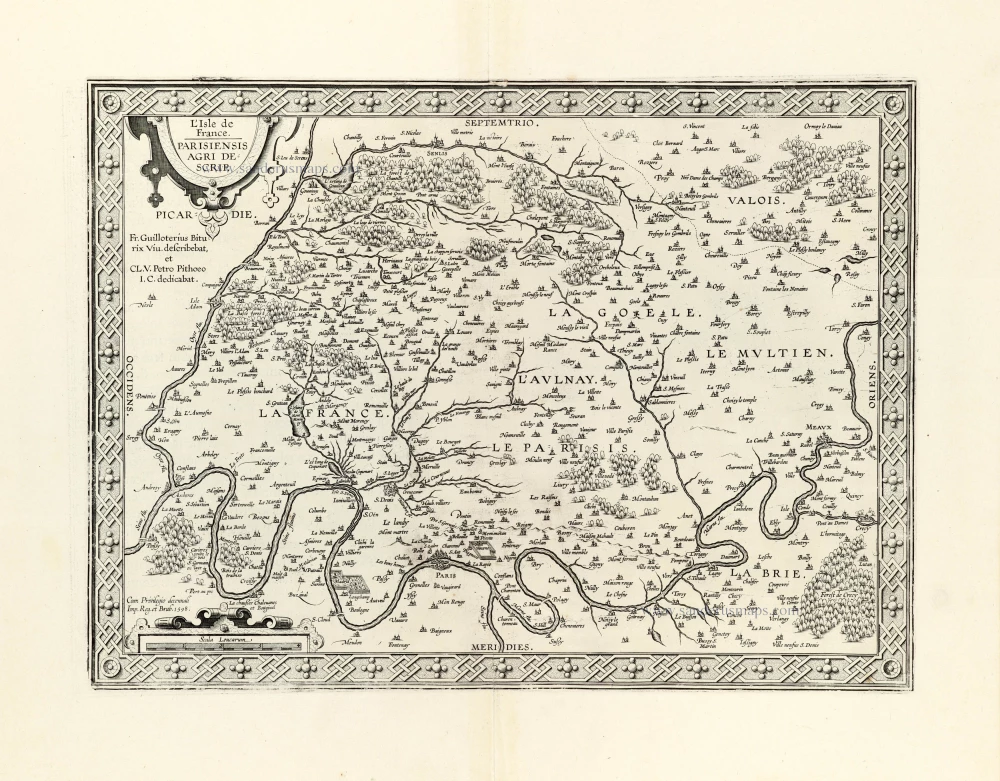
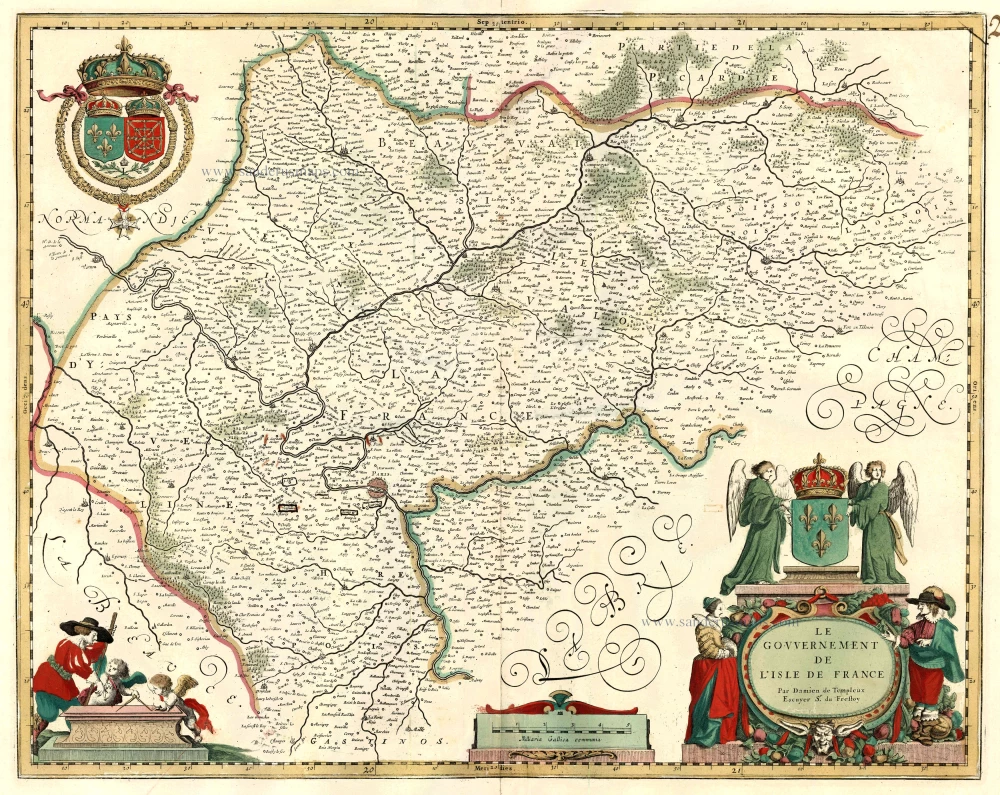
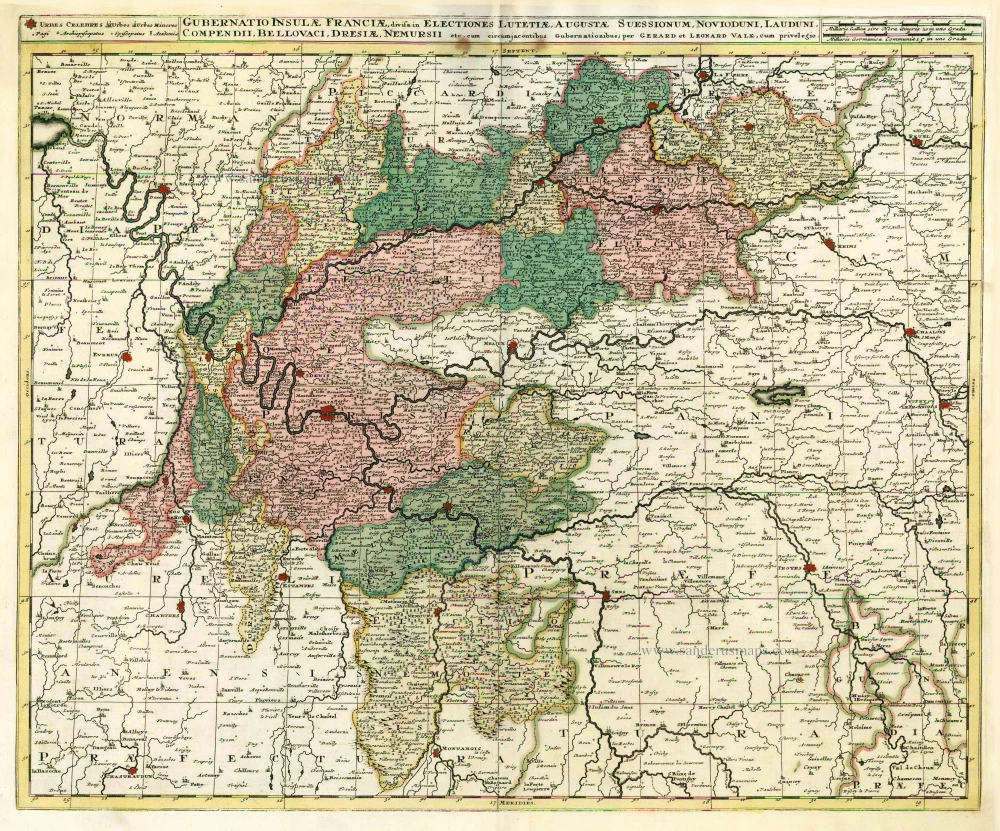
Ile de France by Guillaume Delisle, published by Covens & Mortier. 1721-41
Covens & Mortier. A Map Publishing House in Amsterdam. 1721-1866.
For almost two centuries, the Amsterdam firm of Covens & Mortier was the most significant and crucial Dutch publishing house in commercial cartography. In terms of quantity, it was the biggest contemporary map-trading house worldwide, distributing innumerable maps, atlases, globes, and books.
