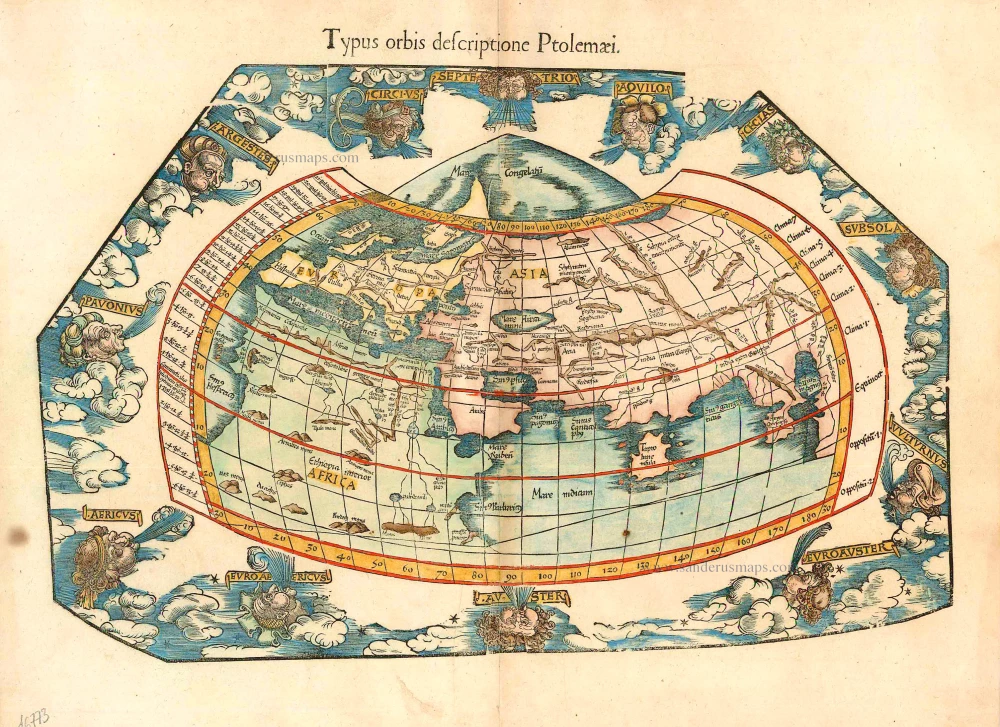
Antique map of the Ptolemaic World by C. Ptolemy - L. Fries 1541
Lorenz Fries* (c. 1485 – 1532)
Lorenz Fries, a physician, astrologer, and cartographic editor, was a native Alsatian. Nothing is known about his youth and early schooling. His university education in philosophy and medicine has been acquired at several schools. He probably attended Vienna, Montpellier, Piacenza, and Pavia. He obtained a Doctor of Arts degree at one of these institutions.
His first professional position was in Sélestat, near Strasbourg. He practised medicine in Colmar from 1514 to 1518. He wrote several medical works, including a practice entitled Spiegel der Artzny (Mirror of Medicine), a trendy book with seven editions up to 1546. After 1519, he moved to Strasbourg, where he stayed until about 1527.
In 1520, Fries became involved in publishing new editions of maps by Martin Waldseemüller. He collaborated with Peter Apian to publish a much-reduced version of Waldseemüller's map of 1507.
In the meantime, Fries was preparing a new edition of Ptolemy's Geographia. The book was printed in 1522 by Johannes Grüninger, an esteemed printer from Strasbourg who had previously published the Waldseemüller. It was based on Waldseemüller's editions of 1513 and 1520. Fries says in a note to the reader: "…, we declare that Martin Waldseemüller, piously deceased, originally constructed these maps and that they have been drawn in a format smaller than they ever had". The book sold well, and new editions would follow, printed with the same woodblocks.
In 1525, Willibald Pirkheimer, the Nuremberg humanist, published a new edition with Grüninger. The volume was published jointly with the Nuremberg printer Johannes Koberger. It included the same fifty Waldseemüller/Fries maps as the 1522 edition.
Michael Servetus (= Michael Villanovus) printed two more editions in Lyon in 1535 and 1541. Servetus was tried for heresy in 1553. One of the allegations was that he had written a statement on the verso of the map of the Holy Land describing it as primarily infertile. The idea originated in Fries's edition in 1522. Servetus was burned at the stake, and at Calvin's orders, many copies of Servetus's books followed him into the flames.
Fries also published other books on astrology and medicine. In addition, he undertook a reduction of Waldseemüller's large map of 1516, the Carta Marina Navigatoria, which he translated into German simultaneously. The map was published in 1525, but no copy of this edition survived. The earliest copy known is dated 1530.
