Antique map of Ancient World by Ortelius A. - Moretus B. 1624
Abraham Ortelius (1527-1598)
The maker of the 'first atlas', the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570), was born on 4 April 1527 into an old Antwerp family. He learned Latin and studied Greek and mathematics.
Abraham and his sisters Anne and Elizabeth took up map colouring. He was admitted to the Guild of St. Luke as an "illuminator of maps." Besides colouring maps, Ortelius was a dealer in antiques, coins, maps, and books, with the book and map trade gradually becoming his primary occupation.
Business went well because his means permitted him to start an extensive collection of medals, coins, antiques, and a library of many volumes. In addition, he travelled a lot and visited Italy and France, made contacts everywhere with scholars and editors, and maintained extensive correspondence with them.
In 1564 he published his first map, a large and ambitious world wall map. The inspiration for this map may well have been Gastaldi's large world map. In 1565 he published a map of Egypt and a map of the Holy Land, a large map of Asia followed.
In 1568 the production of individual maps for his atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was already in full swing. He completed the atlas in 1569, and in May of 1570, the Theatrum was available for sale. It was one of the most expensive books ever published.
This first edition contained seventy maps on fifty-three sheets. Franciscus Hogenberg engraved the maps.
Later editions included Additamenta (additions), resulting in Ortelius' historical atlas, the Parergon, mostly bound together with the atlas. The Parergon can be called a truly original work of Ortelius, who drew the maps based on his research.
The importance of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum for geographical knowledge in the last quarter of the sixteenth century is difficult to overemphasize. Nothing was like it until Mercator's atlas appeared twenty-five years later. Demand for the Theatrum was remarkable. Some 24 editions appeared during Ortelius's lifetime and another ten after his death in 1598. Editions were published in Dutch, German, French, Spanish, English, and Italian. The number of map sheets grew from 53 in 1570 to 167 in 1612 in the last edition.
In 1577, engraver Philip Galle and poet-translator Pieter Heyns published the first pocket-sized edition of the Theatrum, the Epitome. The work was trendy. Over thirty editions of this Epitome were published in different languages.
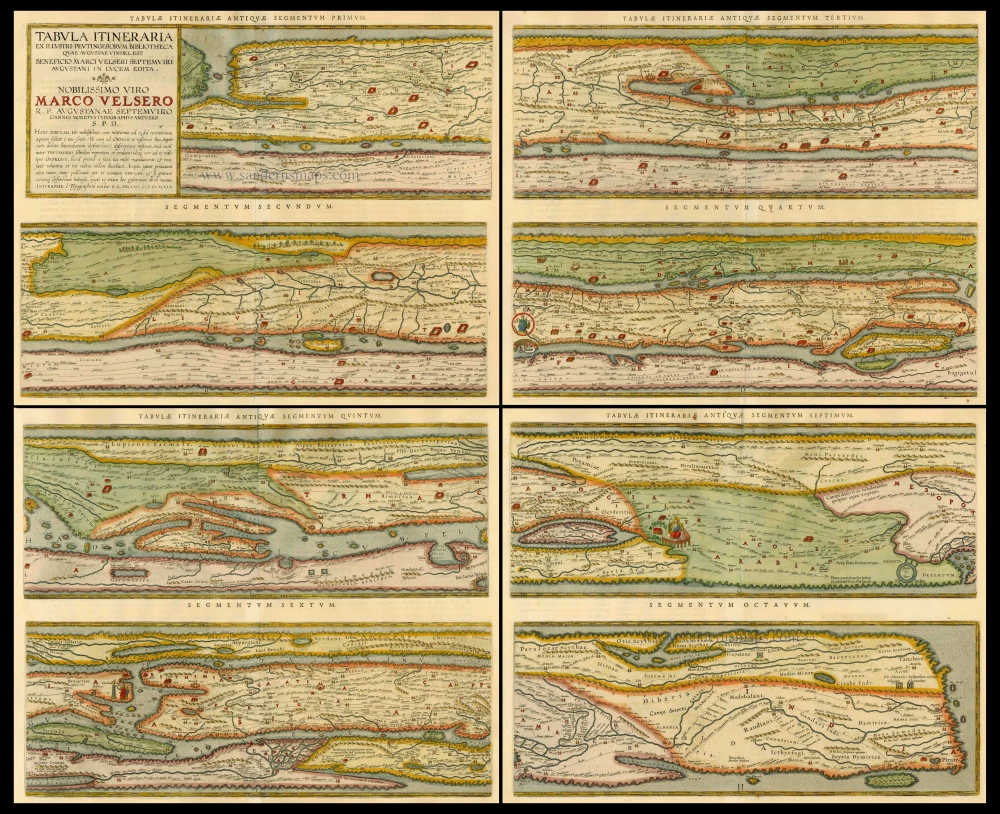
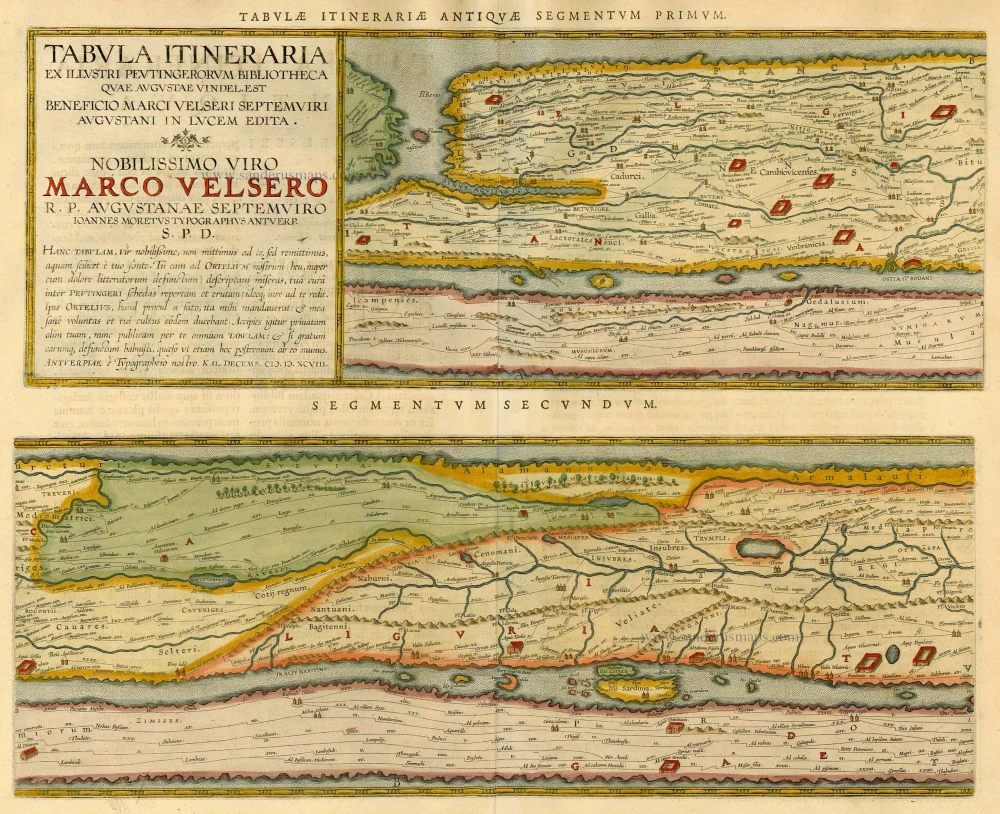
Tabula Itineraria ex illustri Peutingerorum Bibliotheca Quae Augustae Vindeli.Est Beneficio Marci Velseri Septemviri Augustani In lucem edita.
Item Number: 14767 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > World and Polar
Eight segments on 4 sheets, copper engraving
Approximate size of each plate: 19.5 x 51.5cm (8 x 20 inches)
Verso text: Latin
Condition: Old coloured, excellent.
References: Van der Krogt 3, 0940/1:31 - 4:1; Van den Broecke, 227-230; Shirley (World) 212.
