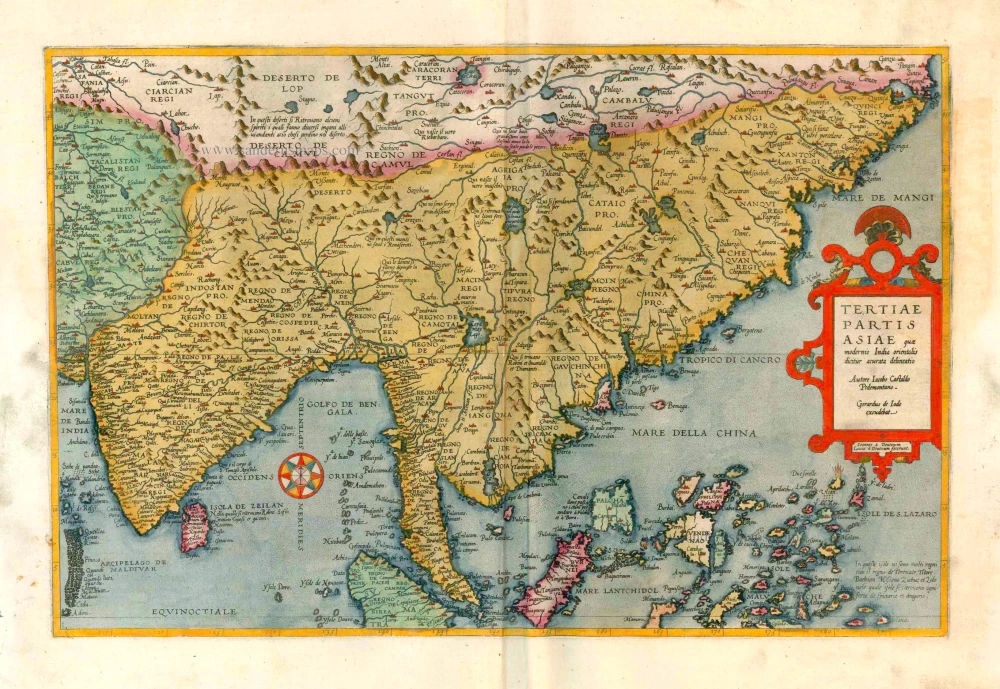
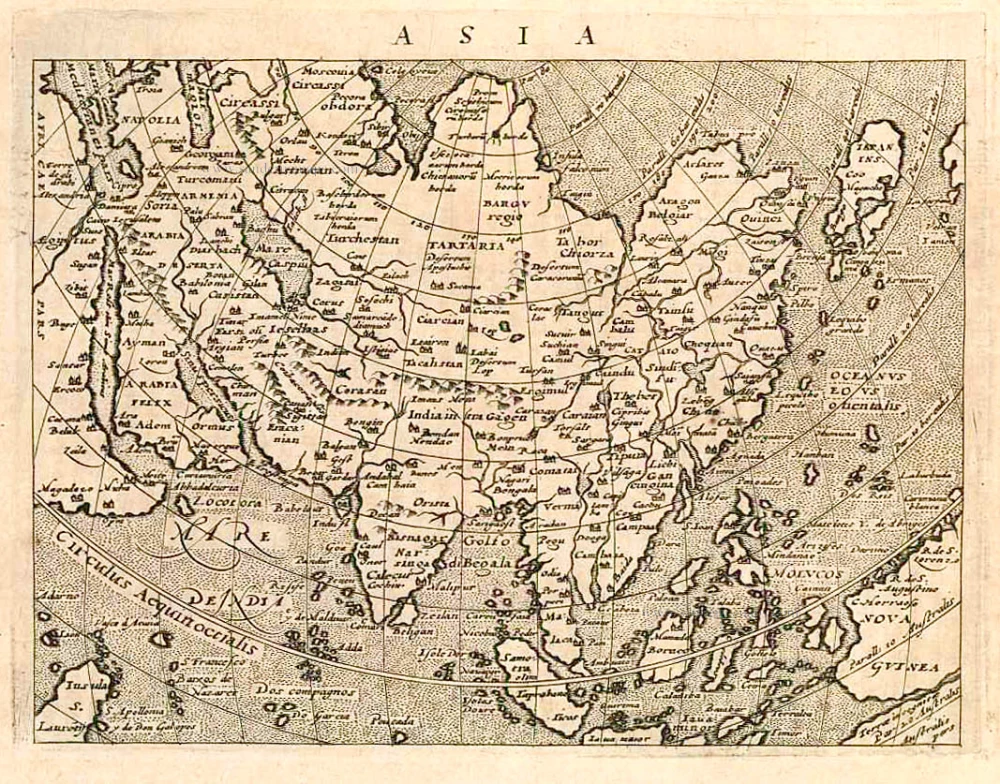
Old antique map of Southeast Asia by G. de Jode. 1593
This map is almost an exact copy of Giacomo Gastaldi's two-sheet map of the region published in 1561 except that de Jode omits any suggestion of Japan, part of which is shown on Gastaldi's map at the extreme right-hand edge.
