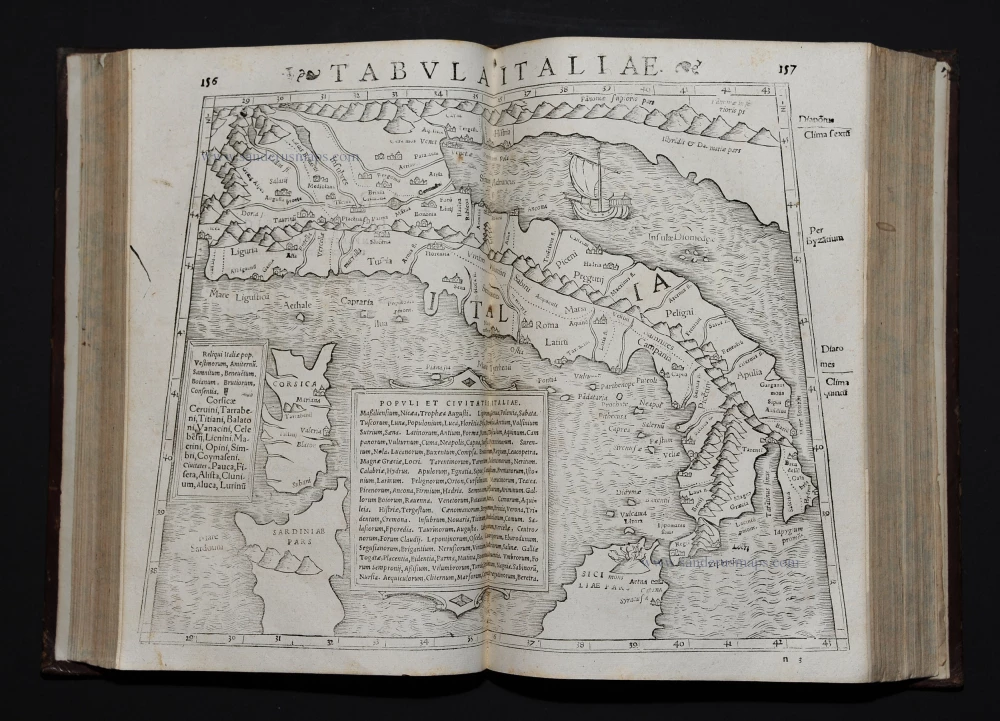
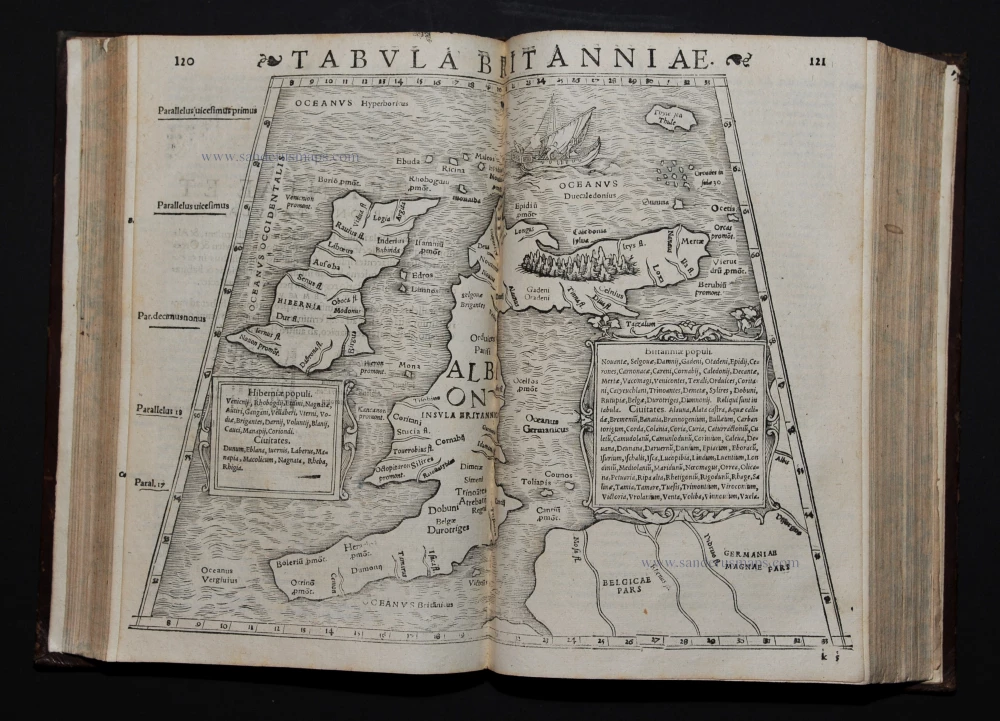
Strabo, Rerum Geographicum Libri Septemdecim. 1571.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
Claudius Ptolemaeus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria in the 2nd century. His ideas influenced much of medieval astronomy and geography. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. His idea of a global coordinate system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise, now known as the Almagest. The second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. However, the maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts that were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.
Strabo (c. 63 BC - c. 21 AD)
Strabo was a Greek geographer and historian who travelled in Europe, Africa and Asia and influenced later geographers. He compiled the Geographia, a world geography presenting a descriptive history of people and places from different regions of the world known during his lifetime.
His work was first published in 1469, and many later editions followed in the 15th and 16th centuries, some of them illustrated with Ptolemy maps.
Rerum Geographicum Libri Septemdecim.
Item Number: 21593 Authenticity Guarantee
STRABO (63 BC – c. AD 24) Strabonis Nobilissimi Et Doctissimi Philosophi Ac Geographi RERUM GEOGRAPHICUM commentarij libris XVII contenti Latini facti Gvilielmo Xylandro Augustano interprete. Basel, Henricpetri, 1571.
Contemporary calf binding. 27 double-page woodcut maps and 7 small woodcuts in text.
This is the 3rd edition translated and edited by Xylander (= pseudonym for Holzman, 1532-1576) with Greek and Latin parallel texts. The blocks used were the same that Münster used for four editions of Ptolemy's Geographia.
Claudius Ptolemy (c.100 – c.170 AD)
Claudius Ptolemaeus was a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and geographer who lived in Alexandria in the 2nd century. His ideas influenced much of medieval astronomy and geography. He was the first to use longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates. His idea of a global coordinate system was highly influential, and we use a similar system today.
Ptolemy wrote several scientific treatises. The first is the astronomical treatise, now known as the Almagest. The second is the Geography, which is a thorough discussion of the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the Apotelesmatika, an astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day.
The Geographia is a compilation of geographical coordinates of the part of the world known to the Roman Empire during his time. However, the maps in surviving manuscripts of Ptolemy's Geography only date from about 1300, after Maximus Planudes rediscovered the text. It seems likely that the topographical tables are cumulative texts that were altered and added to as new knowledge became available in the centuries after Ptolemy.
The earliest printed edition with engraved maps was produced in Bologna in 1477, followed quickly by a Roman edition in 1478. An edition printed at Ulm in 1482, including woodcut maps, was the first one published north of the Alps.
Strabo (c. 63 BC - c. 21 AD)
Strabo was a Greek geographer and historian who travelled in Europe, Africa and Asia and influenced later geographers. He compiled the Geographia, a world geography presenting a descriptive history of people and places from different regions of the world known during his lifetime.
His work was first published in 1469, and many later editions followed in the 15th and 16th centuries, some of them illustrated with Ptolemy maps.