In 1525, Strasbourg had become a thoroughly reformed city, and the Roman church's adherents found themselves increasingly unwelcome. For this reason, Fries probably renounced his citizenship and moved to Metz. During this period, he published his last two medical works.
*He should be distinct from the historian Lorenz Fries of Mergentheim (1491-1550).
Lorenz Fries* (c. 1485 – 1532)
Lorenz Fries, a physician, astrologer, and cartographic editor, was a native Alsatian. Nothing is known about his youth and early schooling. His university education in philosophy and medicine seems to have been acquired at several schools. Probably he attended the universities of Vienna, Montpellier, Piacenza, and Pavia. He obtained the degree of doctor of arts at one of these institutions.
His first professional position was in Sélestat, near Strasbourg. He practised medicine in Colmar from 1514 to 1518. He wrote several medical works, among them a practice entitled Spiegel der Artzny (Mirror of Medicine), a trendy book with seven editions up to 1546. After 1519 he moved to Strasbourg, where he stayed until about 1527.
In 1520, Fries became involved in the publication of new editions of maps by Martin Waldseemüller. He collaborated with Peter Apian in the publication of a much-reduced version of Waldseemüller's map of 1507.
In the meantime, Fries was busy preparing a new edition of Ptolemy's Geographia. The book was printed in 1522 by Johannes Grüninger, an esteemed printer from Strasbourg who had previously printed the Waldseemüller. It was based on Waldseemüller's editions of 1513 and 1520. Fries says in a note to the reader: "…, we declare that these maps were originally constructed by Martin Waldseemüller piously deceased and that they have been drawn in a format smaller than that which they ever had before". The book sold well, and new editions would follow, printed with the same woodblocks.
In 1525, Willibald Pirkheimer, the Nuremberg humanist, published a new edition with Grüninger. The volume was published jointly with the Nuremberg printer Johannes Koberger. It included the same fifty Waldseemüller/Fries maps as the 1522 edition.
Two more editions were printed by Michael Servetus (= Michael Villanovus) in Lyon in 1535 and 1541. Servetus was tried for heresy in 1553. One of the allegations was that he had written a statement on the verso of the map of the Holy Land describing it as mostly infertile. The statement originated in Fries's edition in 1522. Servetus was burned at stake, and at Calvin's orders, many copies of Servetus's books followed him into the flames.
Fries also published other books on astrology and medicine. He undertook a reduction of Waldseemüller's large map of 1516, the Carta marina navigatoria, which he translated into German at the same time. The map was published in 1525, but no copy survived of this edition. The earliest copy known is dated 1530.
In 1525 Strasbourg had become a thoroughly reformed city, and the Roman church's adherents found themselves increasingly unwelcome. It was probably for this reason that Fries renounced his citizenship and moved to Metz. In this period, he published his last two medical works.
*He should not be confused with the historian Lorenz Fries of Mergentheim (1491-1550).
Martin Waldseemüller (Ilacomilus) (c. 1473-1519)
Martin Walseemüller and his collaborator, Matthias Ringmann, are credited with the first recorded usage of the word America to name the New World in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci.
He was born about 1475, most probably in the village of Wolfenweiler near Freiburg im Breisgau (southern Germany). He studied at the University of Freiburg where he met Johann Scott, the future printer of Waldseemüller’s edition of Ptolemy and Matthias Ringman, a poet who wrote Waldseemüller’s texts. Gregor Reisch was their tutor. He was noted for a philosophical work, Margaretha Philosophica (1503), a widely read book of which included a world map in Ptolemaic form. He undoubtedly aroused the students’ interest in cosmography.
At the beginning of the 16th century, Walseemüller moved to St.Dié, in the Vosges. He Hellenized his name to Ilacomilus and worked on an edition of Ptolemy. He learned the printing trade in Basle and became professor of cosmography under the patronage of René II, Duke of Lorraine.
Together with a group of scholars, among them were Nicholas Lud and Matthias Ringmann, they installed a printing press in St. Dié. The first book appeared in 1507: Cosmographiae introductio … Few books have generated as much interest and speculation as this book because it contained the suggestion that the new continent is named America in honour of Amerigo Vespucci, whose letters about his American “discoveries” form a large part of the book. Great interest was also attached to the two maps mentioned on the title page as constituting part of the Cosmographiae introductio: a large 12-panel wall map of the world and a set of globe gores. The map and globe were notable for showing the New World as a continent separate from Asia and for naming the southern landmass America.
Ringmann wrote the text of the Cosmographiae introductio in which he used the name ‘America’. He died in 1511, and by then Waldseemüller was having doubts about the name they had coined.
In 1511 Walseemüller published the Carta Itineraria Europae, a road map of Europe that showed essential trade routes as well as pilgrim routes from central Europe to Santiago de Compostela, Spain. It was the first printed wall map of Europe.
