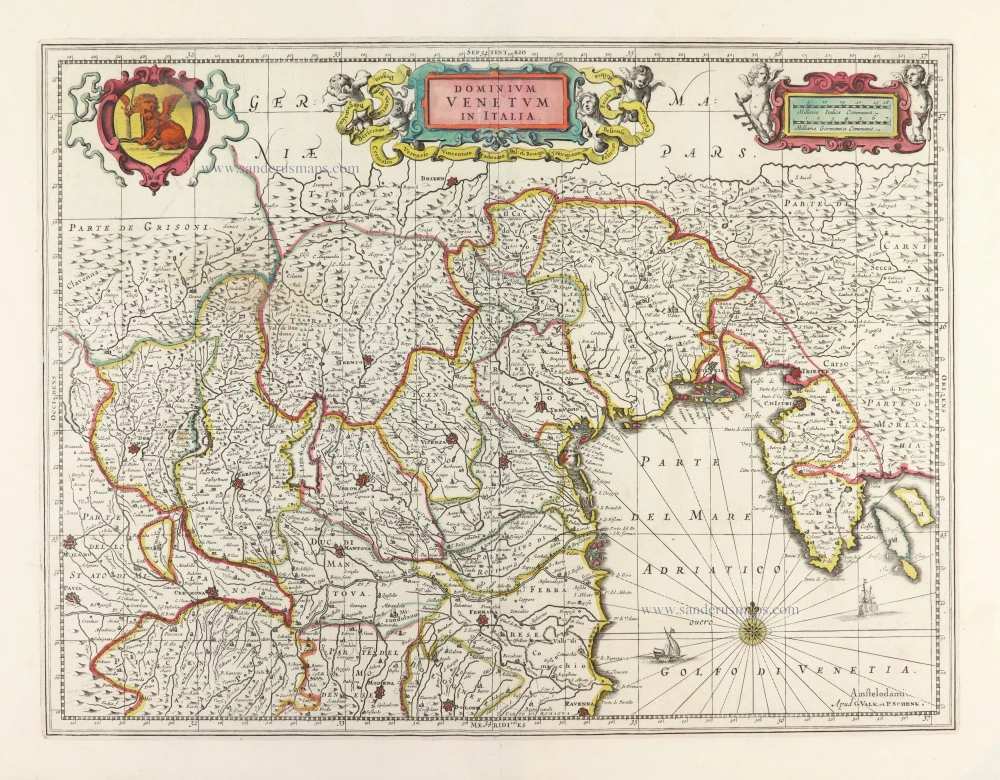
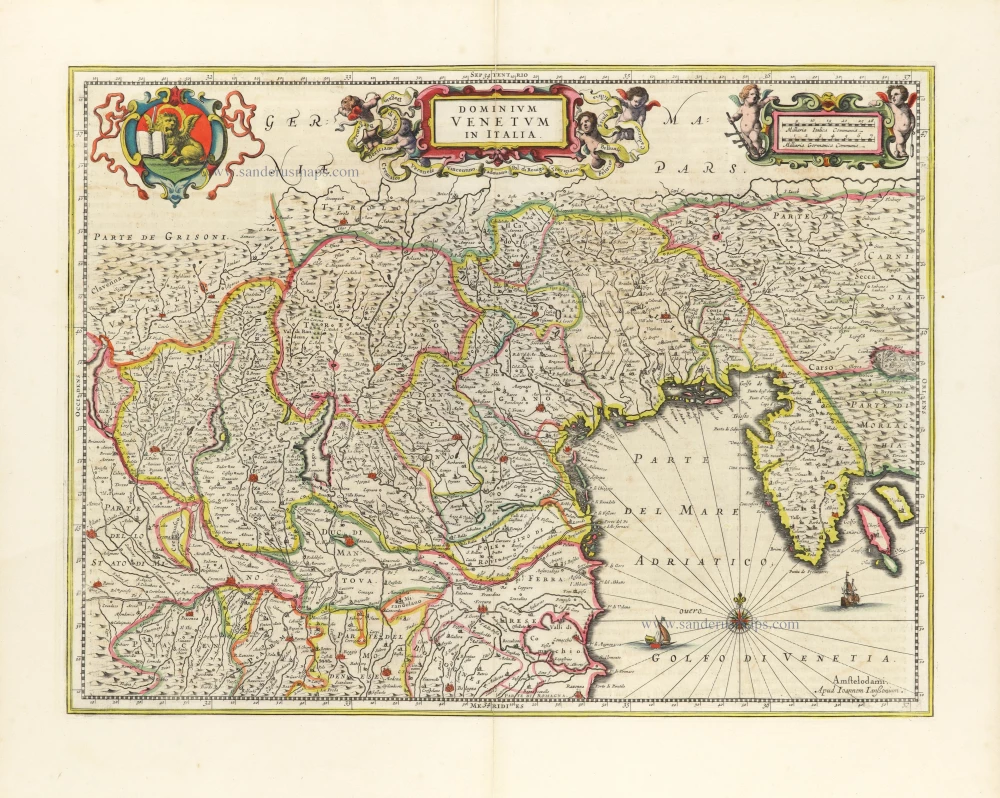
Veneto by Joannes Janssonius, published by G. Valk and P. Schenk. c. 1700
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
The Valk Family
Gerard Valk (Valck) (1652-1726) was Amsterdam's publisher, engraver, art seller, and globemaker. He was trained under Abraham Bloteling, later becoming his assistant. The two moved to London, where Valk worked with various map and print sellers. He married Abraham's sister, Maria Bloteling, in London around 1673; in that city, his son and successor, Leonard, was born in 1675.
Not long after, Bloteling and Valk returned to Amsterdam, where Gerard Valk was registered as a burgher on December 8, 1679.
Around 1680 he began working with the German engraver Petrus Schenk as an engraver, publisher, map and print-sellers. They acquired the plates for the Janssonius Novus Atlas and Sanson's maps. Although they never shared premises, they worked closely together in the publications of editions of these works. Valk and his son Leonard are best known for their globemaking. In addition to globes newly compiled from the latest geographical and astronomical information, the Valk's published theoretical works on astronomy and globes.
In 1710, the family tie between the two partners, Valk and Schenk, became even closer when Gerard's son Leonard Valk (1675-1746) married Maria Schenk (1688-1770), Petrus' daughter.
After the death of Gerard in 1726, the business continued in the hands of his son Leonard and Gerard's widow Maria until she died in 1729, and then by Leonard until he died in 1746.
The Schenk Family
