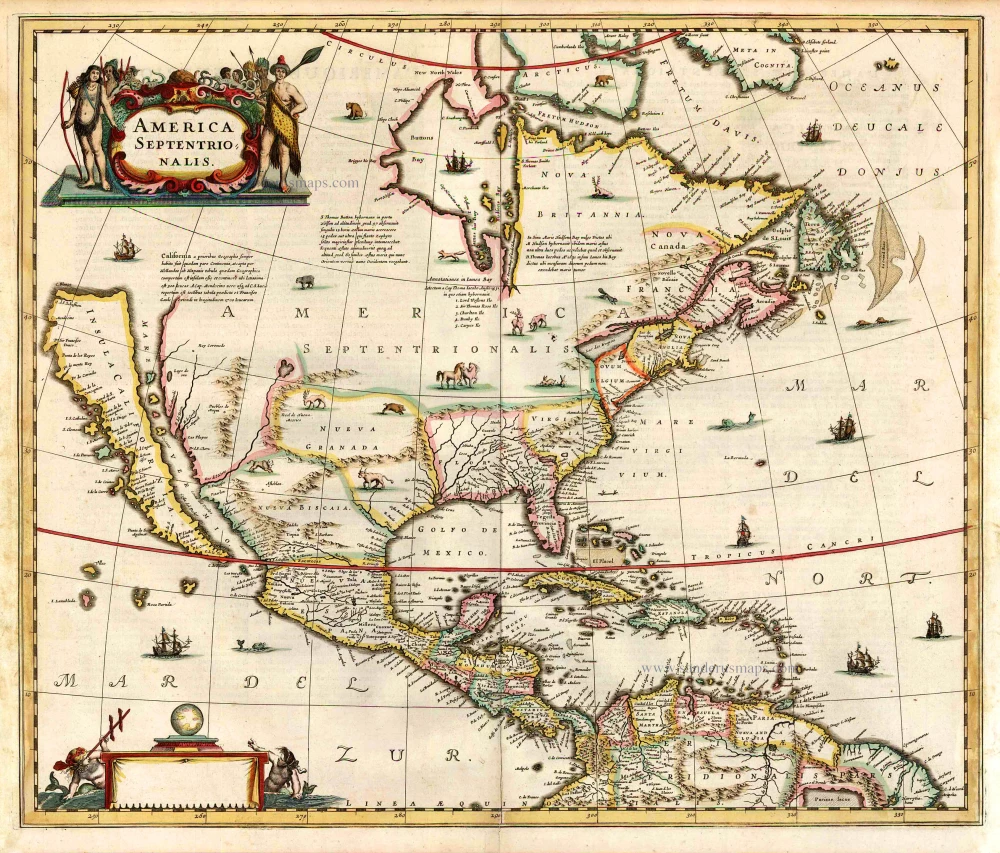
Old antique map of North America, by Henricus Hondius. 1641
"Henricus Hondius' beautifully engraved map of North America had greater influence than any other to date in perpetuating the theory of California as an island. This was because it was disseminated through the medium of his powerful Dutch publishing house. None of the earlier California as an island maps had reached such a wide audience. The 1630s where a decade of constant development in the houses of Blaeu and Hondius. It is interesting to note that Blaeu never produced a single sheet map of North America; both Willem and Joan relied upon that of the whole continent first produced in 1617, throughout their publishing history. During this decade Joannes Janssonius became an active partner of Hondius, and although this map bears no imprint it is assigned to the latter on the basis that at the same time a map of South America appeared displaying his name. Cartographically this map is a careful composition of many different sources and illustrates well the current state of knowledge. The depiction and nomenclature of the west, along with that of the insular California, derive directly from the Henry Briggs The North Part of America, 1625. A legend placed strategically over the north-west coastline offers the opportunity to discontinue a coastline least understood. An unnamed lake still feeds a Rio del Norto flowing incorrectly south-west into what should be the headwaters of the Gulf of California. On the east bank of this river is Real de Nueua Mexico, or Santa Fe. The Gulf of Mexico and the Florida peninsula originate from the Hessel Gerritsz chart of c.1631. The east coast, however, is harder to define; the south-east appears to be quite generic in form. It is the area north of here that does not appear to be from a particular source. The Chesapeake Bay area is defined in about as much detail as the scale and style of the map will allow, Iames Towne being clearly identified. NOVUM BELGIUM is unlike any other before it, the area between the Zuitt Reuier (Delaware River) and the Noort R (Hudson River) being greatly elongated on a north-east to south-west axis. New Amsterdam is curiously not designated although Fort Orange is present. For New England just a select few names have been chosen from John Smith's map of the area, 1616. The Gulf of St. Lawrence appears to follow de Laet more than Champlain. The latter is used to depict a single great Lake; however, its name, Lac des Iroquois, is borrowed from one nearby. Interestingly the author chose not use Champlain's more recent 1632 map but the earlier 1612 CARTE GEOGRAPHIQUE DE LA NOUVELLE FRANSE; To avoid unknown territory he does not venture the river system further west, unlike Champlain. Along the Atlantic coast of Labrador we find for the first time much Dutch Nomenclature, reflecting their increased whaling activities in these waters. Hudson Bay is clearly derived from Briggs, 1625, except for the west coast where he introduces the cartography of Thomas James, 1633. The addition of a fox here could be seen as a veiled reference to Luke Foxe, whose own map of the previous year bears just such an animal. The map was one of many introduced in the late 1630s to be included in the rapidly developing Atlas Novus. After the death of Janssonius in 1664 the business was left to a number of different parties, and it could not be divided in such a way that ensured the continued production of the various atlases. During this period some of the maps were often sold to order; such as for the atlases of Nicolaas Visscher and Carol Allard. This map appears in such atlases unchanged until c. 1694. In that year Petrus Schenk acquired all of the Atlas Major plates at public auction from the heirs of Jansson van Waesberge, and began issuing the map with his own imprint." (Burden)
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
America Septentrionalis.
