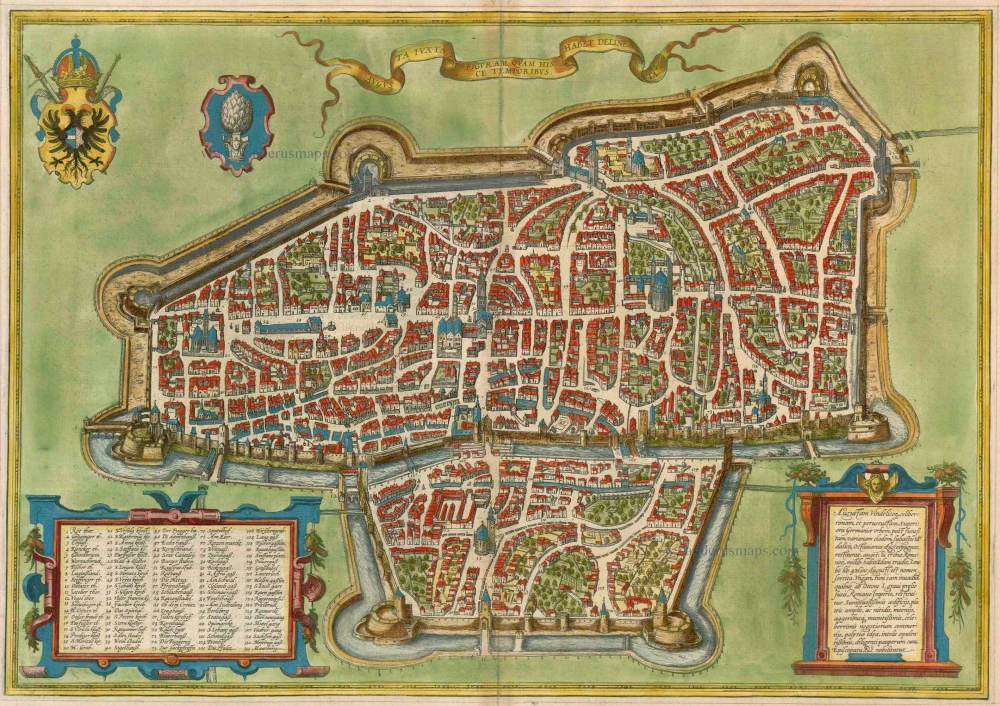
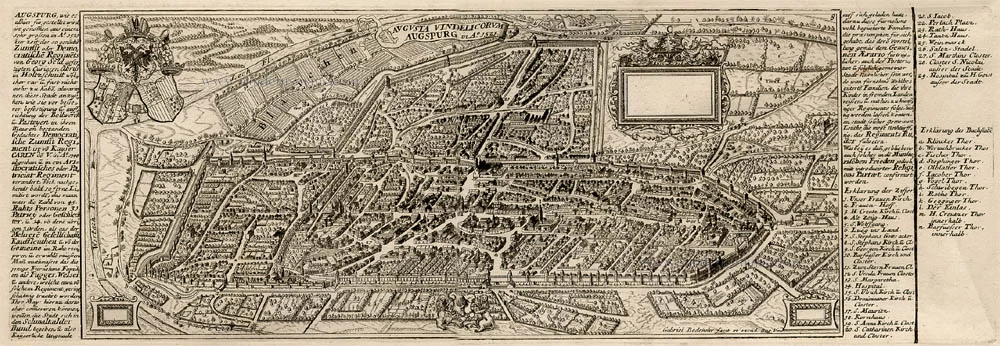
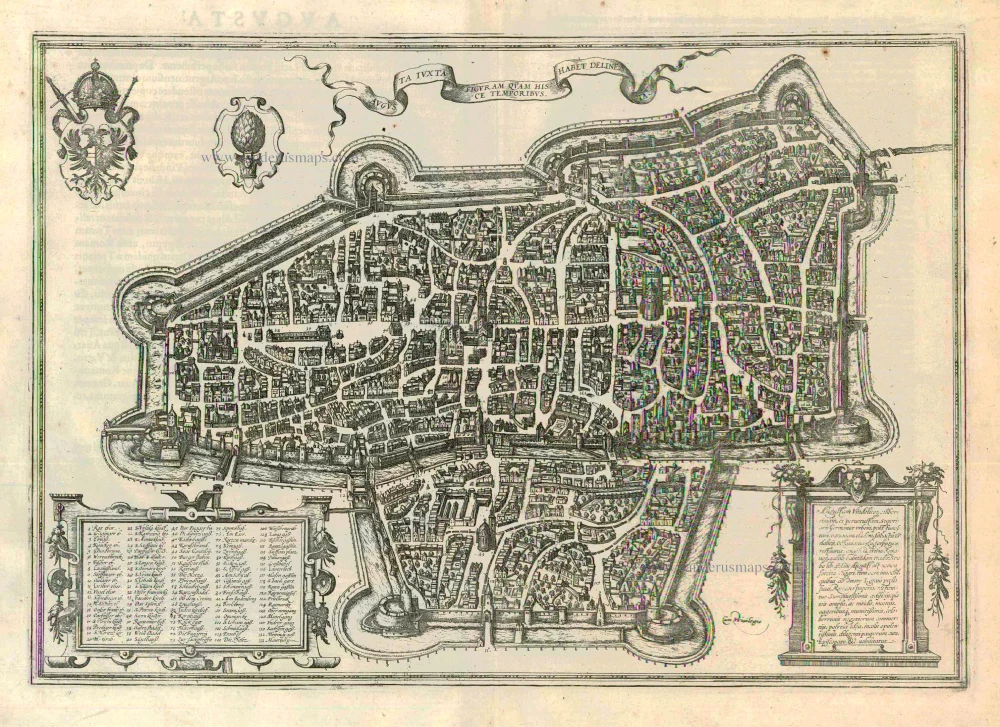
Augsburg, by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg. 1575
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Following the catastrophic defeat of Varus and the subjugation of the Vandals, Octavianus Augustus conquered, rebuilt and enlarged Augusta Vindelicorum [Augsburg], a widely famed and very ancient city in Upper Germany. According to Strabo he settled 3,000 Romans here, from which the city took the name Augusta. Otto I repulsed a Hungarian attack in a heavy battle and restored Augsburg to the Empire. Augsburg's glory is based on lavish buildings, spacious and magnificent squares, extremely defensive walls, moats and embankments, its significant turnover of goods, its internal constitution, its wealthy inhabitants and its care for the poor as well as its episcopal see, among other things.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The authorities of this city dedicate themselves in particular to caring for the poor. For as well as maintaining a hospice and an orphanage, in periods when the plague or syphilis were raging they also established a hospital, the Blatterhaus, to tend to and accommodate the afflicted. Furthermore, in 1519 and at their own expense, the Fugger family built about 100 houses for needy but respectable citizens in the suburb of St James, in effect a distinct quarter, which is called the Fuggerei."
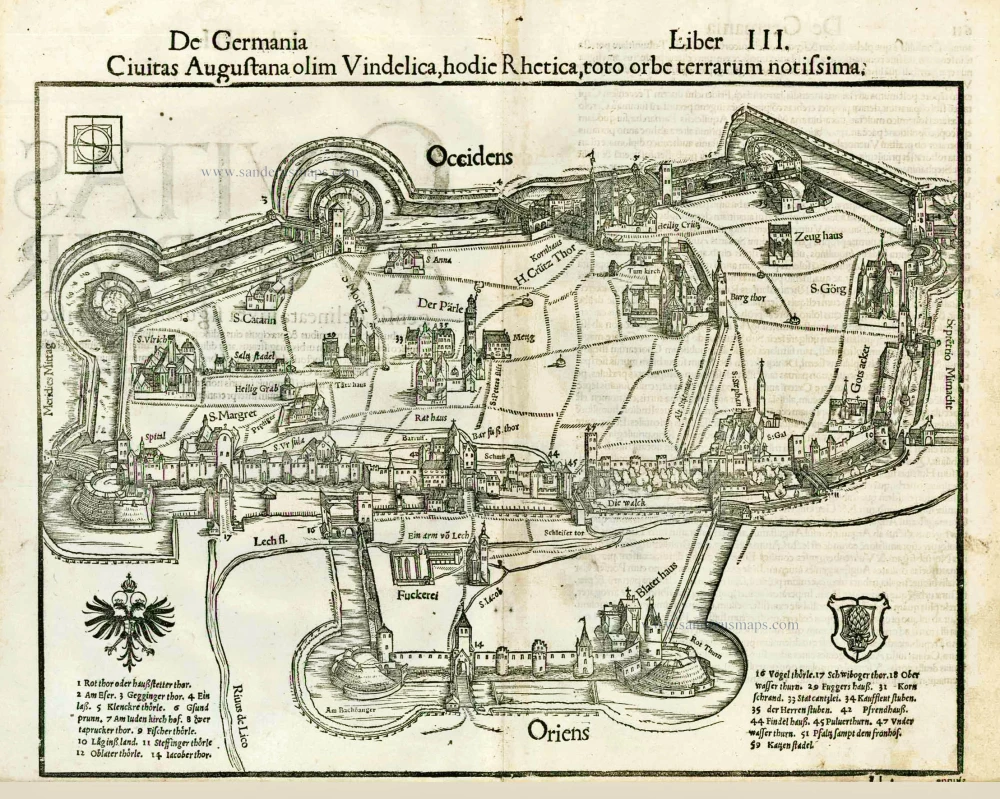
The bird's-eye view of Augsburg shows the individual groups of buildings very clearly, including the Fuggerei (72, bottom left), mentioned by Braun and founded in 1514 as an enclosed housing complex for impoverished citizens. The cathedral (32, right) is a Romanesque building with Gothic elements. Directly beside the town hall (52) in the centre of the city lies the church of St Peter am Perlach (35). Its tall tower, called the Perlachturm, was remodelled in the 17th century