After Ringmann’s death, Waldseemüller concentrated on the new version of Ptolemy’s Geographia. The new edition was finally printed in 1513 by Johannes Scott in Strasbourg and is now regarded as the most important edition. Waldseemüller included twenty modern maps in the new Geographia as a separate appendix.
The 1507 wall map was lost for a long time, but a copy was found in Schloss Wolfegg in southern Germany by Joseph Fischer in 1901. It is the only known copy and was purchased by the United States Library of Congress in May 2003.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
In Latin: Claudius Ptolemaeus, was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria during the 2nd century. Much of medieval astronomy and geography were built on his ideas. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. This idea of a global coordinates system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the Almagest, the second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. The maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography, however, only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts – texts which were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
Claudius Ptolemaeus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria in the 2nd century. His ideas influenced much of medieval astronomy and geography. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. His idea of a global coordinate system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise, now known as the Almagest. The second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. However, the maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts that were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.
Typus orbis descriptione Ptolemaei
Item Number: 16773 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > World and Polar
Antique map of the Ptolemaic World by C. Ptolemy - L. Fries
Waldseemüllers Ptolemaic map of 1513 has been redrawn and reduced in size in this publication by Laurent Fries.
Date of the first edition: 1522
Date of this map: 1541
Woodcut
Size: 30.5 x 46cm (11.9 x 17.9 inches)
Verso text: Latin
Condition: Superb contemporary colour.
Condition Rating: A
References: Shirley, 47.
From: Claudii Ptolemaei Alexandrini geographicae enarrationis libri octo. Lyon, M. Servetus, 1541. (Karrow, 288/G.3)
Lorenz Fries* (c. 1485 – 1532)
Lorenz Fries, a physician, astrologer, and cartographic editor, was a native Alsatian. Nothing is known about his youth and early schooling. His university education in philosophy and medicine has been acquired at several schools. He probably attended Vienna, Montpellier, Piacenza, and Pavia. He obtained a Doctor of Arts degree at one of these institutions.
His first professional position was in Sélestat, near Strasbourg. He practised medicine in Colmar from 1514 to 1518. He wrote several medical works, including a practice entitled Spiegel der Artzny (Mirror of Medicine), a trendy book with seven editions up to 1546. After 1519, he moved to Strasbourg, where he stayed until about 1527.
In 1520, Fries became involved in publishing new editions of maps by Martin Waldseemüller. He collaborated with Peter Apian to publish a much-reduced version of Waldseemüller's map of 1507.
In the meantime, Fries was preparing a new edition of Ptolemy's Geographia. The book was printed in 1522 by Johannes Grüninger, an esteemed printer from Strasbourg who had previously published the Waldseemüller. It was based on Waldseemüller's editions of 1513 and 1520. Fries says in a note to the reader: "…, we declare that Martin Waldseemüller, piously deceased, originally constructed these maps and that they have been drawn in a format smaller than they ever had". The book sold well, and new editions would follow, printed with the same woodblocks.
In 1525, Willibald Pirkheimer, the Nuremberg humanist, published a new edition with Grüninger. The volume was published jointly with the Nuremberg printer Johannes Koberger. It included the same fifty Waldseemüller/Fries maps as the 1522 edition.
Michael Servetus (= Michael Villanovus) printed two more editions in Lyon in 1535 and 1541. Servetus was tried for heresy in 1553. One of the allegations was that he had written a statement on the verso of the map of the Holy Land describing it as primarily infertile. The idea originated in Fries's edition in 1522. Servetus was burned at the stake, and at Calvin's orders, many copies of Servetus's books followed him into the flames.
Fries also published other books on astrology and medicine. In addition, he undertook a reduction of Waldseemüller's large map of 1516, the Carta Marina Navigatoria, which he translated into German simultaneously. The map was published in 1525, but no copy of this edition survived. The earliest copy known is dated 1530.
In 1525, Strasbourg had become a thoroughly reformed city, and the Roman church's adherents found themselves increasingly unwelcome. For this reason, Fries probably renounced his citizenship and moved to Metz. During this period, he published his last two medical works.
*He should be distinct from the historian Lorenz Fries of Mergentheim (1491-1550).
Lorenz Fries* (c. 1485 – 1532)
Lorenz Fries, a physician, astrologer, and cartographic editor, was a native Alsatian. Nothing is known about his youth and early schooling. His university education in philosophy and medicine seems to have been acquired at several schools. Probably he attended the universities of Vienna, Montpellier, Piacenza, and Pavia. He obtained the degree of doctor of arts at one of these institutions.
His first professional position was in Sélestat, near Strasbourg. He practised medicine in Colmar from 1514 to 1518. He wrote several medical works, among them a practice entitled Spiegel der Artzny (Mirror of Medicine), a trendy book with seven editions up to 1546. After 1519 he moved to Strasbourg, where he stayed until about 1527.
