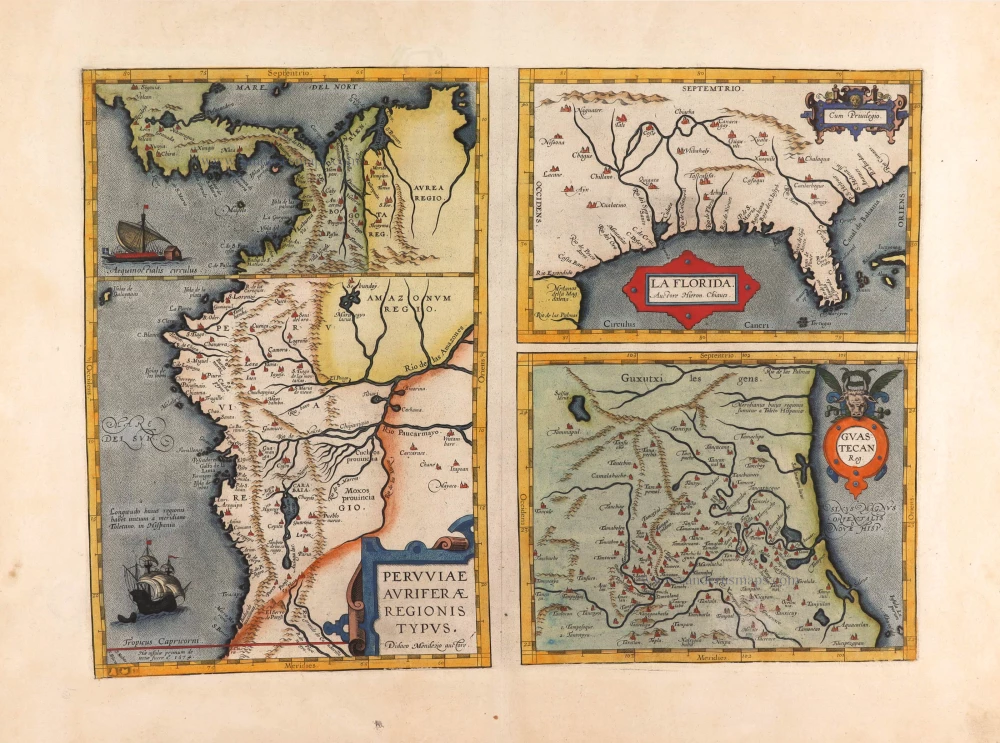
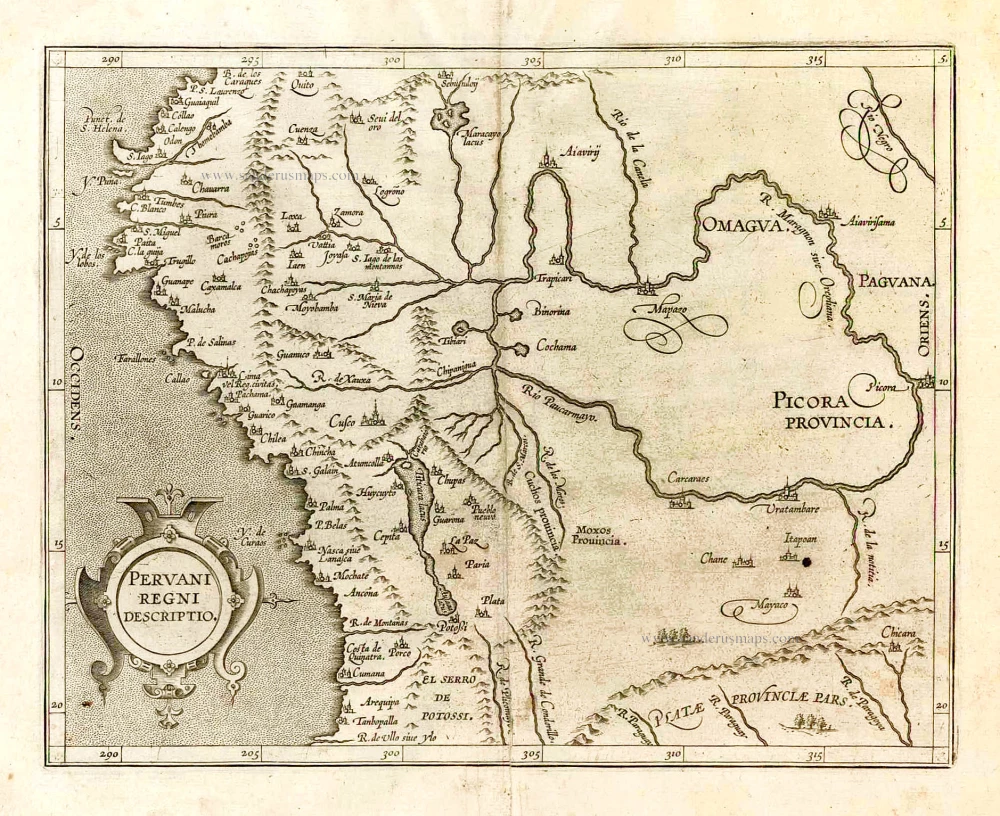
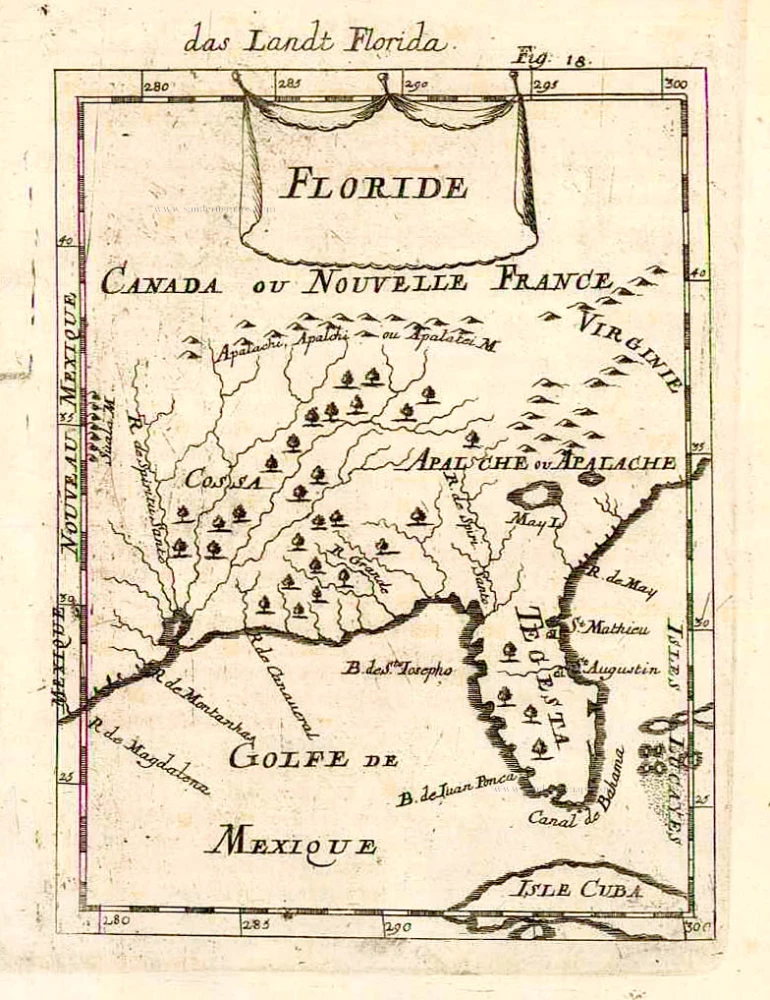
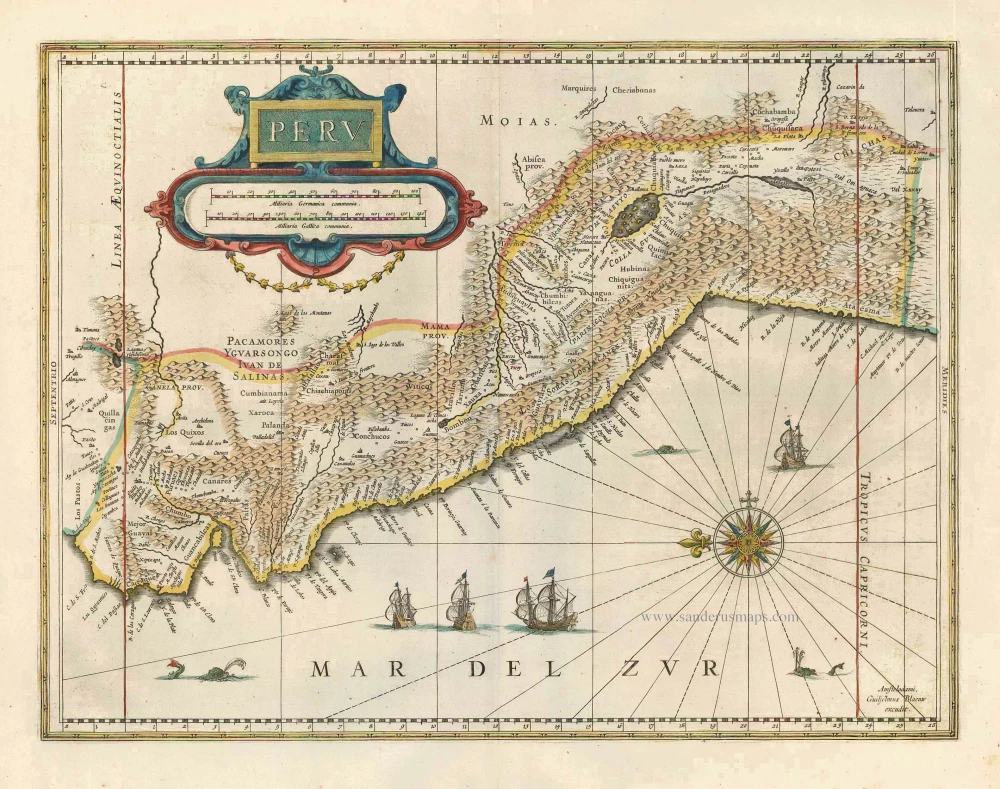
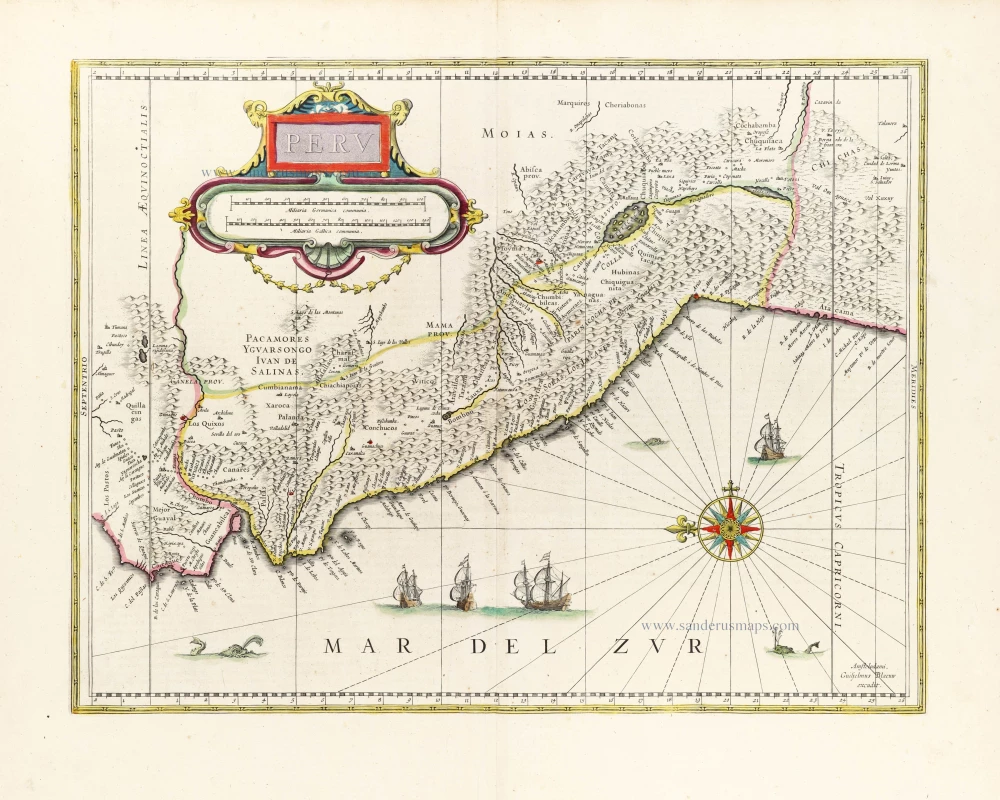
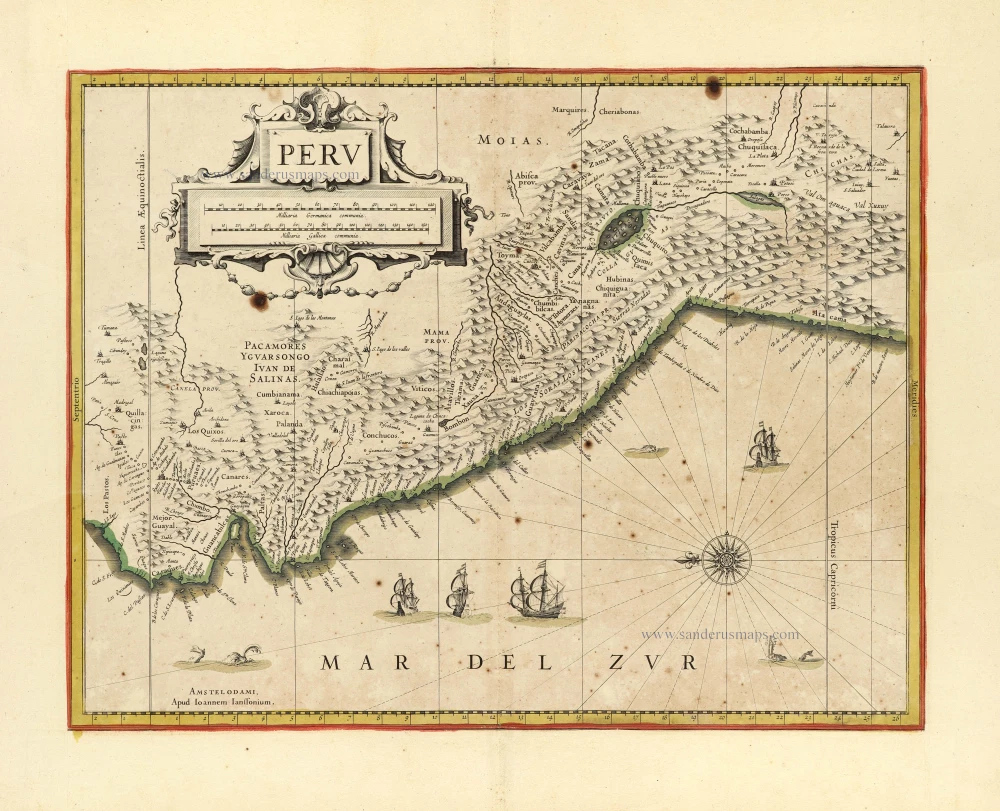
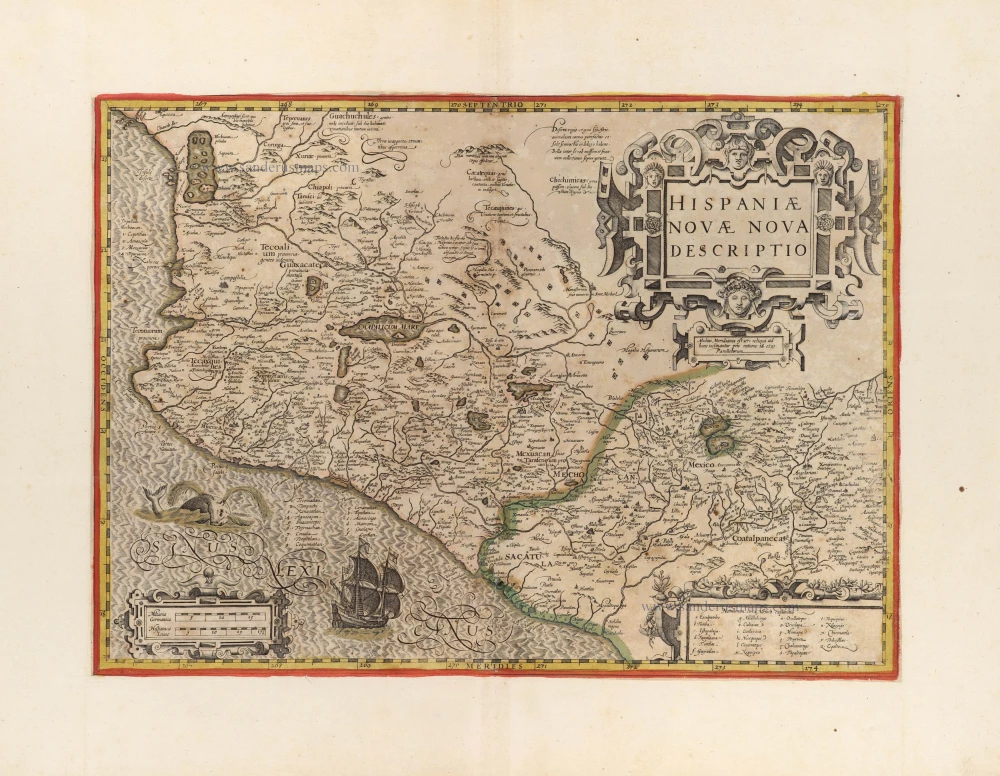
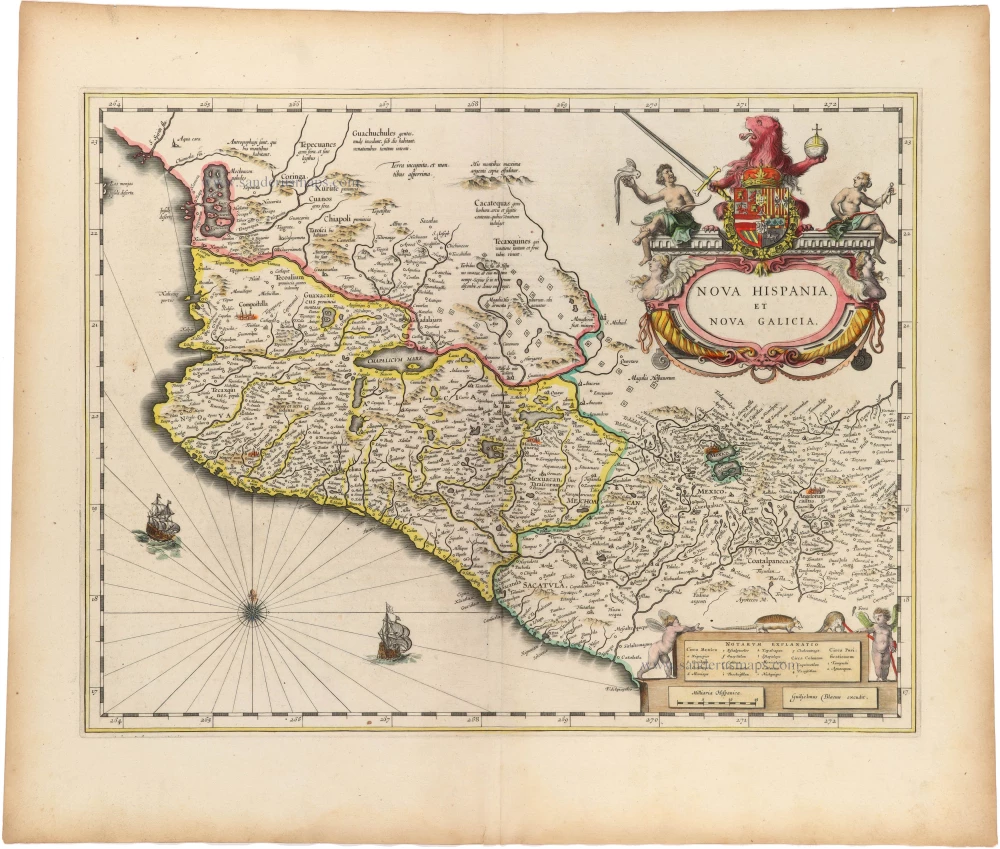
Florida, Peru and Mexico by Abraham Ortelius. 1595
"The Florida map is one of the few maps printed in the sixteenth century based on original Spanish sources. They were very protective of their knowledge of the Americas, a significant source of their wealth. The author of this map, Géronimo de Chaves, was the Cosmographer Royal to Philip II of Spain. His father, Alonso de