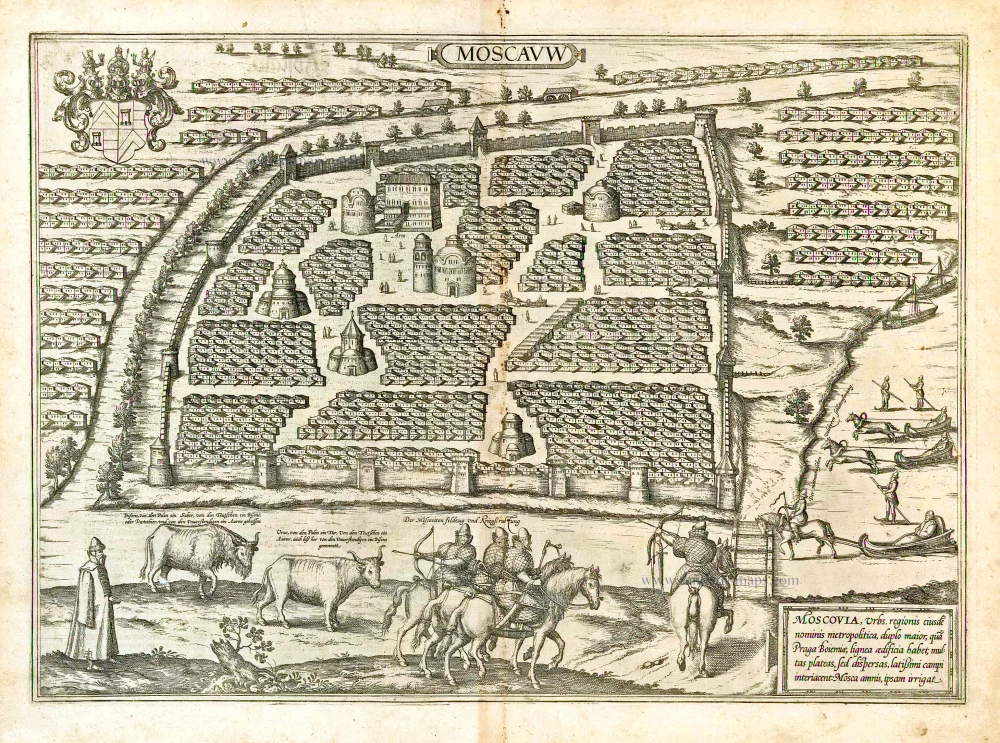
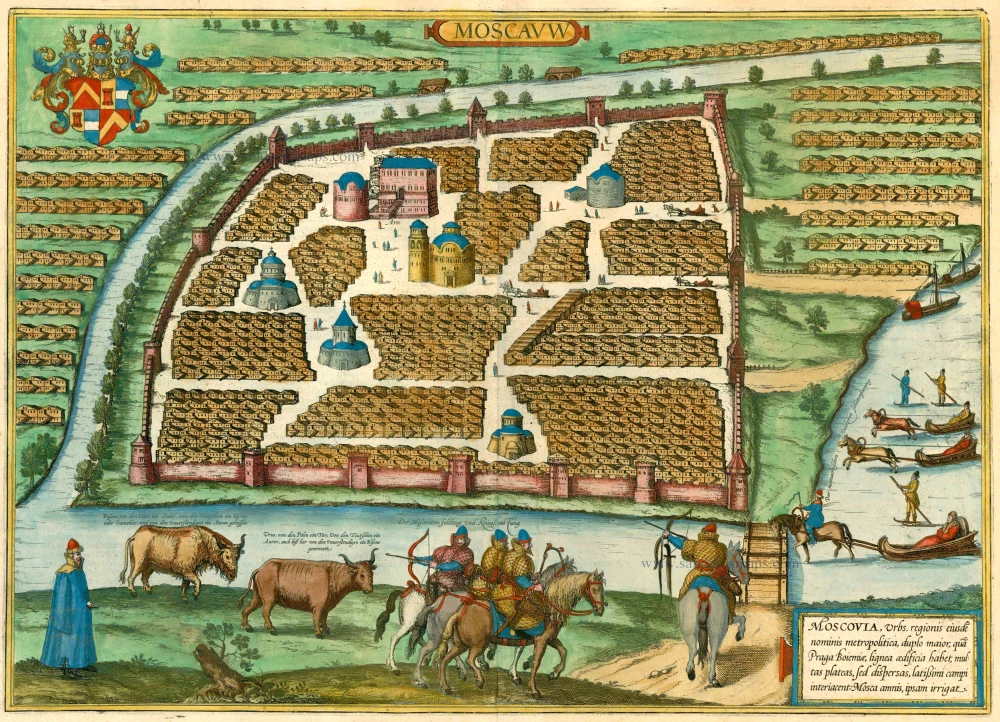
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Moscow, capital of the eponymous region, twice as large as Prague in Bohemia, has wooden buildings, many streets, but scattered, with wide spaces in between them. The Moskva irrigates the city.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "But because of its size the city has no proper end and also it has not been sufficiently fortified with walls, moats or ramparts, but the streets are closed with barriers at several places; when night falls, a strong guard is placed there, so that no one can pass through at night after a certain hour. [...] The Moskva River flows around part of the city, and it is joined very close to the city by the Yauza, which, due to its high bank, can only rarely be waded through."
Moscow is shown very schematically in a bird's-eye view; between the groups of identical houses are e few people and some very simplified large buildings. In contradiction to the text, the city is surrounded by a wall. According to legend, Moscow was founded in 1147 by Yuri Dolgoruki; by the 15th century it had become a large city with decisive wordly and religious power. The symbol of wordly power is the Kremlin, which was constructed from 1485 to 1495 and extended in several stages up to 1530. In 1472, through the marriage of Ivan III with the Byzantine Princess Sophia Palaiologos, the niece of the last East Roman emperor, Moscow also became the centre of the Russian-Orthodox church. By 1600 the fast-growing city already had more than 100,000 inhabitants. On the right people can be seen taking sleigh rides on the Moskva, which is incongruous with the vegetation, and the foreground Russian soldiers, here called "Moscovites", are depicted. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.
Moscauw - Moscovia, Urbs regionis eiusde nominis metropolitica, duplo maior, ...
Item Number: 26914 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Eastern Europe
Old antique bird's-eye view plan of Moscow, by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg.
Date of the first edition: 1575