"In 1578 Gerard de Jode published his Speculum Orbis Terrarum, an atlas aimed at competing with the Theatrum of Ortelius. However, the latter had first been issued in 1570 and had already built a commanding market presence, and so despite de Jode's longer standing reputation the atlas did not sell very well. Only a dozen or so examples have survived. Undeterred, he made plans for another expanded edition, and upon his death in 1591 it was taken on by his son Cornelis. The Speculum Orbis Terrae of 1593 likewise did not sell well and was never reissued. Although more examples than the first edition have survived, it too is very scarce. Many of de Jode's maps are judged to be superior to those of Ortelius, both in detail and style." (Burden)
Gerard and Cornelis de Jode
Gerard de Jode (Judaeus) (1508(?)-1591), a native of Nijmegen, began his career as a printer and engraver in Antwerp about 1550. He lived near the Bourse on the Catelijne Veste, or on "de Catte". He was in regular contact with Christoffel Plantin, to whom he sold many prints and maps. De Jode's business, which must have been a major one among Antwerp's many booksellers and printers, was represented at the Frankfurt fair, where de Jode bought maps that he later copied or re-sold. Most of the maps sold by De Jode have prototypes of Italian or German origin. Apart from his many separately published maps, Gerard de Jode is known for his atlas, Speculum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1578. Part of the engraving was done by himself, and part by brothers Jan and Lucas van Doetecum.
Gerard de Jode and Abraham Ortelius, who partly lived as map sellers, were competitors and only sometimes on good terms.
After the death of Gerard de Jode in 1591, the business was carried on by his widow, Pascale van Gelder and his son, Cornelis (1568-1600). More a publisher than an engraver, the latter reissued the Speculum in 1593, adding new maps and revising others.
Despite all its deficiencies, the Speculum must have had a good reputation. It is mentioned alongside Mercator's Atlas and Ortelius's Theatrum in Petrus Montanus's preface to the Germania Inferior of Pieter van den Keere.
Tertiae Partis Asiae quae modernis India orientalis dicitur acurata delineatio. Autore Iacobo Castaldo Pedemontano.
Item Number: 25494 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Asia > Southeast Asia
Old, antique map of Southeast Asia by G. de Jode.
Cartographer: J. Gastaldi
Date of the first edition: 1578
Date of this map: 1593
Copper engraving
Size (not including margins): 33 x 50.5cm (12.9 x 19.7 inches)
Verso text: Latin
Condition: Original coloured, vertical crease along centrefold.
Condition Rating: A
References: Van der Krogt 3, 8400:32; Karrow, 30/92.2; Parry, Pl.3.15; Yeo (Asia), 11.
From: Speculum Orbis Terrae. Antwerpen, G. De Jode, 1593. (Van der Krogt 3, 2:02)
This map is almost an exact copy of Giacomo Gastaldi's two-sheet map of the region published in 1561 except that de Jode omits any suggestion of Japan, part of which is shown on Gastaldi's map at the extreme right-hand edge.
"In 1578 Gerard de Jode published his Speculum Orbis Terrarum, an atlas aimed at competing with the Theatrum of Ortelius. However, the latter had first been issued in 1570 and had already built a commanding market presence, and so despite de Jode's longer standing reputation the atlas did not sell very well. Only a dozen or so examples have survived. Undeterred, he made plans for another expanded edition, and upon his death in 1591 it was taken on by his son Cornelis. The Speculum Orbis Terrae of 1593 likewise did not sell well and was never reissued. Although more examples than the first edition have survived, it too is very scarce. Many of de Jode's maps are judged to be superior to those of Ortelius, both in detail and style." (Burden)
This map is almost an exact copy of Giacomo Gastaldi's two-sheet map of the region published in 1561 except that de Jode omits any suggestion of Japan, part of which is shown on Gastaldi's map at the extreme right-hand edge.
"In 1578 Gerard de Jode published his Speculum Orbis Terrarum, an atlas aimed at competing with the Theatrum of Ortelius. However, the latter had first been issued in 1570 and had already built a commanding market presence, and so despite de Jode's longer standing reputation the atlas did not sell very well. Only a dozen or so examples have survived. Undeterred, he made plans for another expanded edition, and upon his death in 1591 it was taken on by his son Cornelis. The Speculum Orbis Terrae of 1593 likewise did not sell well and was never reissued. Although more examples than the first edition have survived, it too is very scarce. Many of de Jode's maps are judged to be superior to those of Ortelius, both in detail and style." (Burden)
Gerard and Cornelis de Jode
Gerard de Jode (Judaeus) (1508(?)-1591), a native of Nijmegen, began his career as a printer and engraver in Antwerp about 1550. He lived near the Bourse on the Catelijne Veste, or on "de Catte". He was in regular contact with Christoffel Plantin, to whom he sold many prints and maps. De Jode's business, which must have been a major one among Antwerp's many booksellers and printers, was represented at the Frankfurt fair, where de Jode bought maps that he later copied or re-sold. Most of the maps sold by De Jode have prototypes of Italian or German origin. Apart from his many separately published maps, Gerard de Jode is known for his atlas, Speculum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1578. Part of the engraving was done by himself, and part by brothers Jan and Lucas van Doetecum.
Gerard de Jode and Abraham Ortelius, who partly lived as map sellers, were competitors and only sometimes on good terms.
After the death of Gerard de Jode in 1591, the business was carried on by his widow, Pascale van Gelder and his son, Cornelis (1568-1600). More a publisher than an engraver, the latter reissued the Speculum in 1593, adding new maps and revising others.
Despite all its deficiencies, the Speculum must have had a good reputation. It is mentioned alongside Mercator's Atlas and Ortelius's Theatrum in Petrus Montanus's preface to the Germania Inferior of Pieter van den Keere.