Petrus Schenk (1660-1718), the founder of one of the best-known publishing firms of Amsterdam in the 18th century, was born in Elberfeld, Germany, in 1660. He went to Amsterdam, where he became a pupil of the engraver Gerard Valck. On 19 Nov. 1686, a privilegio was granted to Petrus Schenk and Gerard Valk for the manufacturing and selling their prints—Schenk’s contribution to cartography dates from c. 1695. In 1706, he moved to the Vijgendam in Amsterdam, ‘in Sanson’s Atlas’. After he died in 1718, his son, Leonardus Schenk, continued the art and print shop. The second son, Petrus II (1693-1775), settled in another famous house: ‘in Visscher’s Atlas’, where he continued associating with Gerard and Leonarus Valck.
The Schenk family produced general geographical atlases and special atlases. Apart from seventy original maps, several hundred are known as Schenk, printed from plates obtained from Janssonius and Visscher. Schenk and Valck acquired all the plates of the Janssonius Heir’s Novus Atlas, including the Celestial Atlas. Many of Janssonius’ plates were reworked and amended.
Republishing maps from Janssonius’ Novus Atlas since c. 1680 was followed by engraving new maps copied from Sanson’s better and more modern maps. Petrus Schenk published these maps in his Atlas Contractus sive mapparum geographicarum Sansoniarum auctarum et correctum Nova Congeries, also called Atlas Minor. After 1719, Petrus Schenk II continued the Atlas Contractus.
Petrus Schenk, the elder, enjoyed great fame as a print seller and artist among art and print dealers in the whole of Europe. The great activity in map publishing, displayed by Petrus Schenk, the elder, was continued by his son and grandson. But the number of original atlas maps is small. Like his father, who bought the copperplates of Janssonius’ atlas, Petrus Schenk II bought many of the plates formerly owned by Nicolaas Visscher.
