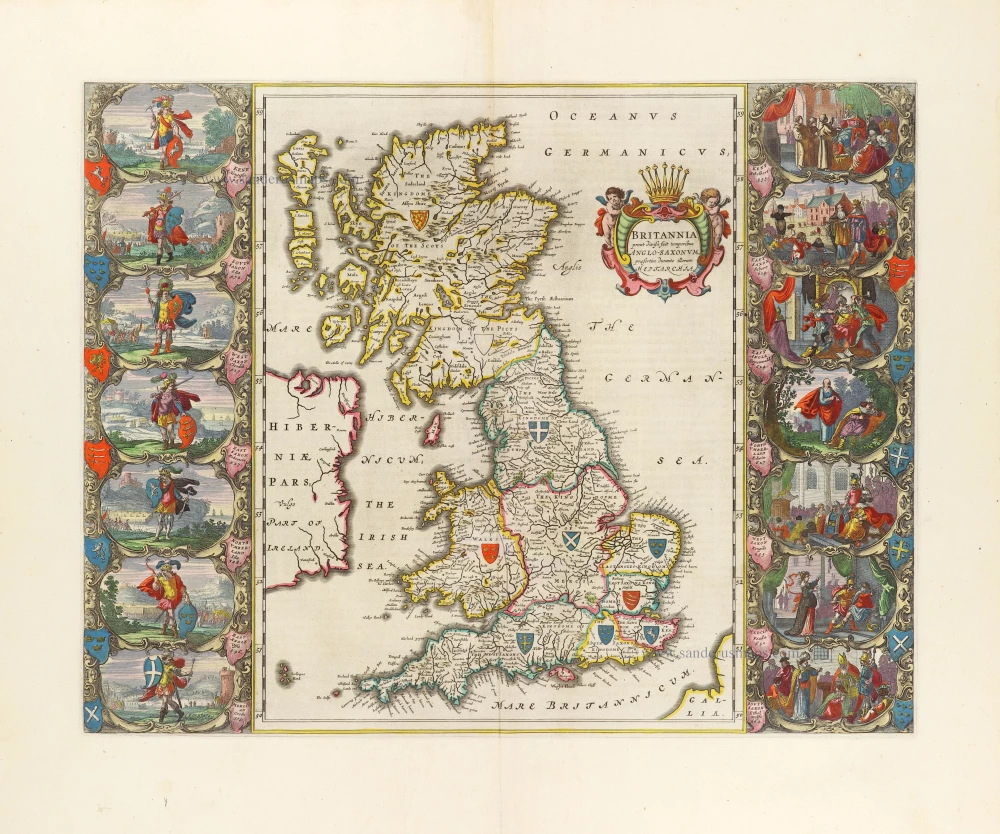
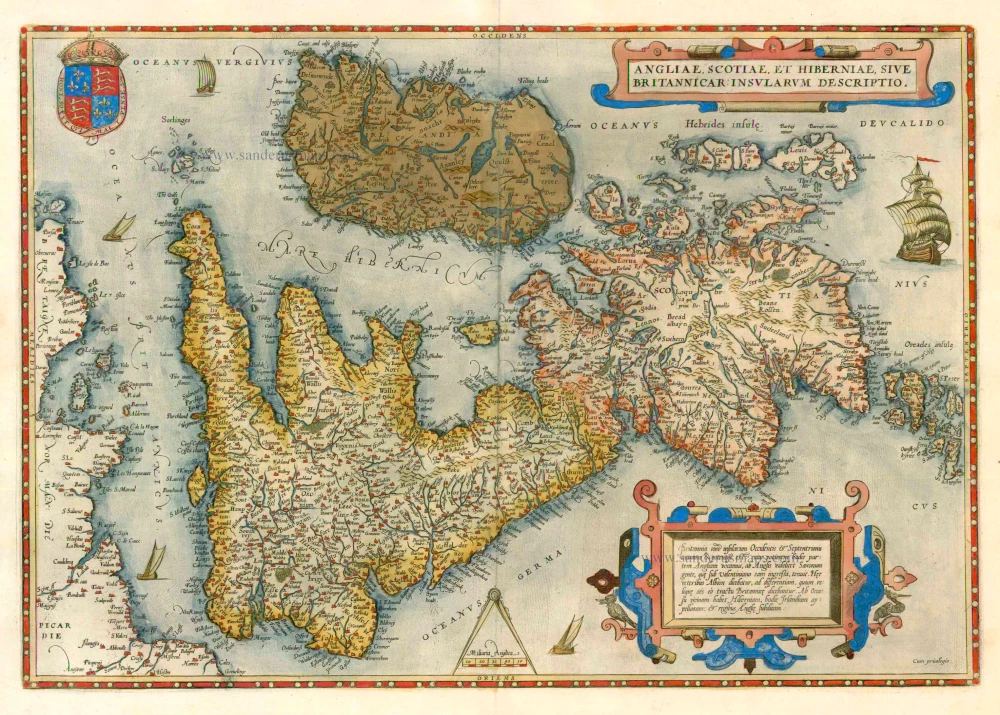
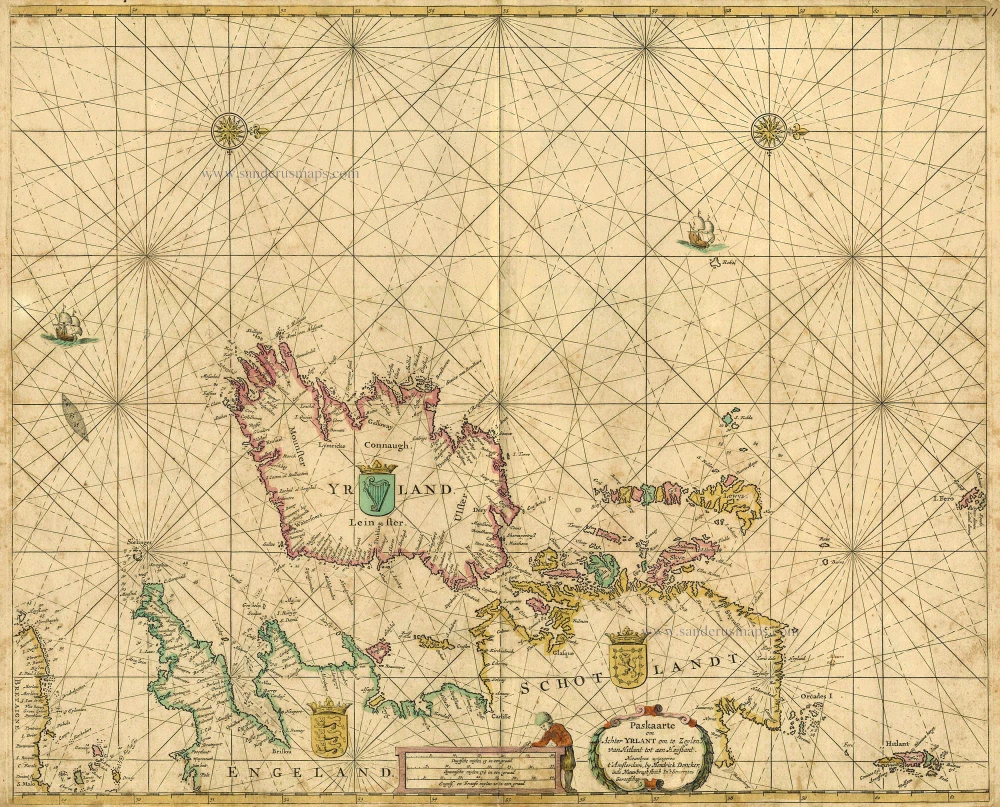
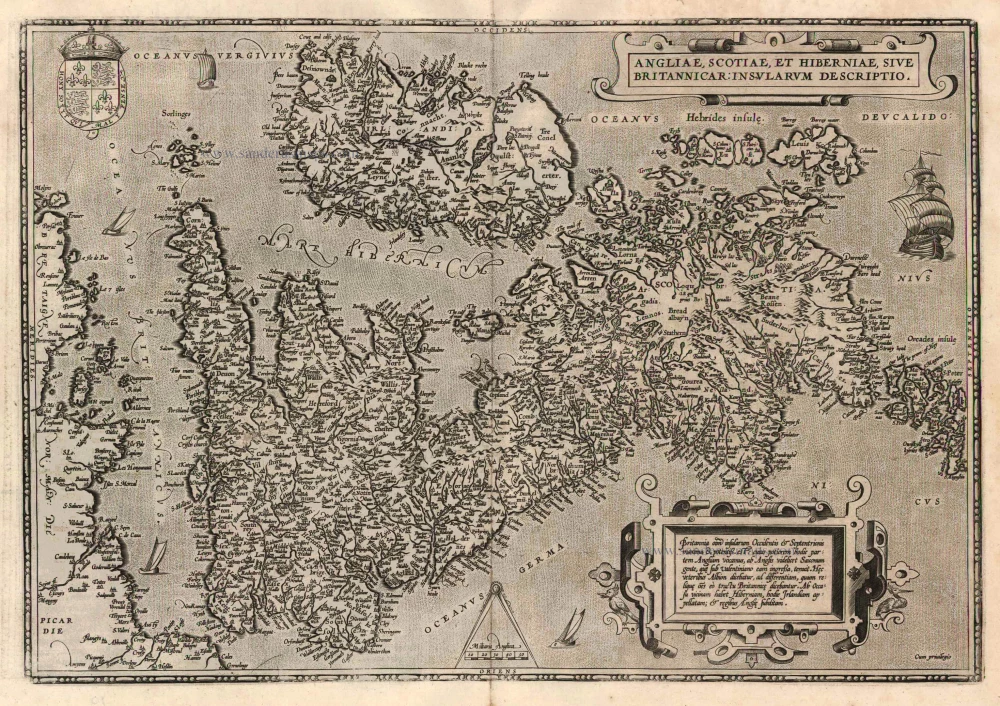
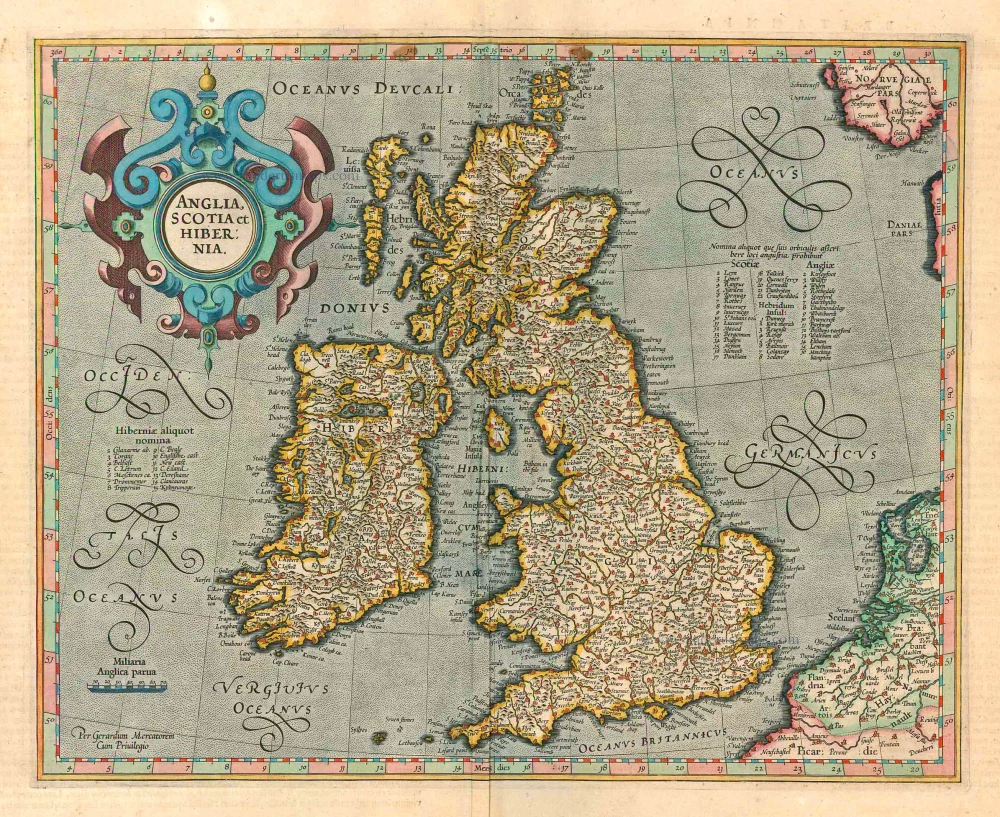
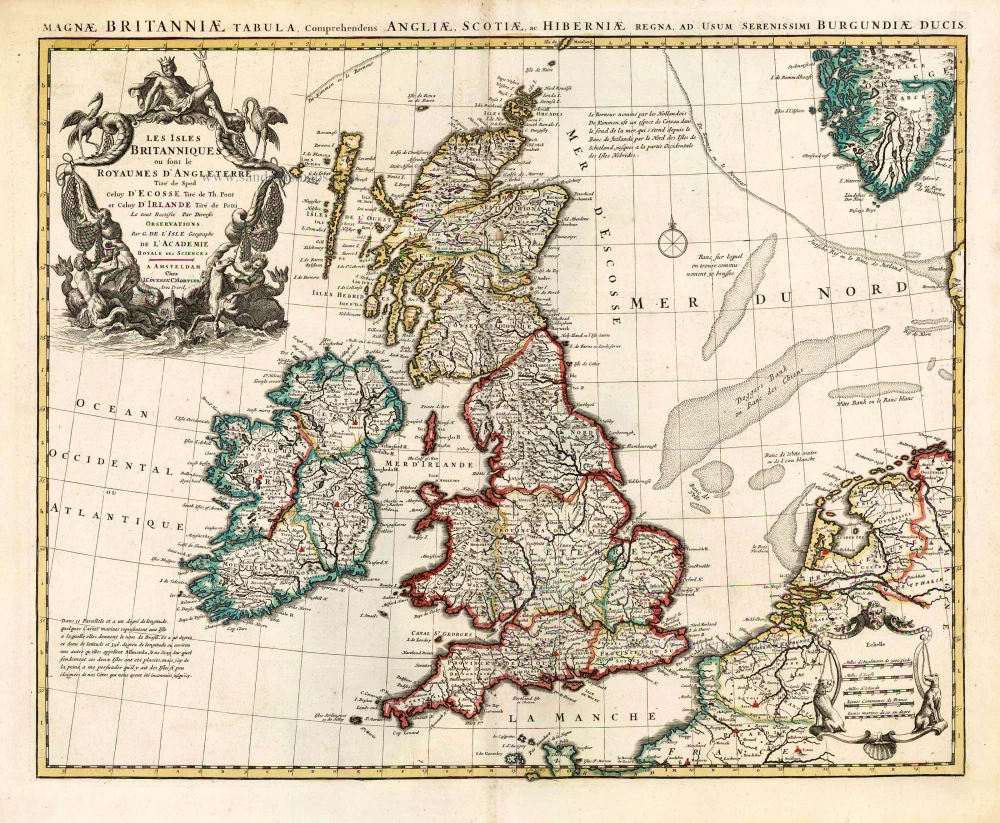
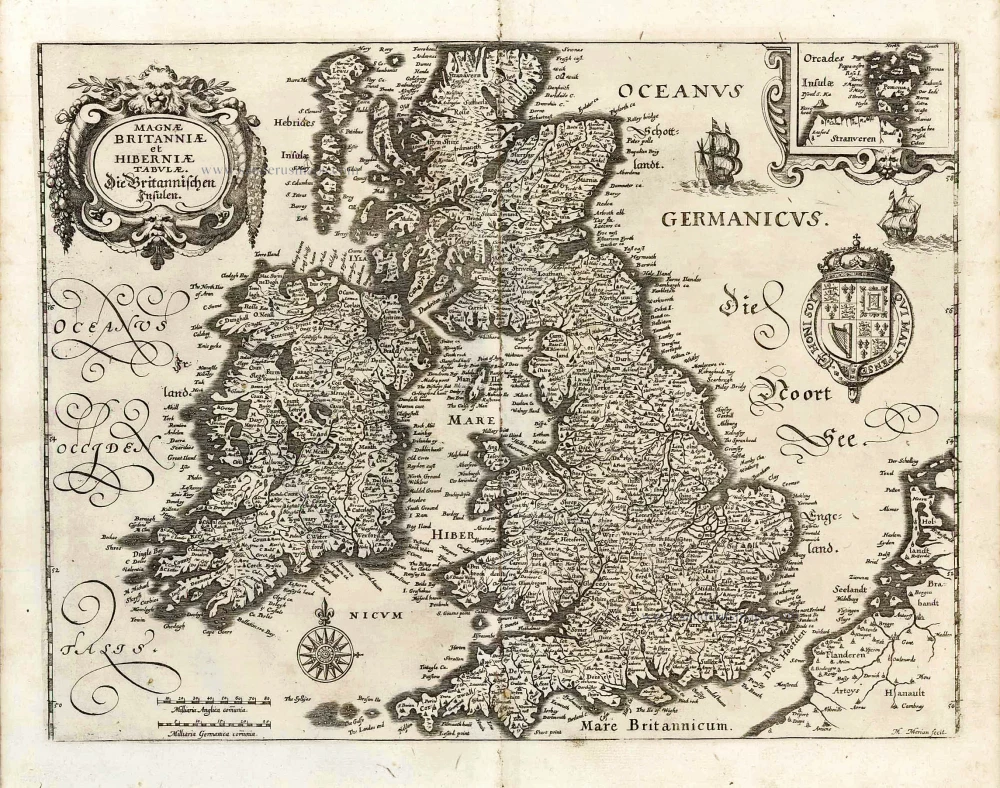
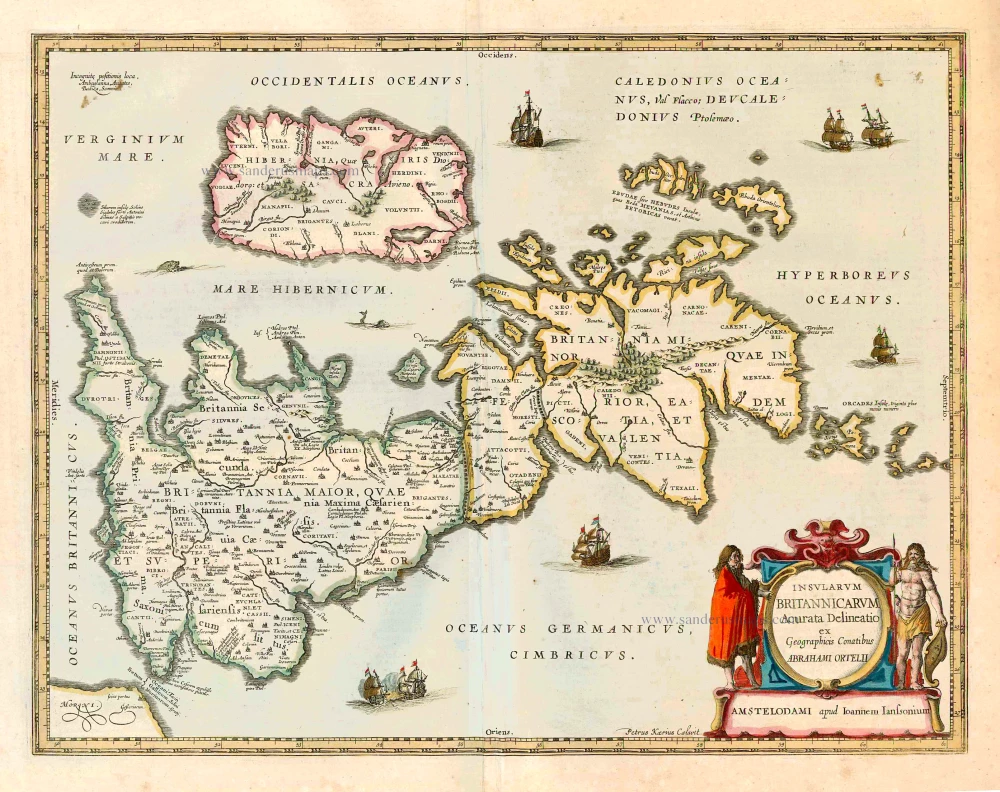