Date of this map: 1576
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 35 x 49cm (13.7 x 19.1 inches)
Verso text: German
Condition: Excellent
Condition Rating: A+
References: Van der Krogt 4, #2862, State 1; Fauser, #9198; Taschen, Br. Hog., p.179.
From: Beschreibung und Contrafactur von den vornembsten Stetten der Welt. Dass ander Buch. Köln, 1576. (Van der Krogt 4, 41:2.2)
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Moscow, capital of the eponymous region, twice as large as Prague in Bohemia, has wooden buildings, many streets, but scattered, with wide spaces in between them. The Moskva irrigates the city.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "But because of its size the city has no proper end and also it has not been sufficiently fortified with walls, moats or ramparts, but the streets are closed with barriers at several places; when night falls, a strong guard is placed there, so that no one can pass through at night after a certain hour. [...] The Moskva River flows around part of the city, and it is joined very close to the city by the Yauza, which, due to its high bank, can only rarely be waded through."
Moscow is shown very schematically in a bird's-eye view; between the groups of identical houses are e few people and some very simplified large buildings. In contradiction to the text, the city is surrounded by a wall. According to legend, Moscow was founded in 1147 by Yuri Dolgoruki; by the 15th century it had become a large city with decisive wordly and religious power. The symbol of wordly power is the Kremlin, which was constructed from 1485 to 1495 and extended in several stages up to 1530. In 1472, through the marriage of Ivan III with the Byzantine Princess Sophia Palaiologos, the niece of the last East Roman emperor, Moscow also became the centre of the Russian-Orthodox church. By 1600 the fast-growing city already had more than 100,000 inhabitants. On the right people can be seen taking sleigh rides on the Moskva, which is incongruous with the vegetation, and the foreground Russian soldiers, here called "Moscovites", are depicted. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.