Apart from the globes, maps and atlases, Petrus Schenk II published many books. In 1733, he was older men of the booksellers guild in 1733.
Petrus Schenk Junior (1728-1803) was an engraver and artseller. He continued to publish many of the titles his father and grandfather issued, and the globes of his uncle Leonard Valk.
Dominium Venetum in Italia.
Item Number: 30233 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Italy
Veneto by Joannes Janssonius, published by G. Valk and P. Schenk.
Title: Dominium Venetum in Italia.
Amstelodami Apud G. Valk et P. Schenk.
Date of the first edition: 1644.
Date of this map: c. 1700.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 370 x 490mm (14.57 x 19.29 inches).
Sheet size: 520 x 610mm (20.47 x 24.02 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Composite Atlas. Amsterdam, c.1700.
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
The Valk Family
Gerard Valk (Valck) (1652-1726) was Amsterdam's publisher, engraver, art seller, and globemaker. He was trained under Abraham Bloteling, later becoming his assistant. The two moved to London, where Valk worked with various map and print sellers. He married Abraham's sister, Maria Bloteling, in London around 1673; in that city, his son and successor, Leonard, was born in 1675.
Not long after, Bloteling and Valk returned to Amsterdam, where Gerard Valk was registered as a burgher on December 8, 1679.
Around 1680 he began working with the German engraver Petrus Schenk as an engraver, publisher, map and print-sellers. They acquired the plates for the Janssonius Novus Atlas and Sanson's maps. Although they never shared premises, they worked closely together in the publications of editions of these works. Valk and his son Leonard are best known for their globemaking. In addition to globes newly compiled from the latest geographical and astronomical information, the Valk's published theoretical works on astronomy and globes.
In 1710, the family tie between the two partners, Valk and Schenk, became even closer when Gerard's son Leonard Valk (1675-1746) married Maria Schenk (1688-1770), Petrus' daughter.
After the death of Gerard in 1726, the business continued in the hands of his son Leonard and Gerard's widow Maria until she died in 1729, and then by Leonard until he died in 1746.
The Schenk Family
Petrus Schenk (1660-1718), the founder of one of the best-known publishing firms of Amsterdam in the 18th century, was born in Elberfeld, Germany, in 1660. He went to Amsterdam, where he became a pupil of the engraver Gerard Valck. On 19 Nov. 1686, a privilegio was granted to Petrus Schenk and Gerard Valk for the manufacturing and selling their prints—Schenk’s contribution to cartography dates from c. 1695. In 1706, he moved to the Vijgendam in Amsterdam, ‘in Sanson’s Atlas’. After he died in 1718, his son, Leonardus Schenk, continued the art and print shop. The second son, Petrus II (1693-1775), settled in another famous house: ‘in Visscher’s Atlas’, where he continued associating with Gerard and Leonarus Valck.
The Schenk family produced general geographical atlases and special atlases. Apart from seventy original maps, several hundred are known as Schenk, printed from plates obtained from Janssonius and Visscher. Schenk and Valck acquired all the plates of the Janssonius Heir’s Novus Atlas, including the Celestial Atlas. Many of Janssonius’ plates were reworked and amended.
Republishing maps from Janssonius’ Novus Atlas since c. 1680 was followed by engraving new maps copied from Sanson’s better and more modern maps. Petrus Schenk published these maps in his Atlas Contractus sive mapparum geographicarum Sansoniarum auctarum et correctum Nova Congeries, also called Atlas Minor. After 1719, Petrus Schenk II continued the Atlas Contractus.
Petrus Schenk, the elder, enjoyed great fame as a print seller and artist among art and print dealers in the whole of Europe. The great activity in map publishing, displayed by Petrus Schenk, the elder, was continued by his son and grandson. But the number of original atlas maps is small. Like his father, who bought the copperplates of Janssonius’ atlas, Petrus Schenk II bought many of the plates formerly owned by Nicolaas Visscher.
Apart from the globes, maps and atlases, Petrus Schenk II published many books. In 1733, he was older men of the booksellers guild in 1733.
Petrus Schenk Junior (1728-1803) was an engraver and artseller. He continued to publish many of the titles his father and grandfather issued, and the globes of his uncle Leonard Valk.