Pieter (Pierre) Mortier (Leiden, 1661 – Amsterdam, 1711)
Nothing is known about the youth of Pieter Mortier. He studied in Paris from 1681 to approximately 1685. He must have come into contact with French 'libraires' and learned the bookselling trade there. In 1685, he returned to Amsterdam and opened a small bookshop. He joined the Book, Art Sellers' and Printers' Guild the same year.
Pieter sold books in Dutch and foreign languages but also published books himself, usually in French. His business flourished so much that in 1688, he was forced to rent another house on the Vijgendam.
Pieter Mortier's first privilege for maps was granted by the States of Holland and West Friesland on September 15, 1690. It refers to Sanson's maps, which he 'is printing and correcting with great pains and care'.
Pieter began publishing maps and atlases on a large scale. By the beginning of the 18th century, he had become so wealthy that he could purchase three houses in Amsterdam: the Beurssluis, on the Vijgendam, and the Heremietensteeg. He rebuilt the Vijgendam house into a large, prestigious structure that would serve for over a century as a shop, business, and residential structure for Covens & Mortier's publishing house.
He died on February 13, 1711, after a brief illness. The company continued under the management of Pieter's widow, Amelia' s-Gravesande.
After she died in 1719, her son, Cornelis, took over the management for a few years.
On November 20, 1721, a company was founded by Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I. The latter was married the same year to Cornelis's sister. From that year on, the name of :
Covens & Mortier.
Their firm would see a massive expansion in the next 140 years. In 1732, the heirs sold the property to their brother Cornelis and his partner Covens. Their main competitors were Reinier & Josua Ottens and Gerard Valck & Petrus Schenck. After the death of Johannes Covens I (1774), his son Johannes Covens II (1722-1794) entered the business. In 1778, Johannes added a new company name :
J. Covens & Son.
Johannes Covens II was succeeded by his son Cornelis Covens (1764-1825), who, in turn, brought Peter Mortier IV, the great-grandson of Petrus Mortier I, into the business. The name was from 1794 to 1866:
Mortier, Covens & Son.
The last Covens in the series was Cornelis Johannes Covens (1806-1880).
Covens & Mortier had a large stock of atlases and maps, including Delisle, Jaillot, Johannes Janssonius, Sanson, and Claes Jansz. Visscher, Nicolaas Visscher, and Frederik de Wit. For decades, the press produced an impressive number of atlases.
Guillaume Delisle (Paris, 1675 – 1726)
Guillaume Delisle (de L’Isle), one of the key figures in the development of French cartography, is the son of Claude Delisle, a cartographer, and the half-brother of astronomers Joseph-Nicolas Delisle and Louis de l'Isle de la Croyère.
While his father has to be given credit for educating Guillaume, the boy showed early signs of being an exceptional talent. He soon contributed to the family workshop by drawing maps for his father's historical works. To perfect his skills, Guillaume Delisle became the student of the astronomer Jean-Dominique Cassini. Early on, he produced high-quality maps, the first being his Carte de la Nouvelle-France et des Pays Voisins in 1696. Delisle's first atlas appeared around 1700, and in 1702 he became a member of the French Académie Royale des Sciences. He taught geography to the young Louis XV, and in 1718 he received the title of Premier Géographe du Roi. On a commission from Peter the Great, he produced a map of the Caspian Sea, a region barely known. Many of the place names he gave are still in use. His Carte de la Louisiane et du cours du Mississippi (1718) is the first detailed map of this region.
A six-year-long plagiarism trial pits Delisle against Jean-Baptiste Nolin, cartographer. It is Nolin, the real plagiarist, who loses.
Delisle has remained famous for his astronomical-based corrections and the completeness of its topography. The high scientific quality of the work produced by the Delisle family contrasted with the workshop of Sanson. While Sanson knowingly published outdated facts and mistakes, Delisle constantly updated his maps to reflect widening knowledge of the world.
Nova Territorii Parisiensis Tabula ad Usum Serenissimi Burgundiae Ducis.
Item Number: 23769 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > France
Old, antique map of Ile de France, by Guillaume Delisle published by Covens & Mortier.
Title: Nova Territorii Parisiensis Tabula ad Usum Serenissimi Burgundiae Ducis.
Cartographer: Guillaume Delisle.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 470 x 610mm (18.5 x 24.02 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original body colour, on heavy paper, no centrefold (from a plano bound atlas), excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Composite Atlas. Amsterdam, Covens & Mortier, 1721-41.