Chaves, was an examiner of Pilots at the Casa de Contratacion, and in 1552 his son followed him by being appointed to the Chair of Cartography. The plate contains two other maps of similar Spanish regions of influence. They are PERUVVIAE and <GUASTECAN, which combine with LA FLORIDA to extend the coastline of the Gulf of Mexico further south. The map LA FLORIDA is one of the handfuls of prototypes produced, and its influence was considerable. Showing a semblance of internal detail for the first time, it draws heavily upon the findings of Hernando de Soto's expedition through the region in 1539-42, derived largely from Gonzalo de Oviedo's account. However, nothing learnt from the French or Spanish explorations on the Atlantic coastline during the 1560s is incorporated. The map provided the foundation cartography for the region, particularly noticeable by the depiction of the river system. The map appeared for the first time in the Additamentum from 1584 and was issued in all future editions of the Theatrum." (Burden)
Abraham Ortelius (1527-1598)
The maker of the 'first atlas', the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570), was born on 4 April 1527 into an old Antwerp family. He learned Latin and studied Greek and mathematics.
Abraham and his sisters Anne and Elizabeth took up map colouring. Ortelius was admitted to the Guild of St. Luke as an "illuminator of maps." In addition to colouring maps, Ortelius was a dealer in antiques, coins, maps, and books, and the book and map trade gradually became his primary occupation.
Business went well because his means permitted him to start an extensive collection of medals, coins, antiques, and a library of many volumes. In addition, he travelled a lot, visited Italy and France, made contacts everywhere with scholars and editors, and maintained extensive correspondence with them.
In 1564, he published his first map, a large and ambitious world wall map. The inspiration for this map may well have been Gastaldi's large world map. In 1565, he published a map of Egypt and a map of the Holy Land; a large map of Asia followed.
In 1568, the production of individual maps for his atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was already in full swing. He completed the atlas in 1569, and in May 1570, it was available for sale. It was one of the most expensive books ever published.
This first edition contained seventy maps on fifty-three sheets. Franciscus Hogenberg engraved the maps.
Later editions included Additamenta (additions), resulting in Ortelius' historical atlas, the Parergon, which is mainly bound together with the atlas. The Parergon can be considered a truly original work by Ortelius, who drew the maps based on his research.
The importance of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum for geographical knowledge in the last quarter of the sixteenth century is difficult to overemphasize. Nothing was like it until Mercator's atlas appeared twenty-five years later. Demand for the Theatrum was remarkable. Some 24 editions appeared during Ortelius's lifetime and another 10 after he died in 1598. Editions were published in Dutch, German, French, Spanish, English, and Italian. The number of map sheets grew from 53 in 1570 to 167 in 1612 in the last edition.
In 1577, engraver Philip Galle and poet-translator Pieter Heyns published the first pocket-sized edition of the Theatrum, the Epitome. The work was trendy. Over thirty editions of this Epitome were published in different languages.