From: Theatri Orbis Terrarum Parergon. Antwerpen. Balthasar Moretus, 1624. (Van der Krogt 3, 31:711)
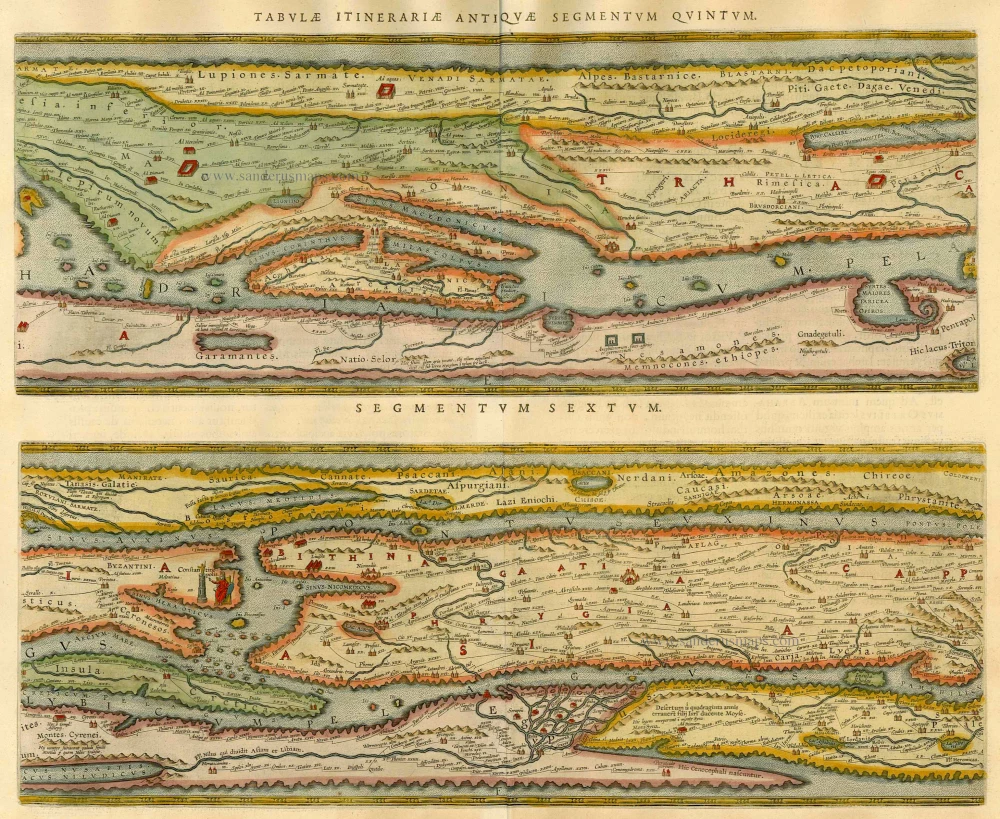
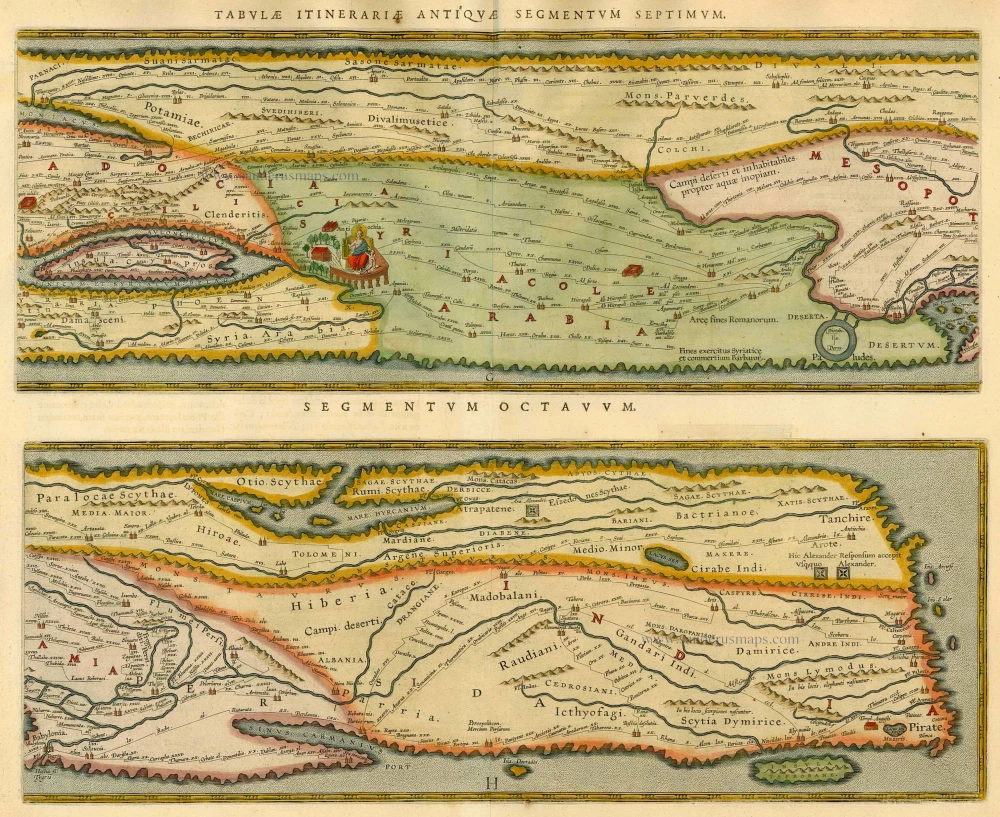
The Tabula Peutingeriana is the sole surviving copy of the Roman cursus publicus; it was made by a monk in Colmar in the thirteenth century. It is a parchment scroll, 0.34 m high and 6.75 m long, assembled from eleven sections, a medieval reproduction of the original scroll. It is a very schematic map: the land masses are distorted, especially in the east-west direction. The map shows many Roman settlements, the roads connecting them, rivers, mountains, forests and seas. The distances between the settlements are also given. Three most important cities of the Roman Empire, Rome, Constantinople and Antioch, are represented with special iconic decoration. Besides the totality of the Empire, the map shows the Near East, India and the Ganges, Sri Lanka (Insula Trapobane), even an indication of China. In the west, the absence of the Iberian Peninsula indicates that a twelfth original section has been lost in the surviving copy.
Abraham Ortelius (1527-1598)
The maker of the 'first atlas', the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570), was born on 4 April 1527 into an old Antwerp family. He learned Latin and studied Greek and mathematics.
Abraham and his sisters Anne and Elizabeth took up map colouring. He was admitted to the Guild of St. Luke as an "illuminator of maps." Besides colouring maps, Ortelius was a dealer in antiques, coins, maps, and books, with the book and map trade gradually becoming his primary occupation.
Business went well because his means permitted him to start an extensive collection of medals, coins, antiques, and a library of many volumes. In addition, he travelled a lot and visited Italy and France, made contacts everywhere with scholars and editors, and maintained extensive correspondence with them.