In 1520, Fries became involved in the publication of new editions of maps by Martin Waldseemüller. He collaborated with Peter Apian in the publication of a much-reduced version of Waldseemüller's map of 1507.
In the meantime, Fries was busy preparing a new edition of Ptolemy's Geographia. The book was printed in 1522 by Johannes Grüninger, an esteemed printer from Strasbourg who had previously printed the Waldseemüller. It was based on Waldseemüller's editions of 1513 and 1520. Fries says in a note to the reader: "…, we declare that these maps were originally constructed by Martin Waldseemüller piously deceased and that they have been drawn in a format smaller than that which they ever had before". The book sold well, and new editions would follow, printed with the same woodblocks.
In 1525, Willibald Pirkheimer, the Nuremberg humanist, published a new edition with Grüninger. The volume was published jointly with the Nuremberg printer Johannes Koberger. It included the same fifty Waldseemüller/Fries maps as the 1522 edition.
Two more editions were printed by Michael Servetus (= Michael Villanovus) in Lyon in 1535 and 1541. Servetus was tried for heresy in 1553. One of the allegations was that he had written a statement on the verso of the map of the Holy Land describing it as mostly infertile. The statement originated in Fries's edition in 1522. Servetus was burned at stake, and at Calvin's orders, many copies of Servetus's books followed him into the flames.
Fries also published other books on astrology and medicine. He undertook a reduction of Waldseemüller's large map of 1516, the Carta marina navigatoria, which he translated into German at the same time. The map was published in 1525, but no copy survived of this edition. The earliest copy known is dated 1530.
In 1525 Strasbourg had become a thoroughly reformed city, and the Roman church's adherents found themselves increasingly unwelcome. It was probably for this reason that Fries renounced his citizenship and moved to Metz. In this period, he published his last two medical works.
*He should not be confused with the historian Lorenz Fries of Mergentheim (1491-1550).
Martin Waldseemüller (Ilacomilus) (c. 1473-1519)
Martin Walseemüller and his collaborator, Matthias Ringmann, are credited with the first recorded usage of the word America to name the New World in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci.
He was born about 1475, most probably in the village of Wolfenweiler near Freiburg im Breisgau (southern Germany). He studied at the University of Freiburg where he met Johann Scott, the future printer of Waldseemüller’s edition of Ptolemy and Matthias Ringman, a poet who wrote Waldseemüller’s texts. Gregor Reisch was their tutor. He was noted for a philosophical work, Margaretha Philosophica (1503), a widely read book of which included a world map in Ptolemaic form. He undoubtedly aroused the students’ interest in cosmography.
At the beginning of the 16th century, Walseemüller moved to St.Dié, in the Vosges. He Hellenized his name to Ilacomilus and worked on an edition of Ptolemy. He learned the printing trade in Basle and became professor of cosmography under the patronage of René II, Duke of Lorraine.
Together with a group of scholars, among them were Nicholas Lud and Matthias Ringmann, they installed a printing press in St. Dié. The first book appeared in 1507: Cosmographiae introductio … Few books have generated as much interest and speculation as this book because it contained the suggestion that the new continent is named America in honour of Amerigo Vespucci, whose letters about his American “discoveries” form a large part of the book. Great interest was also attached to the two maps mentioned on the title page as constituting part of the Cosmographiae introductio: a large 12-panel wall map of the world and a set of globe gores. The map and globe were notable for showing the New World as a continent separate from Asia and for naming the southern landmass America.
Ringmann wrote the text of the Cosmographiae introductio in which he used the name ‘America’. He died in 1511, and by then Waldseemüller was having doubts about the name they had coined.
In 1511 Walseemüller published the Carta Itineraria Europae, a road map of Europe that showed essential trade routes as well as pilgrim routes from central Europe to Santiago de Compostela, Spain. It was the first printed wall map of Europe.
After Ringmann’s death, Waldseemüller concentrated on the new version of Ptolemy’s Geographia. The new edition was finally printed in 1513 by Johannes Scott in Strasbourg and is now regarded as the most important edition. Waldseemüller included twenty modern maps in the new Geographia as a separate appendix.
The 1507 wall map was lost for a long time, but a copy was found in Schloss Wolfegg in southern Germany by Joseph Fischer in 1901. It is the only known copy and was purchased by the United States Library of Congress in May 2003.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
In Latin: Claudius Ptolemaeus, was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria during the 2nd century. Much of medieval astronomy and geography were built on his ideas. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. This idea of a global coordinates system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the Almagest, the second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. The maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography, however, only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts – texts which were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
Claudius Ptolemaeus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria in the 2nd century. His ideas influenced much of medieval astronomy and geography. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. His idea of a global coordinate system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise, now known as the Almagest. The second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. However, the maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts that were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.