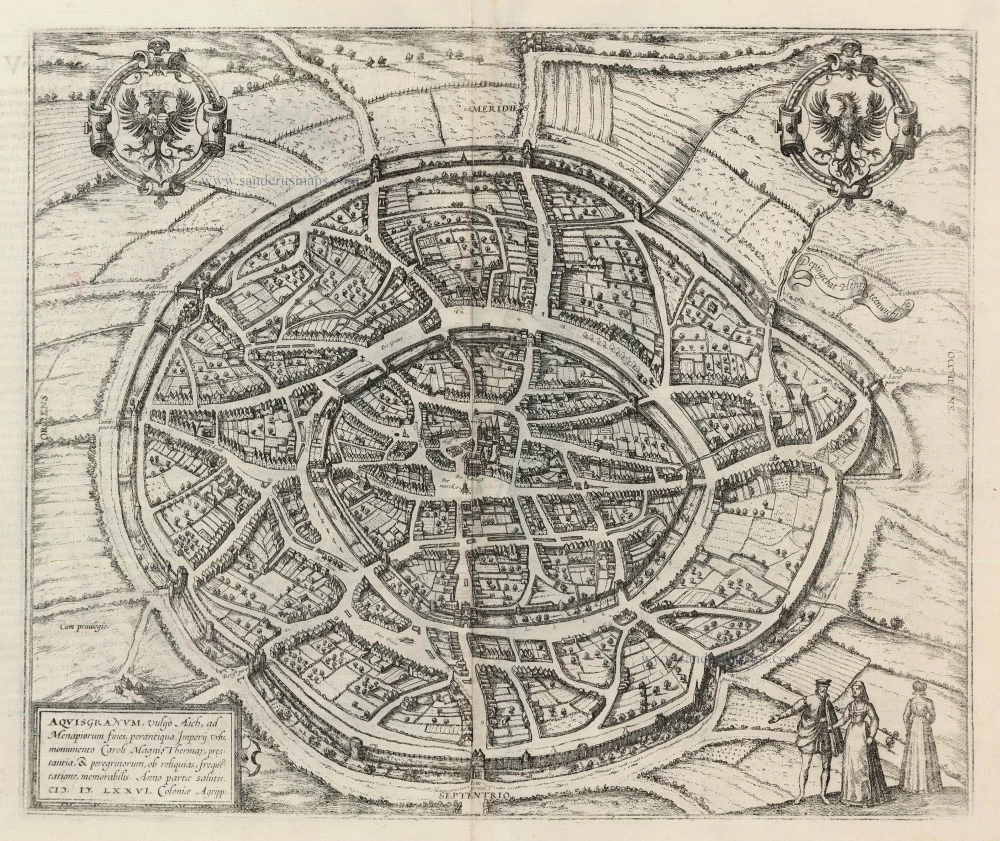
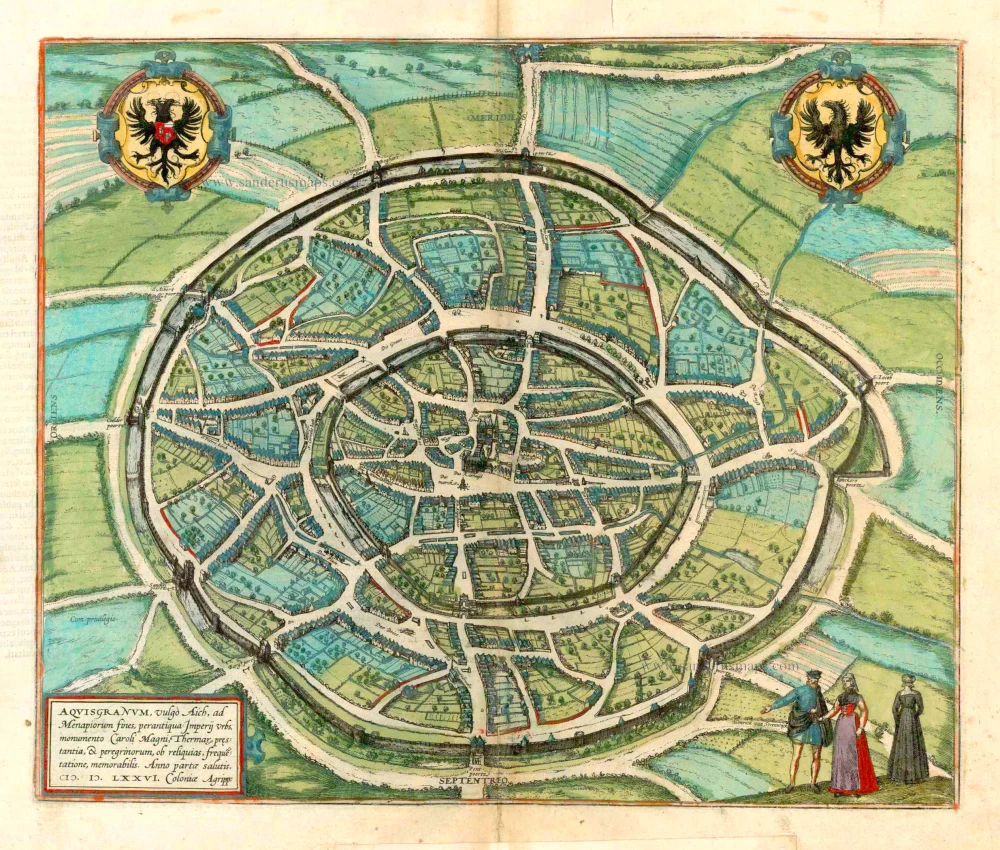
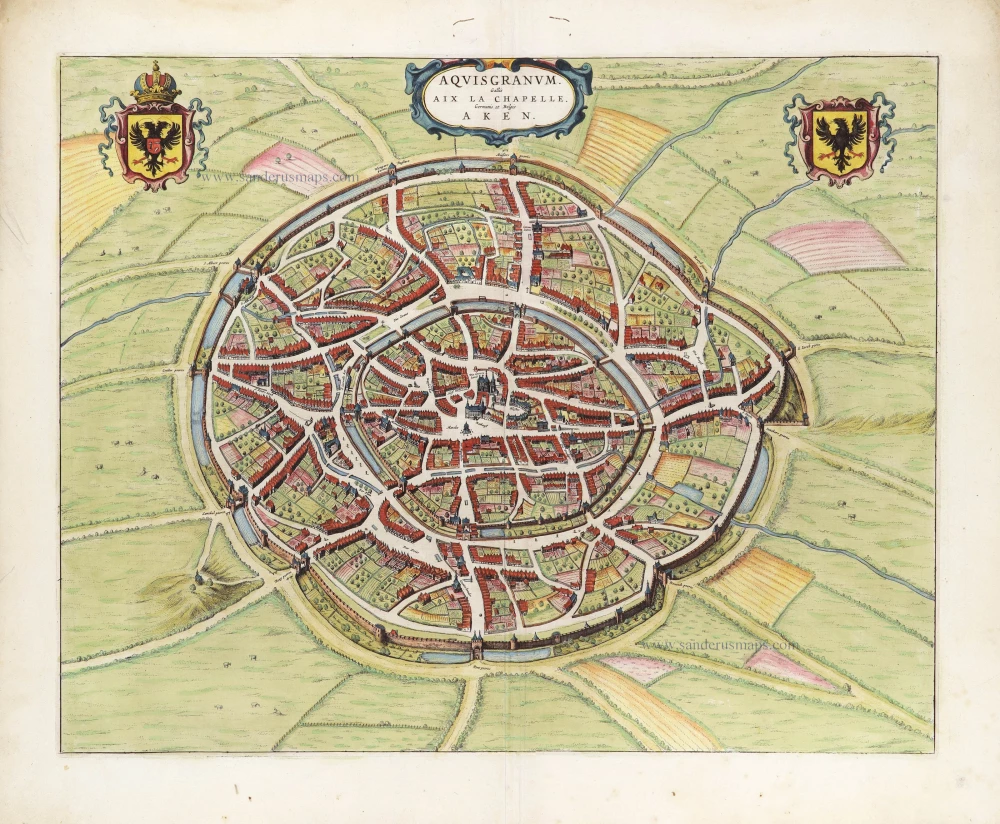
Optical view of Aachen, published in Paris by Jacques Chereau. c. 1740
Optical View (French: Vue d'optique)
An optical view is a type of 18th-century hand-coloured engraved print to be viewed through a special optical device. It depicts architectural, city, or landscape scenes and is designed to give a strong illusion of depth and perspective when seen through a magnifying lens or viewing box. Characteristic of an optical view is the reversed inscription: The titles or captions were often printed backwards, because the viewing device used a mirror that would flip the image right-side up again. The artists enhanced depth with bold converging lines and bright colours. The optical views were used for popular entertainment and education, a way for people to "travel" visually. They originated in France and England around the 1740s and became fashionable across Europe. They were often sold by travelling print sellers or displayed in fairs and parlours.
Vue de la Fontaine des Eaux chaudes et de la place d'Aix la Chapelle.
Item Number: 32310 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Germany - Cities
Optical view of Aachen, published in Paris by Jacques Chereau.
Title: Vue de la Fontaine des Eaux chaudes et de la place d'Aix la Chapelle.
A Paris chez Jacques Chereau rue St. Jacques au desous de la Fontaine St. Severin.
Date: c. 1740.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 300 x 440mm (11¾ x 17¼ inches).
Sheet size: 330 x 475mm (13 x 18¾ inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original coloured, good.
Condition Rating: A.
Separate publication.
Optical View (French: Vue d'optique)
An optical view is a type of 18th-century hand-coloured engraved print to be viewed through a special optical device. It depicts architectural, city, or landscape scenes and is designed to give a strong illusion of depth and perspective when seen through a magnifying lens or viewing box. Characteristic of an optical view is the reversed inscription: The titles or captions were often printed backwards, because the viewing device used a mirror that would flip the image right-side up again. The artists enhanced depth with bold converging lines and bright colours. The optical views were used for popular entertainment and education, a way for people to "travel" visually. They originated in France and England around the 1740s and became fashionable across Europe. They were often sold by travelling print sellers or displayed in fairs and parlours.