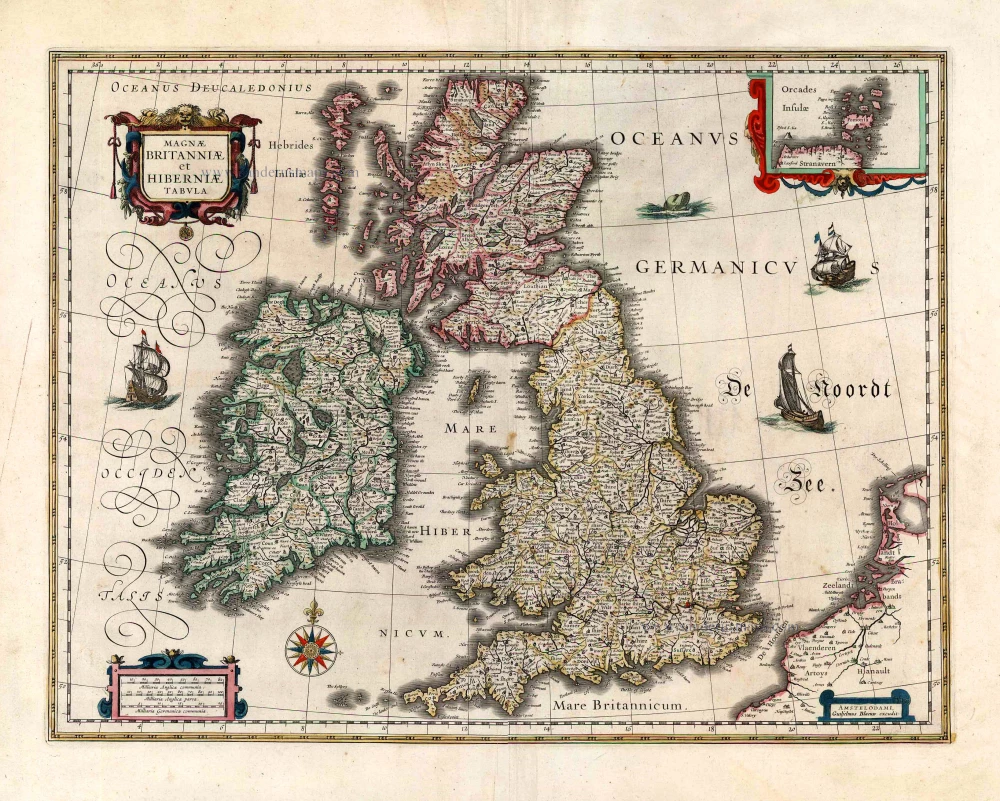
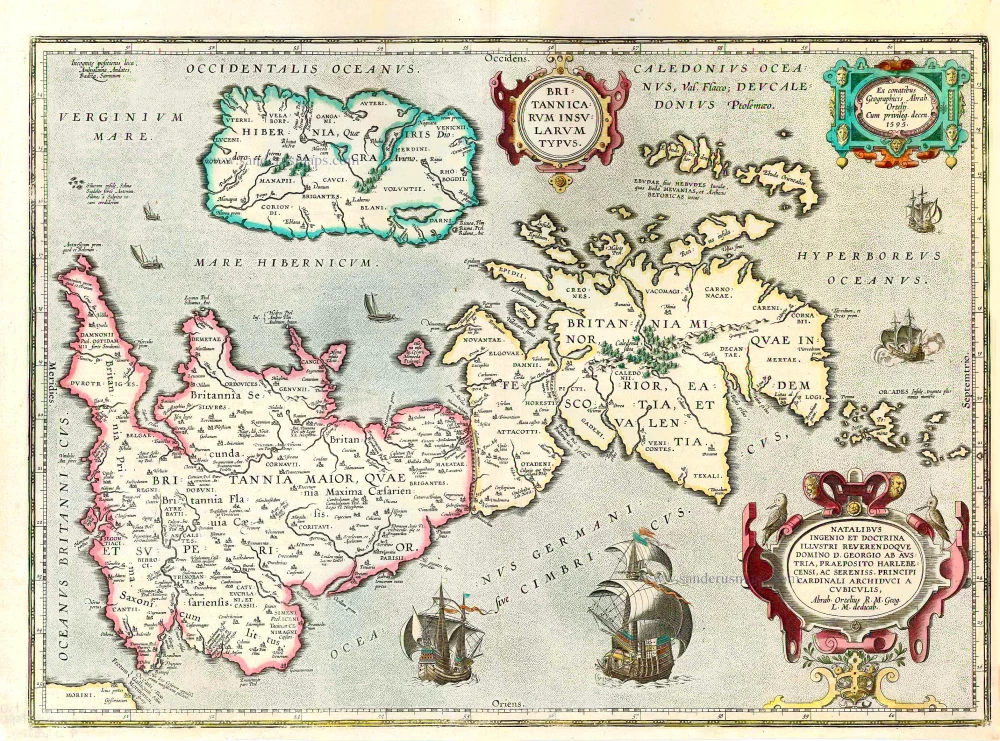
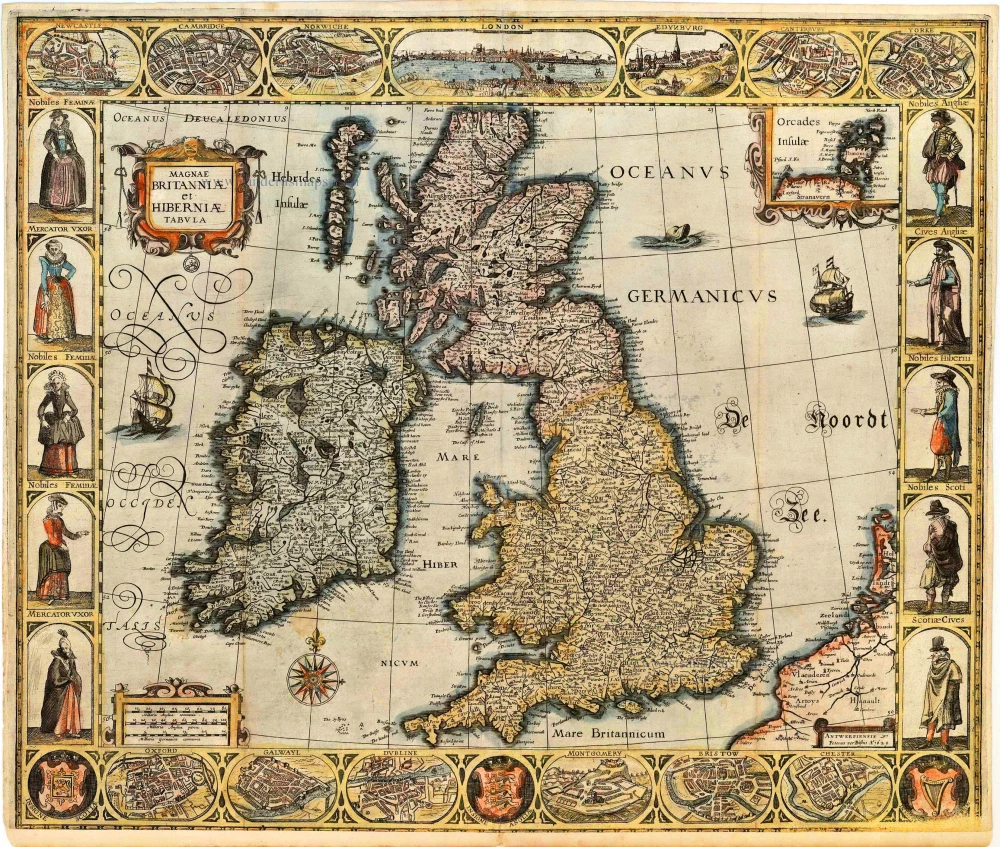
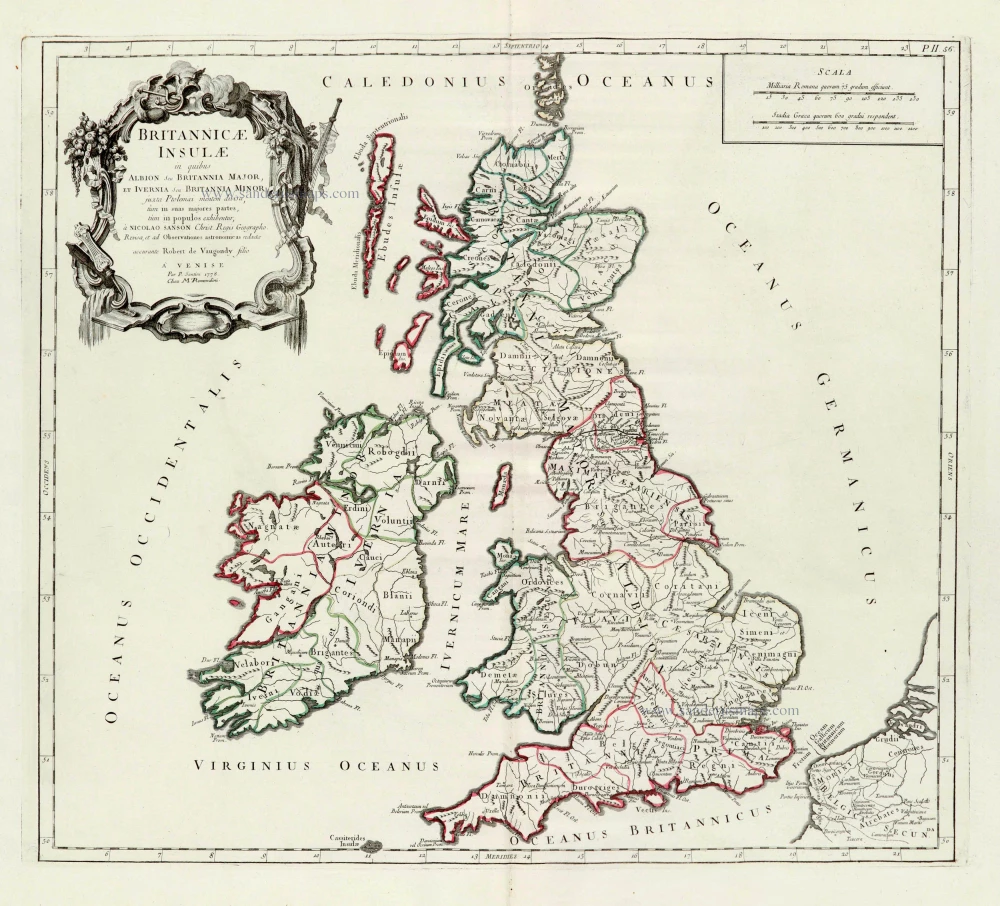
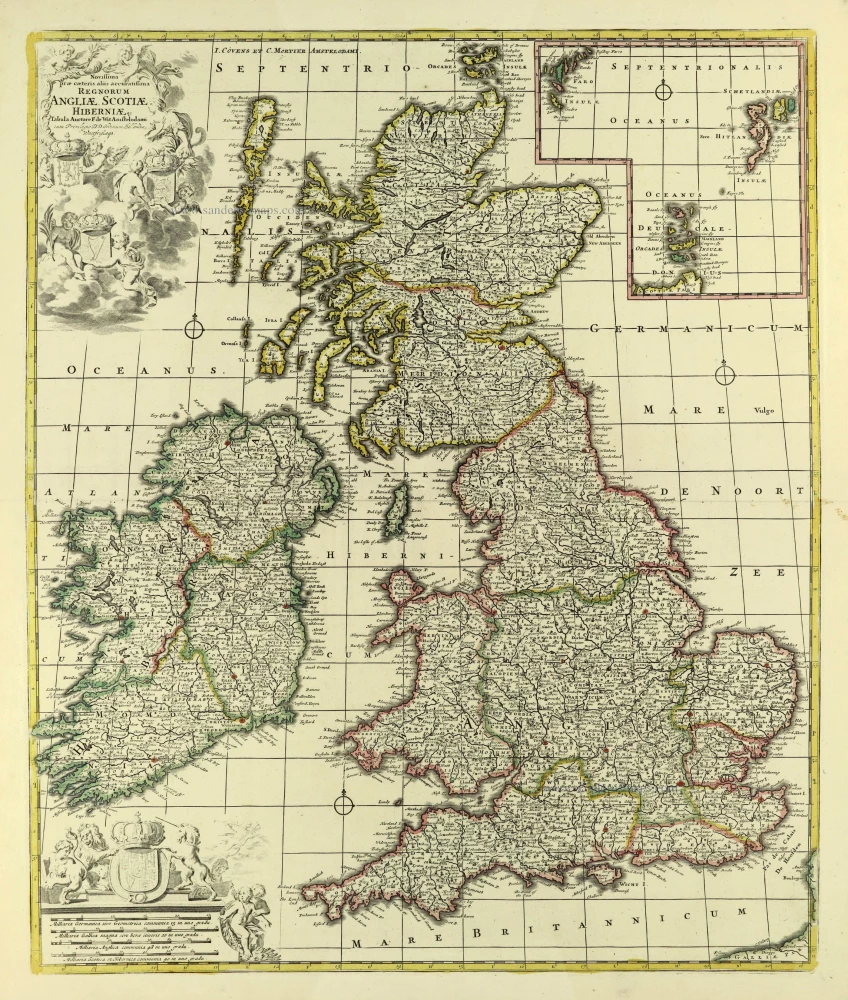
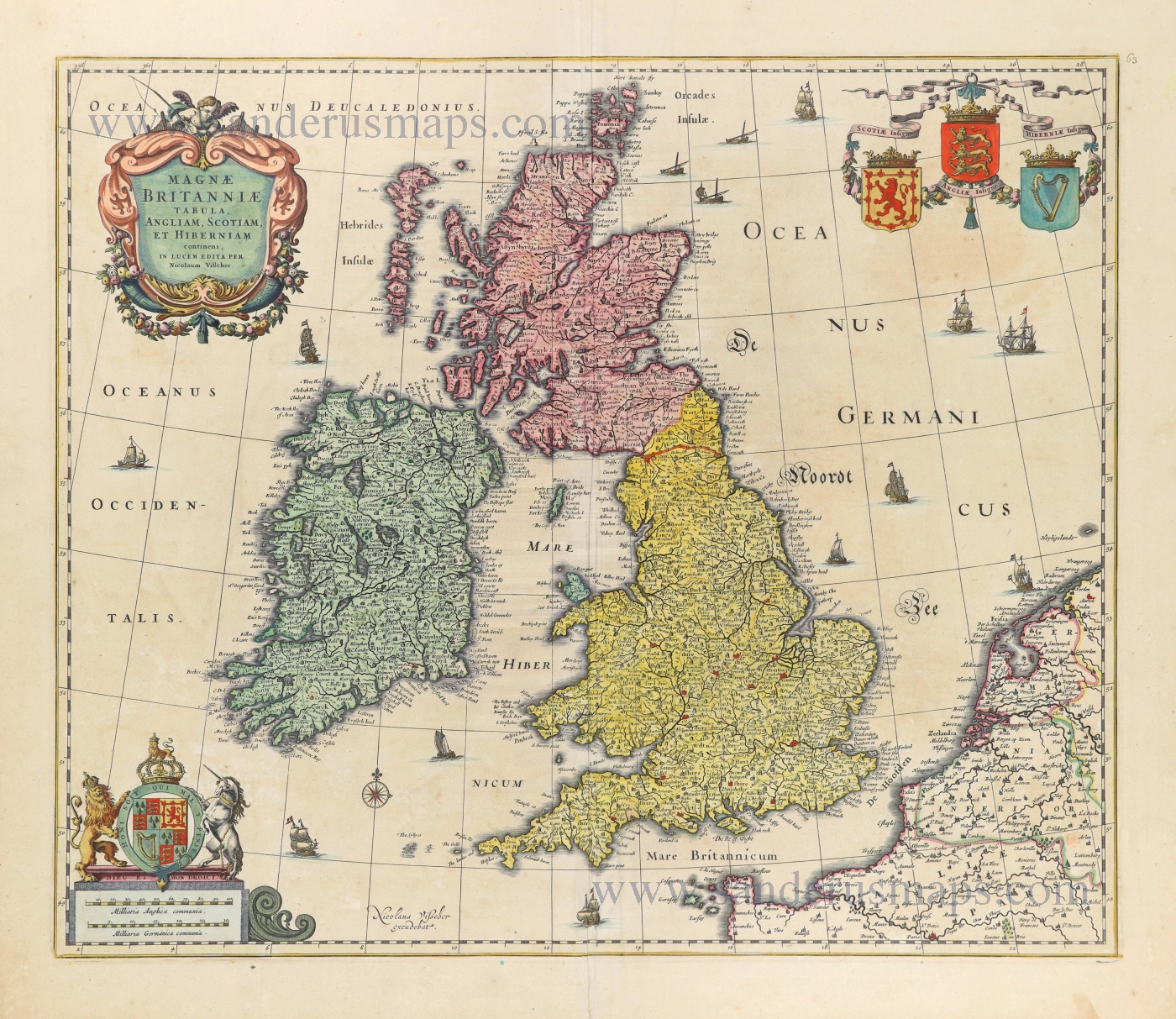
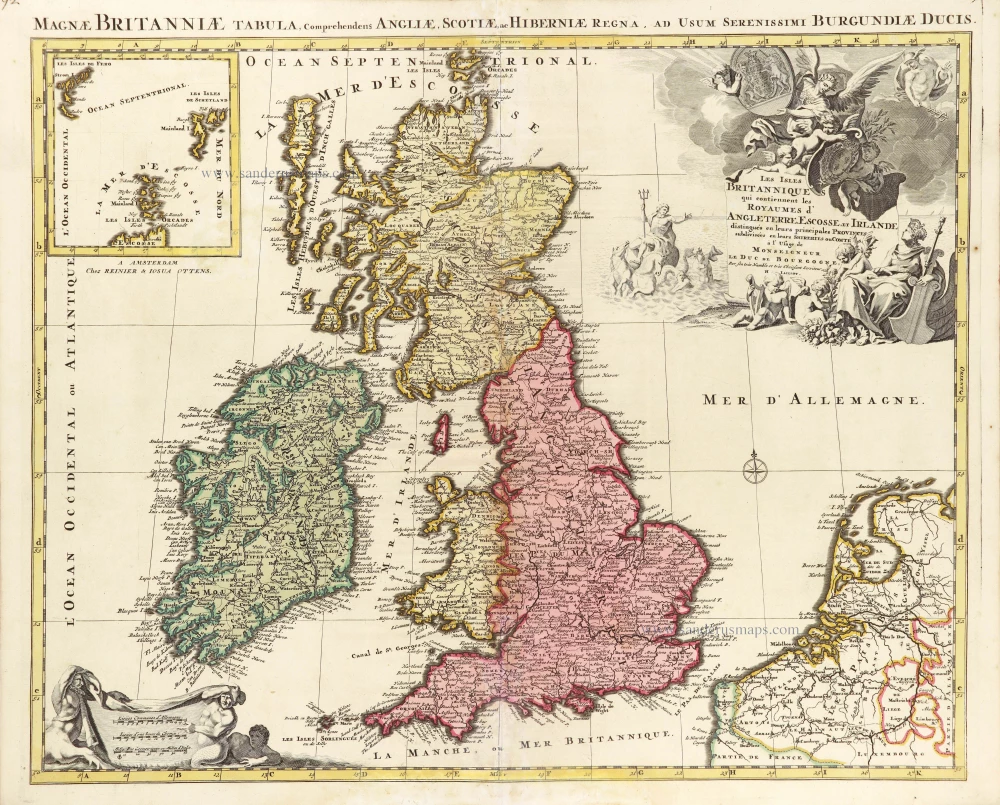