Covens & Mortier. A Map Publishing House in Amsterdam. 1721-1866.
For almost two centuries, the Amsterdam firm of Covens & Mortier was the most significant and crucial Dutch publishing house in commercial cartography. In terms of quantity, it was the biggest contemporary map-trading house worldwide, distributing innumerable maps, atlases, globes, and books.
Pieter (Pierre) Mortier (Leiden, 1661 – Amsterdam, 1711)
Nothing is known about the youth of Pieter Mortier. He studied in Paris from 1681 to approximately 1685. He must have come into contact with French 'libraires' and learned the bookselling trade there. In 1685, he returned to Amsterdam and opened a small bookshop. He joined the Book, Art Sellers' and Printers' Guild the same year.
Pieter sold books in Dutch and foreign languages but also published books himself, usually in French. His business flourished so much that in 1688, he was forced to rent another house on the Vijgendam.
Pieter Mortier's first privilege for maps was granted by the States of Holland and West Friesland on September 15, 1690. It refers to Sanson's maps, which he 'is printing and correcting with great pains and care'.
Pieter began publishing maps and atlases on a large scale. By the beginning of the 18th century, he had become so wealthy that he could purchase three houses in Amsterdam: the Beurssluis, on the Vijgendam, and the Heremietensteeg. He rebuilt the Vijgendam house into a large, prestigious structure that would serve for over a century as a shop, business, and residential structure for Covens & Mortier's publishing house.
He died on February 13, 1711, after a brief illness. The company continued under the management of Pieter's widow, Amelia' s-Gravesande.
After she died in 1719, her son, Cornelis, took over the management for a few years.
On November 20, 1721, a company was founded by Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I. The latter was married the same year to Cornelis's sister. From that year on, the name of :
Covens & Mortier.
Their firm would see a massive expansion in the next 140 years. In 1732, the heirs sold the property to their brother Cornelis and his partner Covens. Their main competitors were Reinier & Josua Ottens and Gerard Valck & Petrus Schenck. After the death of Johannes Covens I (1774), his son Johannes Covens II (1722-1794) entered the business. In 1778, Johannes added a new company name :
J. Covens & Son.
Johannes Covens II was succeeded by his son Cornelis Covens (1764-1825), who, in turn, brought Peter Mortier IV, the great-grandson of Petrus Mortier I, into the business. The name was from 1794 to 1866:
Mortier, Covens & Son.
The last Covens in the series was Cornelis Johannes Covens (1806-1880).
Covens & Mortier had a large stock of atlases and maps, including Delisle, Jaillot, Johannes Janssonius, Sanson, and Claes Jansz. Visscher, Nicolaas Visscher, and Frederik de Wit. For decades, the press produced an impressive number of atlases.
Guillaume Delisle (Paris, 1675 – 1726)
Guillaume Delisle (de L’Isle), one of the key figures in the development of French cartography, is the son of Claude Delisle, a cartographer, and the half-brother of astronomers Joseph-Nicolas Delisle and Louis de l'Isle de la Croyère.
While his father has to be given credit for educating Guillaume, the boy showed early signs of being an exceptional talent. He soon contributed to the family workshop by drawing maps for his father's historical works. To perfect his skills, Guillaume Delisle became the student of the astronomer Jean-Dominique Cassini. Early on, he produced high-quality maps, the first being his Carte de la Nouvelle-France et des Pays Voisins in 1696. Delisle's first atlas appeared around 1700, and in 1702 he became a member of the French Académie Royale des Sciences. He taught geography to the young Louis XV, and in 1718 he received the title of Premier Géographe du Roi. On a commission from Peter the Great, he produced a map of the Caspian Sea, a region barely known. Many of the place names he gave are still in use. His Carte de la Louisiane et du cours du Mississippi (1718) is the first detailed map of this region.
A six-year-long plagiarism trial pits Delisle against Jean-Baptiste Nolin, cartographer. It is Nolin, the real plagiarist, who loses.
Delisle has remained famous for his astronomical-based corrections and the completeness of its topography. The high scientific quality of the work produced by the Delisle family contrasted with the workshop of Sanson. While Sanson knowingly published outdated facts and mistakes, Delisle constantly updated his maps to reflect widening knowledge of the world.