and is a city landmark. The present town hall was begun in 1615 in the Renaissance style. The church of St Anne houses the burial chapel of the Fugger family; Martin Luther stayed at the affiliated monastery (23, above St Peter am Perlach) when he was summoned to Augsburg to defend his theses before the imperial diet in 1518. The Benedictine abbey of SS Ulrich and Afra (17) on the left-hand edge of the map dates from the 15th century, when Augsburg was home to some 30,000 inhabitants. During this period Augsburg was a centre of German economic and intellectual life and frequently played host to imperial diets. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a broader audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. Seven more editions followed the first volume in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.
Augusta Iuxta Figuram ...
Item Number: 6425 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Germany - Cities
Old, antique map - bird's-eye view plan of Augsburg by Braun and Hogenberg.
With a key to locations.
Date of the first edition: 1572
Date of this map: 1575
Copper engraving
Size: 33 x 47cm (12.9 x 18.3 inches)
Verso text: Latin
Condition: Old coloured.
Condition Rating: A
References: Van der Krogt 4, 307, state 2 (with privilege); Taschen, Braun and Hogenberg, p.101.
From: Civitates Orbis Terrarum, Liber Primus. Antwerp, Gilles van den Rade, 1575. (Van der Krogt 4, 41:1.1)
TRANSLATION OF CARTOUCHE TEXT: Following the catastrophic defeat of Varus and the subjugation of the Vandals, Octavianus Augustus conquered, rebuilt and enlarged Augusta Vindelicorum [Augsburg], a widely famed and very ancient city in Upper Germany. According to Strabo he settled 3,000 Romans here, from which the city took the name Augusta. Otto I repulsed a Hungarian attack in a heavy battle and restored Augsburg to the Empire. Augsburg's glory is based on lavish buildings, spacious and magnificent squares, extremely defensive walls, moats and embankments, its significant turnover of goods, its internal constitution, its wealthy inhabitants and its care for the poor as well as its episcopal see, among other things.