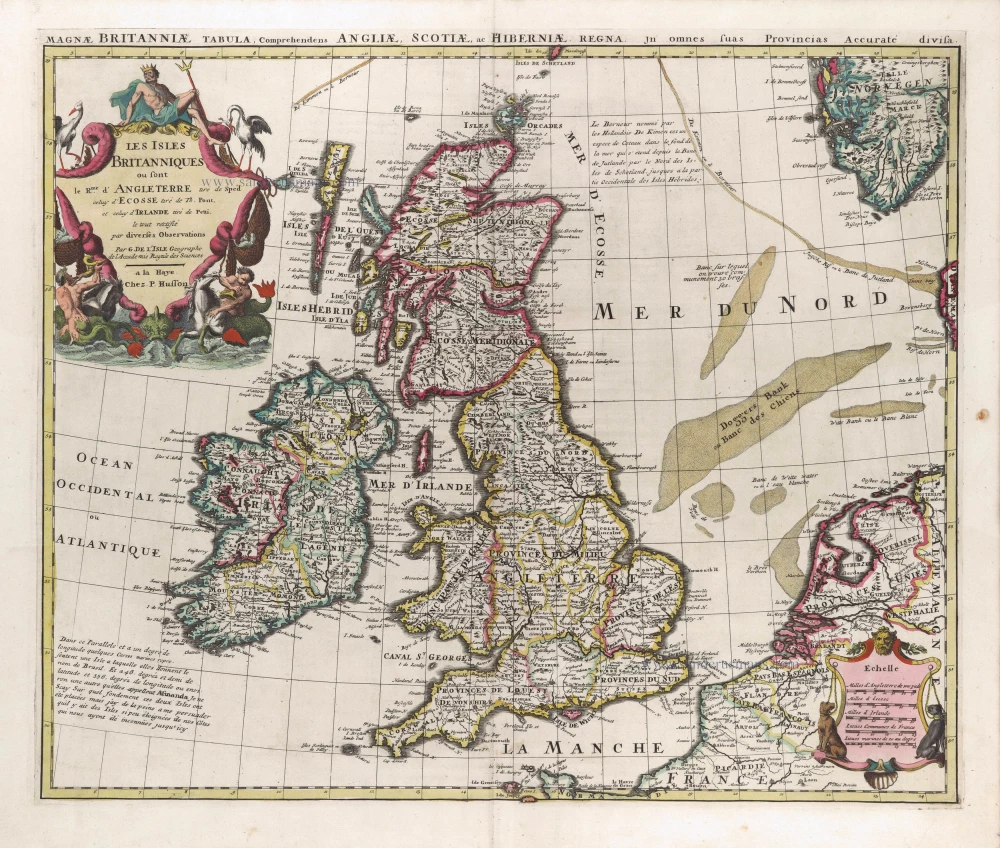
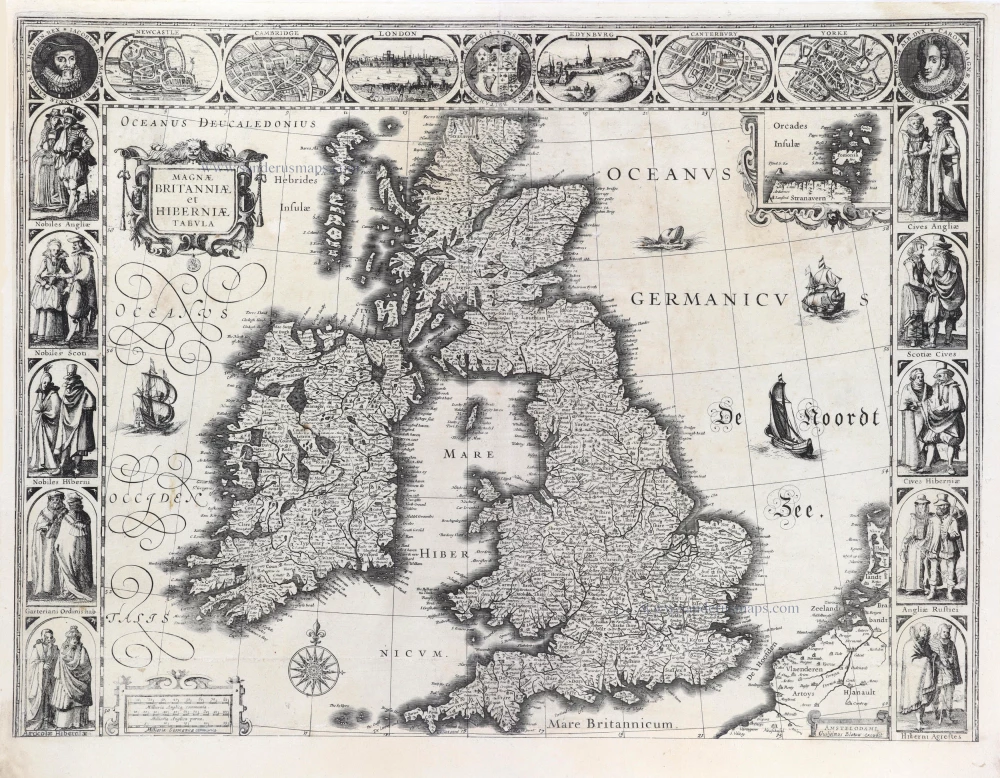
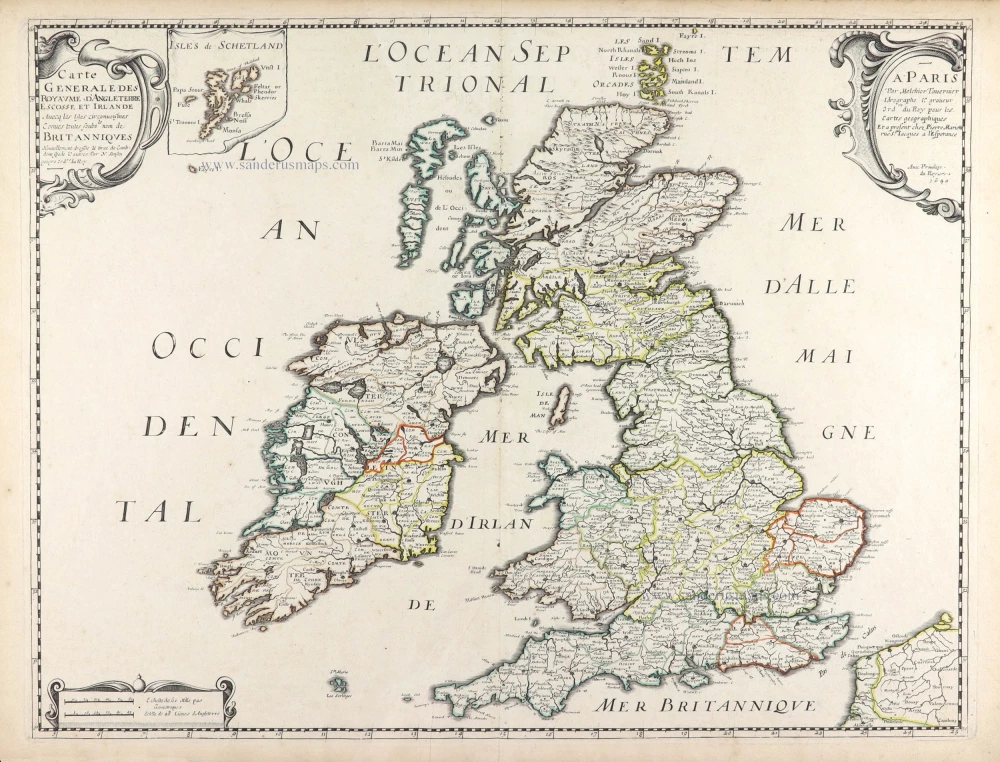
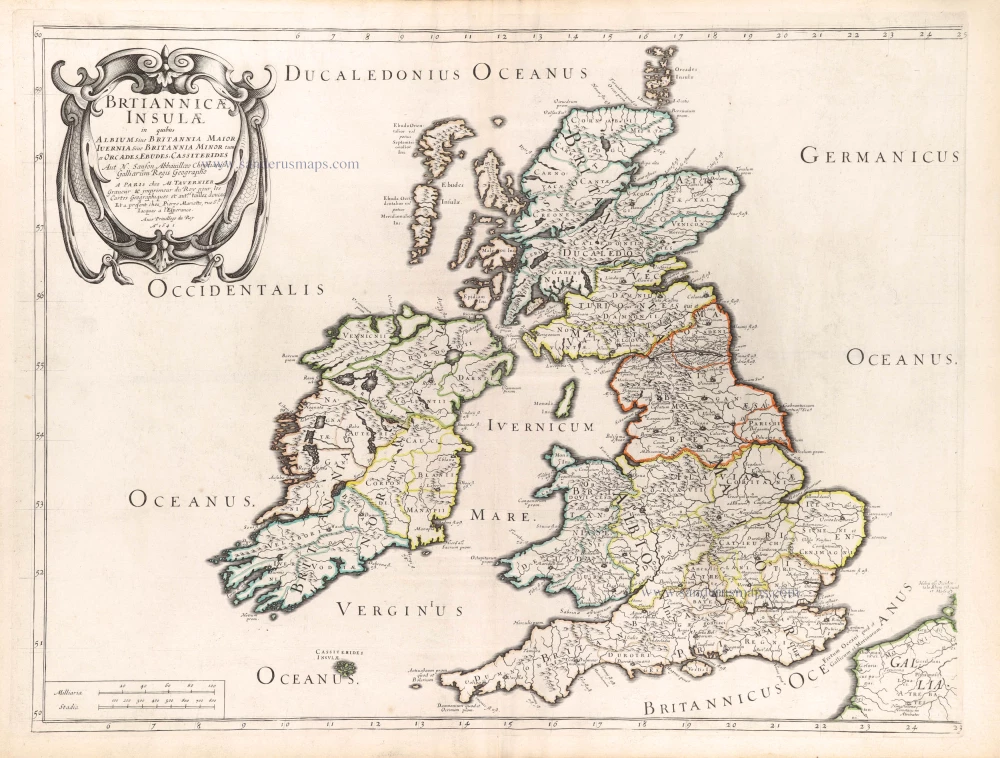
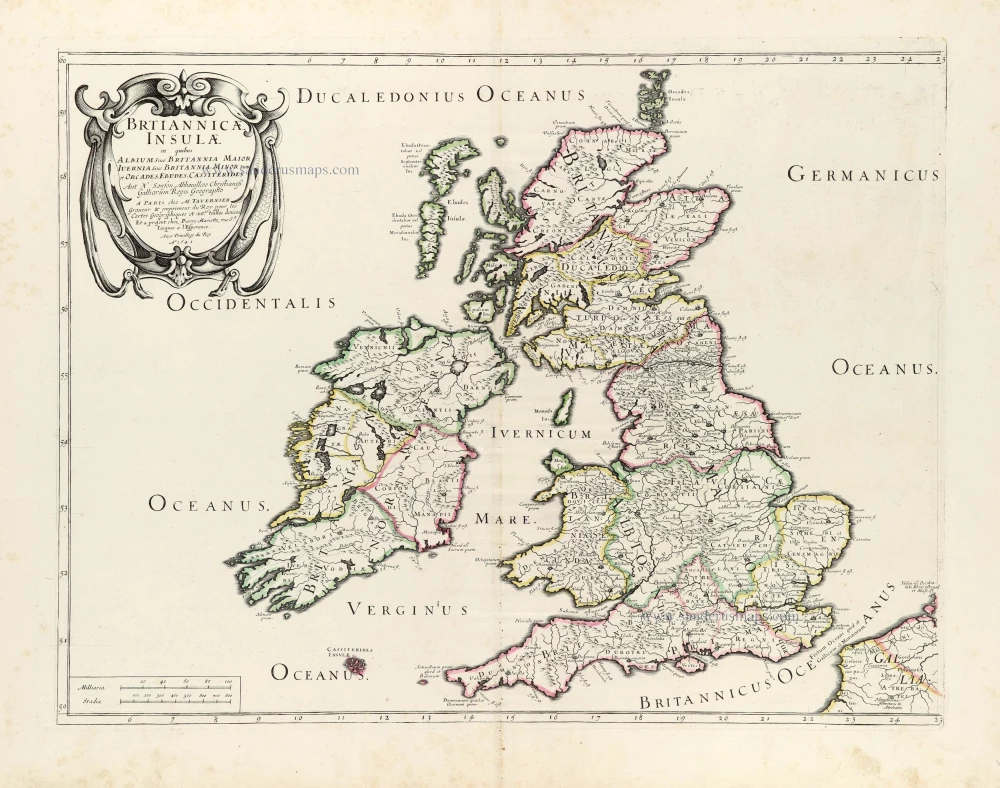
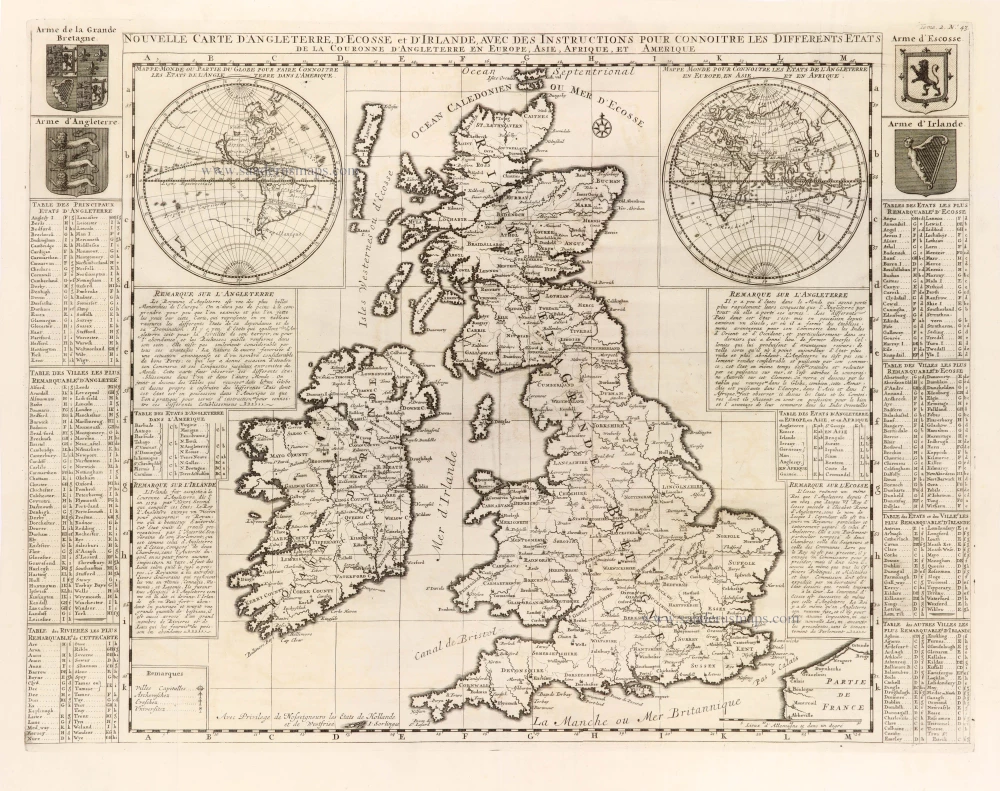
The Ancient British Isles, by Joan Blaeu. 1645
"This is the only map of the British Isles published under the aegis of Joan Blaeu, who took over the publishing house upon his father's death, Willem, in 1638. Arguably one of the finest maps published anywhere in the seventeenth century, Blaeu used Speed's map of 1611 as source material. It is generally accepted that the copy is far finer than the original. Each of the fourteen vignettes - seven on each side of the map - is a work of art in its own right, miniatures in the style of renowned Dutch painters of the day. The original coloured examples of this map are often wonderful, showing seven Saxon kings down the left-hand side and the conversion to Christianity of a further seven down the right-hand side. This map appeared on several occasions in each issue of Blaeu's Atlas of England and Wales until the destruction (by fire) of the Blaeu workshops in 1672. The text verso may be in Latin, Dutch, French, Spanish or German; issues were also made with blank backs. The text, when present, is not complete in itself and is a translation from William Camden's Britannia." (Moreland and Bannister)
The Blaeus: Willem Janszoon, Cornelis & Joan
Willem Jansz. Blaeu and his son Joan Blaeu are the seventeenth century's most widely known cartographic publishers.
