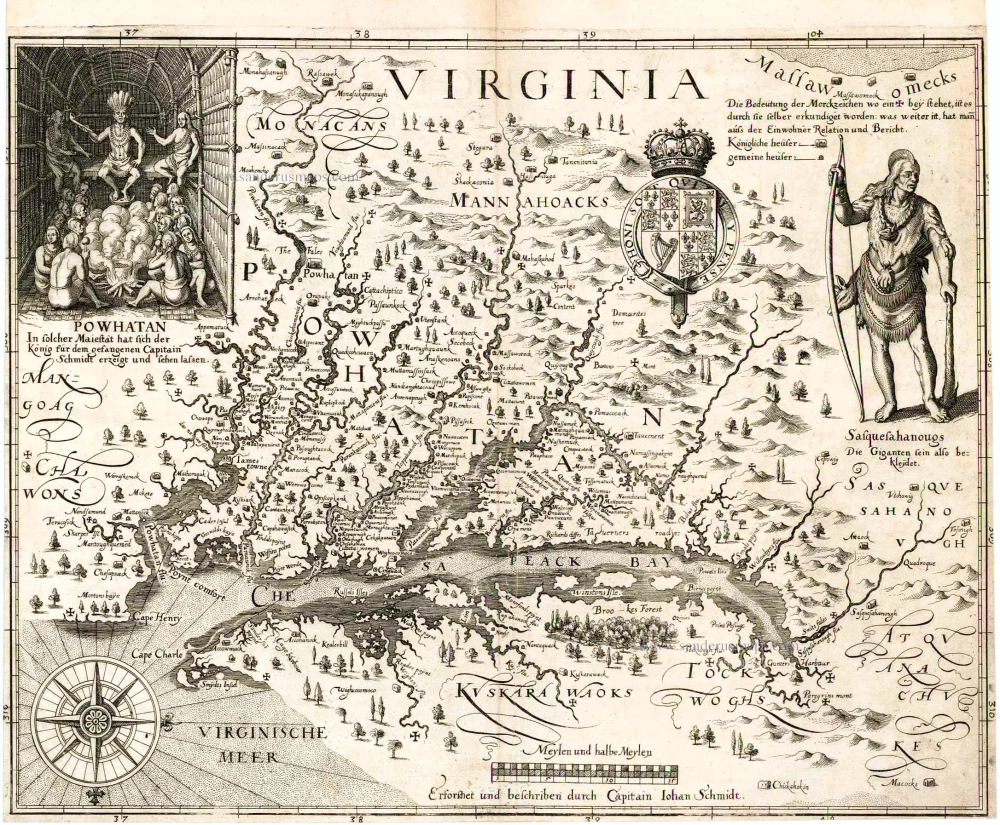
Old antique map of Virginia by M. Merian - de Bry after John Smith. 1627
This derivative of John Smith's map of Virginia accompanied the thirteenth part of Theodore de Bry's Grand Voyages, now published by Matheus Merian. He continued the family business as the son-in-law of Johann Theodore de Bry, who died in about 1623. It was drawn from the sixth state of Smith's map with just a few alterations. The ship on the lower left and the decoration around the scale are missing. The last parts of de Bry's work are scarce and often lack maps. (Burden).
Matthäus Merian the Elder (1593-1650)
Matthäus Merian, the leading German illustrator of the 17th century, was born in Basel in 1593. He learned the art of copperplate engraving in Zurich and subsequently worked and studied in Strasbourg, Nancy, Paris, and the Low Countries. In 1618 he went to Frankfurt, wherein in 1618, he married the eldest daughter of J.T. de Bry, publisher and engraver. After de Bry died in 1623, he took over his business. De Bry’s business remained in Merian’s family until 1726, when a fire destroyed it. In 1635 he began the series Theatrum Europaeum. Between 1642 and 1688, he published Martin Zeiller’s Topographia Germaniae, with more than 2,000 plates etched and engraved by himself and his sons Matthäus and Caspar. He also took over and completed the later parts and editions of the Grand Voyages and Petits Voyages, initially started by de Bry in 1590. Matthäus Merian died after in 1650 in Bad Schwalbach near Wiesbaden.
