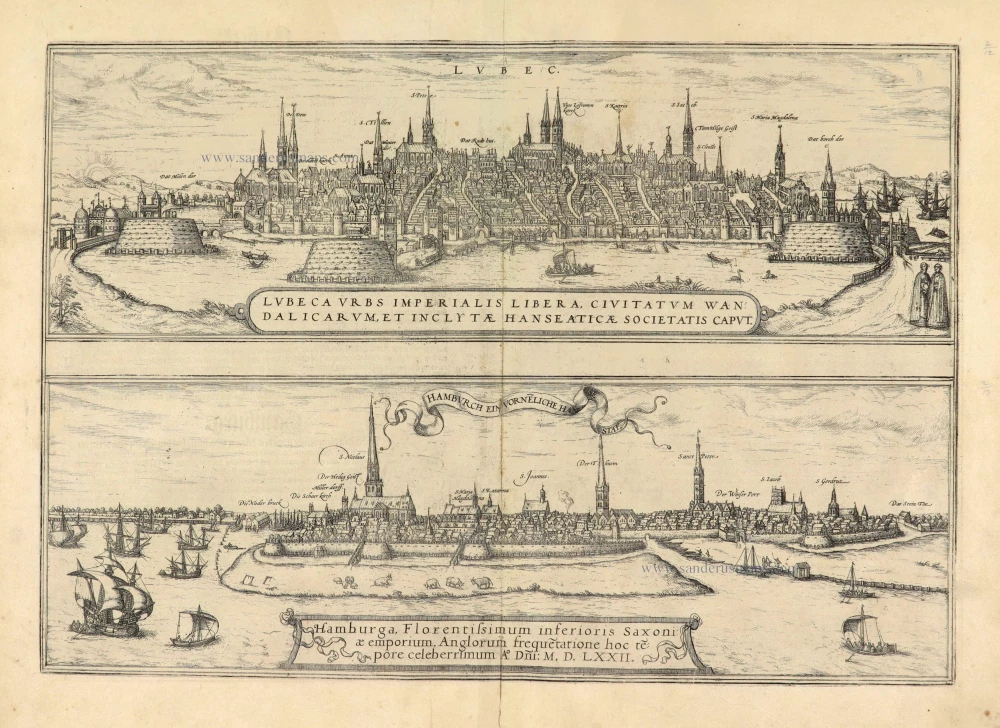
Hamburg, by Braun and Hogenberg. 1588
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The Cimbrian Peninsula, the northernmost region of Germany, went by the name of Hutland, encompassing all the neighbouring islands, Holstein, Stormarn, Wagrien, Dithmarschen and the Duchy of Schleswig. However, during the reign of Charlemagne, the northern part of the peninsula was called Jutland, but the lower part was Holstein-Nordelbien. The latter is, in turn, divided into four regions, namely Holstein, Dithmarschen, Wagrien and Stormarn. Situated between the Rivers Elbe, Stör and Schwaland, Stormarn extends to the Trave and is endowed with the buildings, situation, trade and riches of the powerful city of Hamburg."
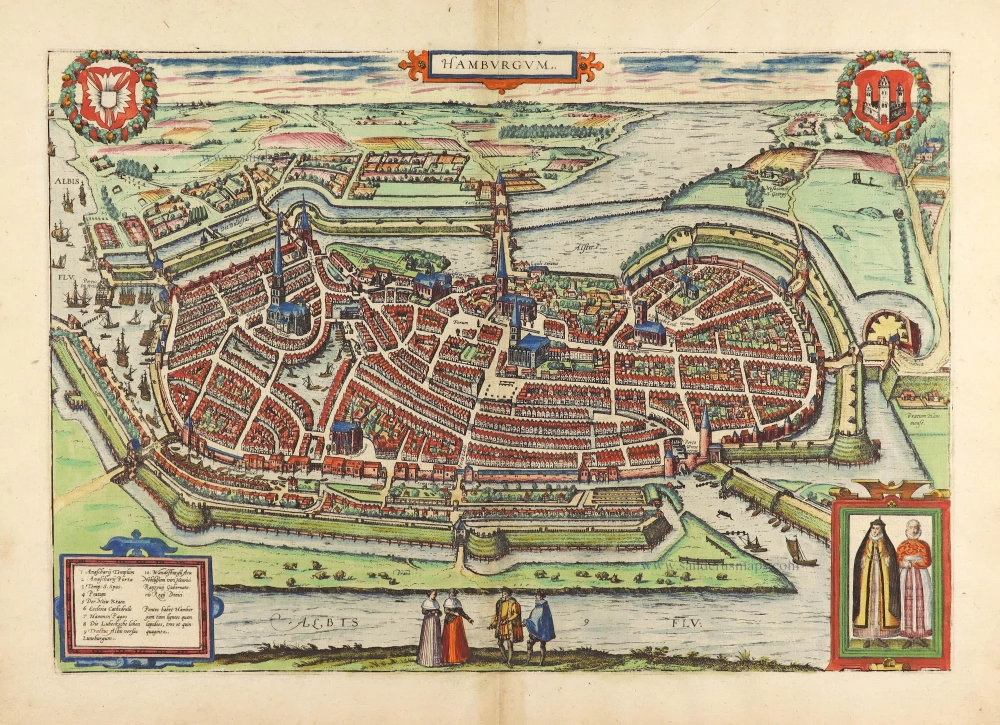
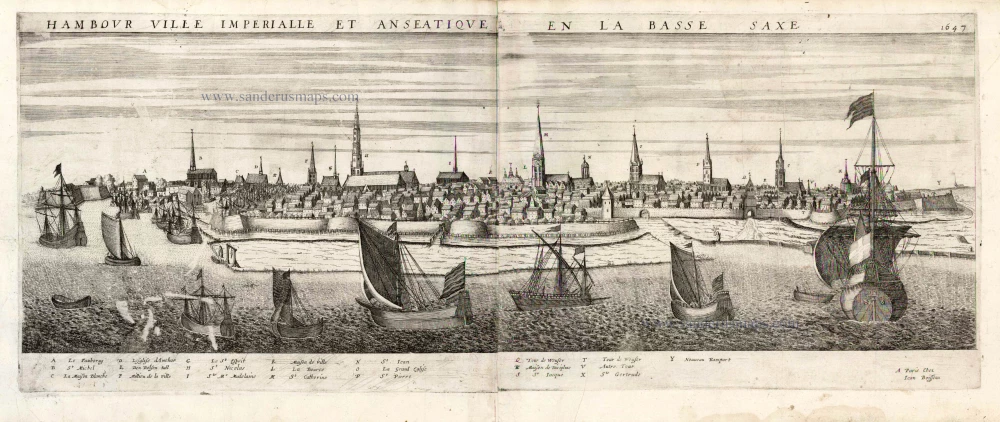
The tranquil illustration of Hamburg in Volume I, showing the city from a low vantage point, reveals its rural character, whereas the present bird's-eye view presents a more modern city. Left of the centre stands the 153-m-high tower of the church of St Nicholas (25). To the right is the spire of St Peter's (18). The modern city landmark, the Hamburger Michel, was finished in 1786 as the tower of the Baroque church of St Michael. After Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa granted the city port rights in 1189 and tax exemption on trading with the entire Lower Elbe region, Hamburg grew into a vibrant commercial hub. Boasting up to 600 breweries, the city was the purveyor of beer to the Hanseatic League. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.
Hamburgum.
Item Number: 28958 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Germany - Cities
Antique city plan of Hamburg, by Braun and Hogenberg.
Title: Hamburgum.
First plate (of two), scarce, appeared only in a few copies of the 1588 and 1594 editions.