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The authorities of this city dedicate themselves in particular to caring for the poor. For as well as maintaining a hospice and an orphanage, in periods when the plague or syphilis were raging they also established a hospital, the Blatterhaus, to tend to and accommodate the afflicted. Furthermore, in 1519 and at their own expense, the Fugger family built about 100 houses for needy but respectable citizens in the suburb of St James, in effect a distinct quarter, which is called the Fuggerei."
The bird's-eye view of Augsburg shows the individual groups of buildings very clearly, including the Fuggerei (72, bottom left), mentioned by Braun and founded in 1514 as an enclosed housing complex for impoverished citizens. The cathedral (32, right) is a Romanesque building with Gothic elements. Directly beside the town hall (52) in the centre of the city lies the church of St Peter am Perlach (35). Its tall tower, called the Perlachturm, was remodelled in the 17th century and is a city landmark. The present town hall was begun in 1615 in the Renaissance style. The church of St Anne houses the burial chapel of the Fugger family; Martin Luther stayed at the affiliated monastery (23, above St Peter am Perlach) when he was summoned to Augsburg to defend his theses before the imperial diet in 1518. The Benedictine abbey of SS Ulrich and Afra (17) on the left-hand edge of the map dates from the 15th century, when Augsburg was home to some 30,000 inhabitants. During this period Augsburg was a centre of German economic and intellectual life and frequently played host to imperial diets. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a broader audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. Seven more editions followed the first volume in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.