Theodore de Bry (1528 – 1598) and his family.
Theodore de Bry was born in 1528 in the Prince-Bishopric of Liège in the southern Netherlands (today Belgium). Trained as a goldsmith in his father's workshop, he left his home town around 1558 and moved to Strasbourg. Religious motives partly inspired his emigration, but commercial incentives were probably more critical for de Bry since Strasbourg was more attractive. Here, he gradually began to shift his focus to copper engraving. In the early 1560s, Theodore married Strasbourg-born Katharina Esslinger, and the couple went on to have four children together before Katharina died c. 1569. Johan Theodore (b. 1563) and Johan Israel (b. 1565) followed in their father's footsteps and took up his trade. He remarried in 1570 to Katharina Rölinger.
In 1577, after the Pacification of Gent had quietened religious tensions in the Netherlands, Theodore and his family moved to Antwerp. There, they lived close to the printing house of Christopher Plantin, and it was there that Theodore began making copper engravings. Copper engraving was a well-developed art in the Low Countries, and Antwerp artists were in great demand. In 1584, when Catholic troops besieged Antwerp, Theodore and his family moved to London, where he made copper engravings for an essential English navigation manual, The Mariners Mirrour. He also found the inspiration to produce the collection to which his name would forever be attached.
He met the artist Jacques Le Moyne de Morgues, a draughtsman who had been to Florida in the 1560s as part of a French expedition. He returned to Europe with watercolours of the natural world he had seen and the indigenous peoples. After Le Moyne's death, thanks to the mediation of Richard Hakluyt, Theodore acquired these drawings.
Hakluyt and de Bry began collaborating on a series of books about America. In 1588, the de Bry family moved to Frankfurt, where Theodore published the first volume of the America series. This first volume was the only one in the collection that appeared in four different languages: German, Latin, French and English. The following volumes appeared only in German and Latin. As a result, the relationship between de Bry and his English partners quickly soured.
Theodore continued publishing and produced a blend of richly illustrated prestigious volumes of the Voyages collection, the family firm's flagship publication.
Theodore de Bry died on March 27th, 1598. At this time, the highly successful and lucrative America series had already extended to seven volumes, and there would be fourteen. To these must be added the 'Elenchus', published in 1634 by Merian, which was a collective title and table of contents of these same volumes.
In 1597, the de Bry brothers published the first volume of the East India series. These were also published in folio but with slightly smaller page sizes than the America volumes. To distinguish the East India series from his America series, the two parallel sets subsequently became known among bibliophiles as de Bry’s Petits Voyages and his Grands Voyages, respectively.
The Petits Voyages consist of thirteen volumes, published between 1597 and 1633.
After Theodore de Bry's death, the business was run by his son, Johann Theodore and then by his grandson, Matthäus Merian and grandson-in-law, William Fitzer. Precisely what part de Bry's widow and his other son played in the business is unclear, but they certainly seemed to have retained some interest. After all, it must have become a very profitable venture for the whole family. Together, they continued to publish volumes of the Grands and Petits Voyages for another 46 years. The last volume, a third edition of Part IV of the America series, finally appeared in 1644.
Virginia / Erforshet und Beschriben durch Capitain Iohan Schmidt.
Item Number: 9482 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > America > North America
Old antique map of Virginia by M. Merian - de Bry after John Smith.
Title: Virginia / Erforshet und Beschriben durch Capitain Iohan Schmidt.
Oriented to the west.
Cartographer: Johan Schmidt.
Date: 1627.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Size (not including margins): 300 x 370mm (11¾ x 14½ inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Trimmed at sides with some loss to gradients, else excellent.
Condition Rating: A.
From: From Part XIII of De Bry's Grands Voyages.
This derivative of John Smith's map of Virginia accompanied the thirteenth part of Theodore de Bry's Grand Voyages, now published by Matheus Merian. He continued the family business as the son-in-law of Johann Theodore de Bry, who died in about 1623. It was drawn from the sixth state of Smith's map with just a few alterations. The ship on the lower left and the decoration around the scale are missing. The last parts of de Bry's work are scarce and often lack maps. (Burden).