Item Number: 26272 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > America > North America
Old antique map of North America, by Henricus Hondius.
Title: America Septentrionalis.
Date of the first edition: 1636.
Date of this map: 1641.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 465 x 550mm (18¼ x 21¾ inches).
Verso: French text.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Nouveau Theatre du Monde ou Nouvel Atlas comprenant Les Tables et Descriptions de toutes les Regions de la Terre. Amsterdam, Henricus Hondius, 1641. (Van der Krogt 1, 412)
"Henricus Hondius' beautifully engraved map of North America had greater influence than any other to date in perpetuating the theory of California as an island. This was because it was disseminated through the medium of his powerful Dutch publishing house. None of the earlier California as an island maps had reached such a wide audience. The 1630s where a decade of constant development in the houses of Blaeu and Hondius. It is interesting to note that Blaeu never produced a single sheet map of North America; both Willem and Joan relied upon that of the whole continent first produced in 1617, throughout their publishing history. During this decade Joannes Janssonius became an active partner of Hondius, and although this map bears no imprint it is assigned to the latter on the basis that at the same time a map of South America appeared displaying his name. Cartographically this map is a careful composition of many different sources and illustrates well the current state of knowledge. The depiction and nomenclature of the west, along with that of the insular California, derive directly from the Henry Briggs The North Part of America, 1625. A legend placed strategically over the north-west coastline offers the opportunity to discontinue a coastline least understood. An unnamed lake still feeds a Rio del Norto flowing incorrectly south-west into what should be the headwaters of the Gulf of California. On the east bank of this river is Real de Nueua Mexico, or Santa Fe. The Gulf of Mexico and the Florida peninsula originate from the Hessel Gerritsz chart of c.1631. The east coast, however, is harder to define; the south-east appears to be quite generic in form. It is the area north of here that does not appear to be from a particular source. The Chesapeake Bay area is defined in about as much detail as the scale and style of the map will allow, Iames Towne being clearly identified. NOVUM BELGIUM is unlike any other before it, the area between the Zuitt Reuier (Delaware River) and the Noort R (Hudson River) being greatly elongated on a north-east to south-west axis. New Amsterdam is curiously not designated although Fort Orange is present. For New England just a select few names have been chosen from John Smith's map of the area, 1616. The Gulf of St. Lawrence appears to follow de Laet more than Champlain. The latter is used to depict a single great Lake; however, its name, Lac des Iroquois, is borrowed from one nearby. Interestingly the author chose not use Champlain's more recent 1632 map but the earlier 1612 CARTE GEOGRAPHIQUE DE LA NOUVELLE FRANSE; To avoid unknown territory he does not venture the river system further west, unlike Champlain. Along the Atlantic coast of Labrador we find for the first time much Dutch Nomenclature, reflecting their increased whaling activities in these waters. Hudson Bay is clearly derived from Briggs, 1625, except for the west coast where he introduces the cartography of Thomas James, 1633. The addition of a fox here could be seen as a veiled reference to Luke Foxe, whose own map of the previous year bears just such an animal. The map was one of many introduced in the late 1630s to be included in the rapidly developing Atlas Novus. After the death of Janssonius in 1664 the business was left to a number of different parties, and it could not be divided in such a way that ensured the continued production of the various atlases. During this period some of the maps were often sold to order; such as for the atlases of Nicolaas Visscher and Carol Allard. This map appears in such atlases unchanged until c. 1694. In that year Petrus Schenk acquired all of the Atlas Major plates at public auction from the heirs of Jansson van Waesberge, and began issuing the map with his own imprint." (Burden)
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.