Peruviae Auriferae Regionis Typus. - La Florida - Guastecan ...
Item Number: 29711 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > America > Central America
Old, antique map - double sheet with 3 maps: Florida, Peru and Mexico by Abraham Ortelius.
Title: Peruviae Auriferae Regionis Typus. - La Florida - Guastecan ...
Peru: Didaco Mendezio auctore.
Florida: Auctore Hieron. Chiaves.
Cartographer: Diego Mendez - Chaves.
Date of the first edition: 1584.
Date of this map: 1595.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 335 x 465mm (13.19 x 18.31 inches).
Sheet size: 445 x 575mm (17.52 x 22.64 inches).
Verso: Latin text.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Theatrum Orbis Terrarum. Antwerp, Plantin Press, 1595. (Van der Krogt 3, 31:051)
"The Florida map is one of the few maps printed in the sixteenth century based on original Spanish sources. They were very protective of their knowledge of the Americas, a significant source of their wealth. The author of this map, Géronimo de Chaves, was the Cosmographer Royal to Philip II of Spain. His father, Alonso de Chaves, was an examiner of Pilots at the Casa de Contratacion, and in 1552 his son followed him by being appointed to the Chair of Cartography. The plate contains two other maps of similar Spanish regions of influence. They are PERUVVIAE and <GUASTECAN, which combine with LA FLORIDA to extend the coastline of the Gulf of Mexico further south. The map LA FLORIDA is one of the handfuls of prototypes produced, and its influence was considerable. Showing a semblance of internal detail for the first time, it draws heavily upon the findings of Hernando de Soto's expedition through the region in 1539-42, derived largely from Gonzalo de Oviedo's account. However, nothing learnt from the French or Spanish explorations on the Atlantic coastline during the 1560s is incorporated. The map provided the foundation cartography for the region, particularly noticeable by the depiction of the river system. The map appeared for the first time in the Additamentum from 1584 and was issued in all future editions of the Theatrum." (Burden)
Abraham Ortelius (1527-1598)
The maker of the 'first atlas', the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570), was born on 4 April 1527 into an old Antwerp family. He learned Latin and studied Greek and mathematics.
Abraham and his sisters Anne and Elizabeth took up map colouring. Ortelius was admitted to the Guild of St. Luke as an "illuminator of maps." In addition to colouring maps, Ortelius was a dealer in antiques, coins, maps, and books, and the book and map trade gradually became his primary occupation.
Business went well because his means permitted him to start an extensive collection of medals, coins, antiques, and a library of many volumes. In addition, he travelled a lot, visited Italy and France, made contacts everywhere with scholars and editors, and maintained extensive correspondence with them.
In 1564, he published his first map, a large and ambitious world wall map. The inspiration for this map may well have been Gastaldi's large world map. In 1565, he published a map of Egypt and a map of the Holy Land; a large map of Asia followed.
In 1568, the production of individual maps for his atlas Theatrum Orbis Terrarum was already in full swing. He completed the atlas in 1569, and in May 1570, it was available for sale. It was one of the most expensive books ever published.
This first edition contained seventy maps on fifty-three sheets. Franciscus Hogenberg engraved the maps.
Later editions included Additamenta (additions), resulting in Ortelius' historical atlas, the Parergon, which is mainly bound together with the atlas. The Parergon can be considered a truly original work by Ortelius, who drew the maps based on his research.
The importance of the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum for geographical knowledge in the last quarter of the sixteenth century is difficult to overemphasize. Nothing was like it until Mercator's atlas appeared twenty-five years later. Demand for the Theatrum was remarkable. Some 24 editions appeared during Ortelius's lifetime and another 10 after he died in 1598. Editions were published in Dutch, German, French, Spanish, English, and Italian. The number of map sheets grew from 53 in 1570 to 167 in 1612 in the last edition.
In 1577, engraver Philip Galle and poet-translator Pieter Heyns published the first pocket-sized edition of the Theatrum, the Epitome. The work was trendy. Over thirty editions of this Epitome were published in different languages.