Date of the first edition: 1588.
Date of this map: 1588.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 330 x 475mm (12.99 x 18.7 inches).
Sheet size: 395 x 535mm (15.55 x 21.06 inches).
Verso: Latin text.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Liber Quartus Urbium Praecipuarum Totius Mundi. Cologne, 1588. (Koeman, B&H4, Van der Krogt 4, 41:1.4)
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The Cimbrian Peninsula, the northernmost region of Germany, went by the name of Hutland, encompassing all the neighbouring islands, Holstein, Stormarn, Wagrien, Dithmarschen and the Duchy of Schleswig. However, during the reign of Charlemagne, the northern part of the peninsula was called Jutland, but the lower part was Holstein-Nordelbien. The latter is, in turn, divided into four regions, namely Holstein, Dithmarschen, Wagrien and Stormarn. Situated between the Rivers Elbe, Stör and Schwaland, Stormarn extends to the Trave and is endowed with the buildings, situation, trade and riches of the powerful city of Hamburg."
The tranquil illustration of Hamburg in Volume I, showing the city from a low vantage point, reveals its rural character, whereas the present bird's-eye view presents a more modern city. Left of the centre stands the 153-m-high tower of the church of St Nicholas (25). To the right is the spire of St Peter's (18). The modern city landmark, the Hamburger Michel, was finished in 1786 as the tower of the Baroque church of St Michael. After Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa granted the city port rights in 1189 and tax exemption on trading with the entire Lower Elbe region, Hamburg grew into a vibrant commercial hub. Boasting up to 600 breweries, the city was the purveyor of beer to the Hanseatic League. (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.