Willem Jansz. (also written Guilielmus Janssonius) = Willem Janszoon Blaeu was born in Uitgeest (Netherlands), near Alkmaar, in 1571. He studied mathematics under Tycho Brahe and learned the theory and practice of astronomical observations and the art of instrument- and globe-making.
In 1596, he came to Amsterdam, where he settled down as a globe-, instrument- and mapmaker. He published his first cartographic work (a globe) in 1599 and probably published his first printed map (a map of the Netherlands) in 1604. He specialised in maritime cartography, published the first edition of the pilot guide Het Licht der Zeevaert in 1608, and was appointed Hydrographer of the V.O.C. (United East India Company) in 1633. After publishing books, wall maps, globes, charts and pilot guides for thirty years, he brought out his first atlas, Atlas Appendix (1630). This was the beginning of the great tradition of atlas-making by the Blaeus.
In 1618, another mapmaker, bookseller and publisher, Johannes Janssonius, established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu's shop. No wonder these two neighbours began accusing each other of copying and stealing their information and became fierce competitors who did not have a good word to say about each other. In about 1621 Willem Jansz. decided to end the confusion between his name and his competitor's and assumed his grandfather's nickname, 'blauwe Willem' ('blue Willem'), as the family name; after that, he called himself Willem Jansz. Blaeu.
Willem Janszoon Blaeu died in 1638, leaving his prospering business to his sons, Cornelis and Joan. We only know that Cornelis's name occurs in the prefaces of books and atlases until c. 1645.
Joan Blaeu, born in Amsterdam in 1596, became a partner in his father's book trade and printing business. 1638, he was appointed his father's successor in the Hydrographic Office of the V.O.C. His efforts culminated in the magnificent Atlas Major and the town books of the Netherlands and Italy – works unsurpassed in history and modern times, giving eternal fame to the name of the Blaeu's.
A fire ruined the business on February 23, 1672, and one year later, Dr. Joan Blaeu died. The fire and the director's passing caused the complete sale of the Blaeu House's stock. Five public auctions dispersed the remaining books, atlases, copperplates, globes, etc., among many other map dealers and publishers in Amsterdam. The majority was acquired by several booksellers acting in partnership.
In the succeeding years, the remaining printing department remained in the hands of the Blaeu family until 1695, when the printing house's inventory was sold at a public auction. That meant the end of the Blaeu family as a printing house of world renown.
Britannia prout divisa fuit temporibus Anglo-Saxonum, praesertim durante illorum Heptarchia.
Item Number: 29220 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > British Isles
Old, antique map of the ancient British Isles, by Joan Blaeu.
Title: Britannia prout divisa fuit temporibus Anglo-Saxonum, praesertim durante illorum Heptarchia.
Date of the first edition: 1645.
Date of this map: 1645.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 420 x 520mm (16.54 x 20.47 inches).
Sheet size: 545 x 645mm (21.46 x 25.39 inches).
Verso: French text.
Condition: Original coloured, heightened in gold, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Le Théâtre du Monde ou Nouvel Atlas. J. Blaeu, 1645. (Van der Krogt 2, 311)
"This is the only map of the British Isles published under the aegis of Joan Blaeu, who took over the publishing house upon his father's death, Willem, in 1638. Arguably one of the finest maps published anywhere in the seventeenth century, Blaeu used Speed's map of 1611 as source material. It is generally accepted that the copy is far finer than the original. Each of the fourteen vignettes - seven on each side of the map - is a work of art in its own right, miniatures in the style of renowned Dutch painters of the day. The original coloured examples of this map are often wonderful, showing seven Saxon kings down the left-hand side and the conversion to Christianity of a further seven down the right-hand side. This map appeared on several occasions in each issue of Blaeu's Atlas of England and Wales until the destruction (by fire) of the Blaeu workshops in 1672. The text verso may be in Latin, Dutch, French, Spanish or German; issues were also made with blank backs. The text, when present, is not complete in itself and is a translation from William Camden's Britannia." (Moreland and Bannister)
The Blaeus: Willem Janszoon, Cornelis & Joan
Willem Jansz. Blaeu and his son Joan Blaeu are the seventeenth century's most widely known cartographic publishers.
Willem Jansz. (also written Guilielmus Janssonius) = Willem Janszoon Blaeu was born in Uitgeest (Netherlands), near Alkmaar, in 1571. He studied mathematics under Tycho Brahe and learned the theory and practice of astronomical observations and the art of instrument- and globe-making.
In 1596, he came to Amsterdam, where he settled down as a globe-, instrument- and mapmaker. He published his first cartographic work (a globe) in 1599 and probably published his first printed map (a map of the Netherlands) in 1604. He specialised in maritime cartography, published the first edition of the pilot guide Het Licht der Zeevaert in 1608, and was appointed Hydrographer of the V.O.C. (United East India Company) in 1633. After publishing books, wall maps, globes, charts and pilot guides for thirty years, he brought out his first atlas, Atlas Appendix (1630). This was the beginning of the great tradition of atlas-making by the Blaeus.
In 1618, another mapmaker, bookseller and publisher, Johannes Janssonius, established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu's shop. No wonder these two neighbours began accusing each other of copying and stealing their information and became fierce competitors who did not have a good word to say about each other. In about 1621 Willem Jansz. decided to end the confusion between his name and his competitor's and assumed his grandfather's nickname, 'blauwe Willem' ('blue Willem'), as the family name; after that, he called himself Willem Jansz. Blaeu.
Willem Janszoon Blaeu died in 1638, leaving his prospering business to his sons, Cornelis and Joan. We only know that Cornelis's name occurs in the prefaces of books and atlases until c. 1645.
Joan Blaeu, born in Amsterdam in 1596, became a partner in his father's book trade and printing business. 1638, he was appointed his father's successor in the Hydrographic Office of the V.O.C. His efforts culminated in the magnificent Atlas Major and the town books of the Netherlands and Italy – works unsurpassed in history and modern times, giving eternal fame to the name of the Blaeu's.
A fire ruined the business on February 23, 1672, and one year later, Dr. Joan Blaeu died. The fire and the director's passing caused the complete sale of the Blaeu House's stock. Five public auctions dispersed the remaining books, atlases, copperplates, globes, etc., among many other map dealers and publishers in Amsterdam. The majority was acquired by several booksellers acting in partnership.
In the succeeding years, the remaining printing department remained in the hands of the Blaeu family until 1695, when the printing house's inventory was sold at a public auction. That meant the end of the Blaeu family as a printing house of world renown.