Matthäus Merian the Elder (1593-1650)
Matthäus Merian, the leading German illustrator of the 17th century, was born in Basel in 1593. He learned the art of copperplate engraving in Zurich and subsequently worked and studied in Strasbourg, Nancy, Paris, and the Low Countries. In 1618 he went to Frankfurt, wherein in 1618, he married the eldest daughter of J.T. de Bry, publisher and engraver. After de Bry died in 1623, he took over his business. De Bry’s business remained in Merian’s family until 1726, when a fire destroyed it. In 1635 he began the series Theatrum Europaeum. Between 1642 and 1688, he published Martin Zeiller’s Topographia Germaniae, with more than 2,000 plates etched and engraved by himself and his sons Matthäus and Caspar. He also took over and completed the later parts and editions of the Grand Voyages and Petits Voyages, initially started by de Bry in 1590. Matthäus Merian died after in 1650 in Bad Schwalbach near Wiesbaden.
Theodore de Bry (1528 – 1598) and his family.
Theodore de Bry was born in 1528 in the Prince-Bishopric of Liège in the southern Netherlands (today Belgium). Trained as a goldsmith in his father's workshop, he left his home town around 1558 and moved to Strasbourg. Religious motives partly inspired his emigration, but commercial incentives were probably more critical for de Bry since Strasbourg was more attractive. Here, he gradually began to shift his focus to copper engraving. In the early 1560s, Theodore married Strasbourg-born Katharina Esslinger, and the couple went on to have four children together before Katharina died c. 1569. Johan Theodore (b. 1563) and Johan Israel (b. 1565) followed in their father's footsteps and took up his trade. He remarried in 1570 to Katharina Rölinger.
In 1577, after the Pacification of Gent had quietened religious tensions in the Netherlands, Theodore and his family moved to Antwerp. There, they lived close to the printing house of Christopher Plantin, and it was there that Theodore began making copper engravings. Copper engraving was a well-developed art in the Low Countries, and Antwerp artists were in great demand. In 1584, when Catholic troops besieged Antwerp, Theodore and his family moved to London, where he made copper engravings for an essential English navigation manual, The Mariners Mirrour. He also found the inspiration to produce the collection to which his name would forever be attached.
He met the artist Jacques Le Moyne de Morgues, a draughtsman who had been to Florida in the 1560s as part of a French expedition. He returned to Europe with watercolours of the natural world he had seen and the indigenous peoples. After Le Moyne's death, thanks to the mediation of Richard Hakluyt, Theodore acquired these drawings.
Hakluyt and de Bry began collaborating on a series of books about America. In 1588, the de Bry family moved to Frankfurt, where Theodore published the first volume of the America series. This first volume was the only one in the collection that appeared in four different languages: German, Latin, French and English. The following volumes appeared only in German and Latin. As a result, the relationship between de Bry and his English partners quickly soured.
Theodore continued publishing and produced a blend of richly illustrated prestigious volumes of the Voyages collection, the family firm's flagship publication.
Theodore de Bry died on March 27th, 1598. At this time, the highly successful and lucrative America series had already extended to seven volumes, and there would be fourteen. To these must be added the 'Elenchus', published in 1634 by Merian, which was a collective title and table of contents of these same volumes.
In 1597, the de Bry brothers published the first volume of the East India series. These were also published in folio but with slightly smaller page sizes than the America volumes. To distinguish the East India series from his America series, the two parallel sets subsequently became known among bibliophiles as de Bry’s Petits Voyages and his Grands Voyages, respectively.
The Petits Voyages consist of thirteen volumes, published between 1597 and 1633.
After Theodore de Bry's death, the business was run by his son, Johann Theodore and then by his grandson, Matthäus Merian and grandson-in-law, William Fitzer. Precisely what part de Bry's widow and his other son played in the business is unclear, but they certainly seemed to have retained some interest. After all, it must have become a very profitable venture for the whole family. Together, they continued to publish volumes of the Grands and Petits Voyages for another 46 years. The last volume, a third edition of Part IV of the America series, finally appeared in 1644.