In 1564 he published his first map, a large and ambitious world wall map. The inspiration for this map may well have been Gastaldi's large world map. In 1565 he published a map of Egypt and a map of the Holy Land, a large map of Asia followed.
In 1568 the production of individual maps for his atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was already in full swing. He completed the atlas in 1569, and in May of 1570, the Theatrum was available for sale. It was one of the most expensive books ever published.
This first edition contained seventy maps on fifty-three sheets. Franciscus Hogenberg engraved the maps.
Later editions included Additamenta (additions), resulting in Ortelius' historical atlas, the Parergon, mostly bound together with the atlas. The Parergon can be called a truly original work of Ortelius, who drew the maps based on his research.
The importance of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum for geographical knowledge in the last quarter of the sixteenth century is difficult to overemphasize. Nothing was like it until Mercator's atlas appeared twenty-five years later. Demand for the Theatrum was remarkable. Some 24 editions appeared during Ortelius's lifetime and another ten after his death in 1598. Editions were published in Dutch, German, French, Spanish, English, and Italian. The number of map sheets grew from 53 in 1570 to 167 in 1612 in the last edition.
In 1577, engraver Philip Galle and poet-translator Pieter Heyns published the first pocket-sized edition of the Theatrum, the Epitome. The work was trendy. Over thirty editions of this Epitome were published in different languages.