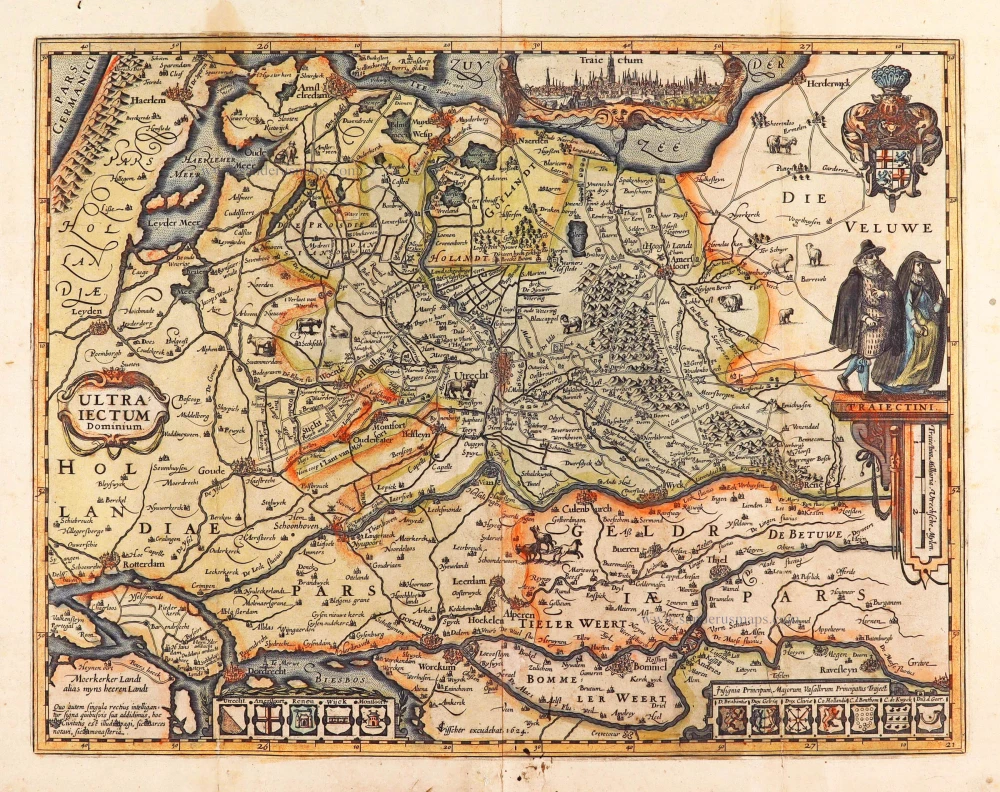
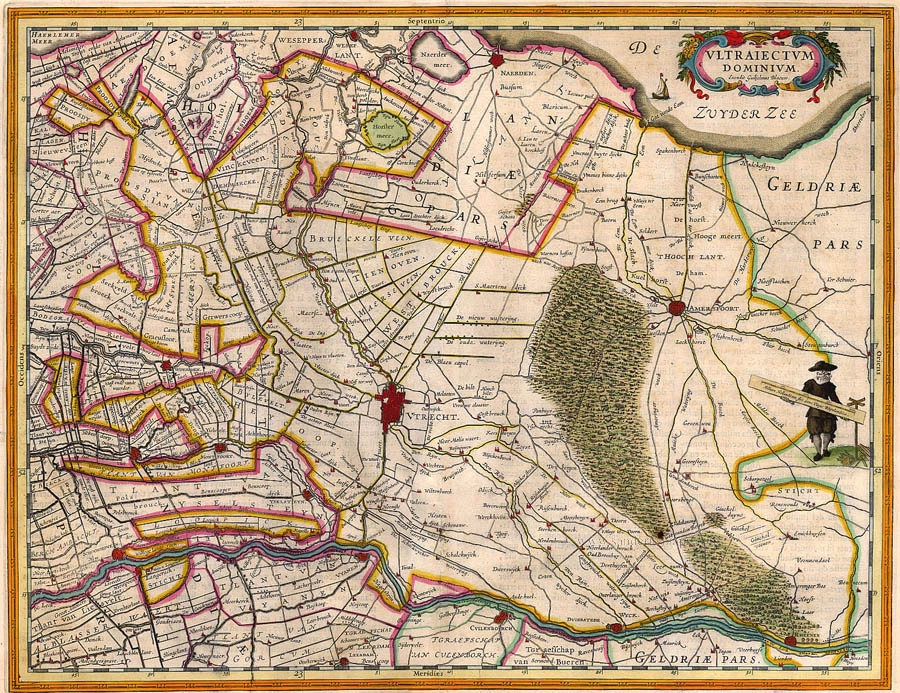
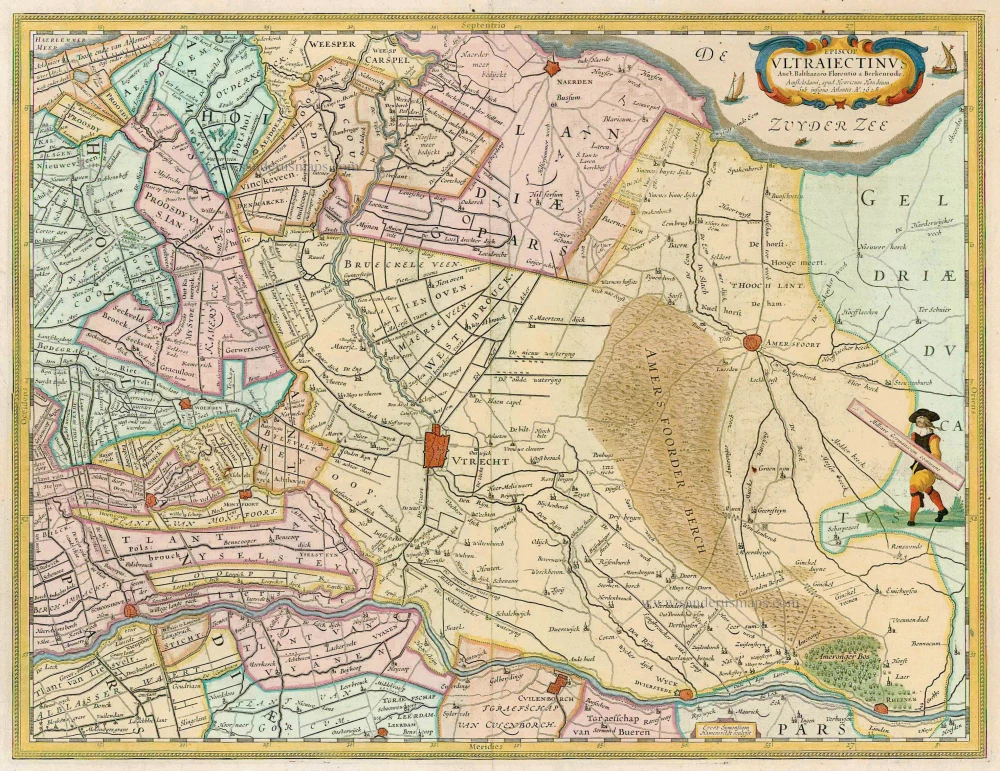
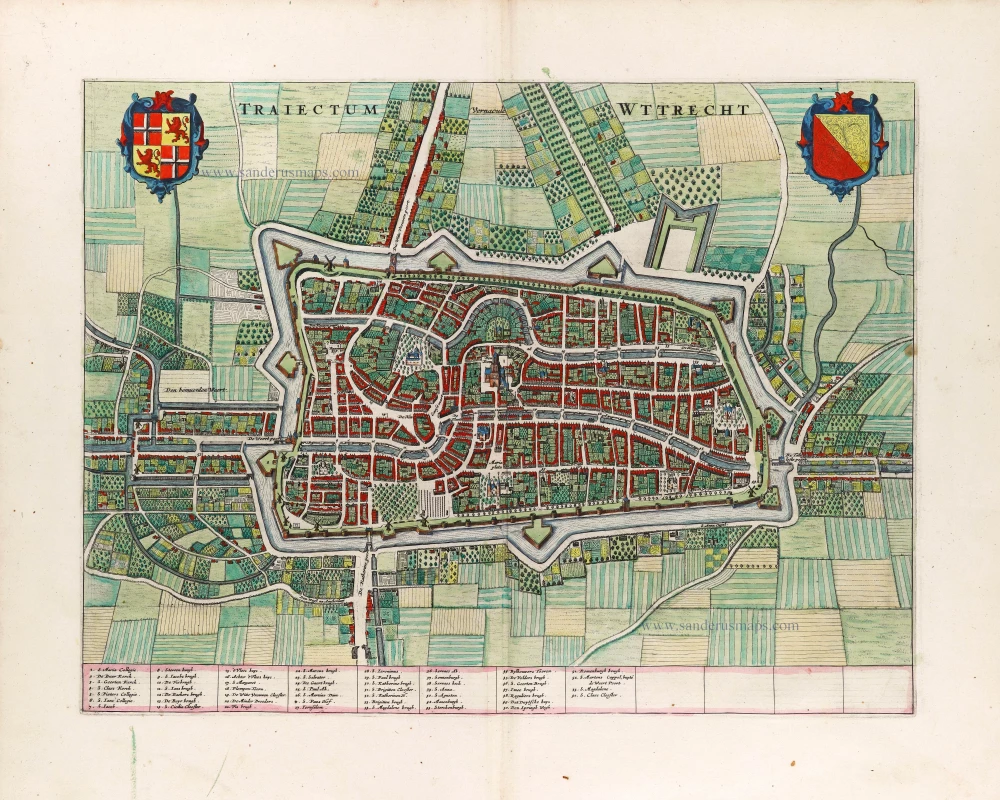
Utrecht by Petrus Kaerius (Pieter Van den Keere), published by Claes Jansz. Visscher. 1624
Rare second edition by Claes Jansz. Visscher of this highly decorative map of the Province of Utrecht.
In the Zuiderzee, a cartouche is located with a view of Utrecht (Traiectum). A shield with the coat of arms of the province of Utrecht is shown in the upper right. Below it, two upright-standing costumed figures (TRAIECTINI) are depicted. Along the bottom border are two rows of coats of arms. The left one shows the arms of the towns in the bishopric Utrecht (Utrecht, Amersfoort, Rhenen, Wijk and Montfort), and the right one shows the coats of arms of the principal vassals and allies of the bishopric Utrecht.
The map content is a reduction of the map of Utrecht by Cornelius Anthonisz. Hornhovius of 1599, now only known from a later edition by Clement de Jonghe. (Schilder)
Pieter Van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius) (1571-c.1650)
Pieter van den Keere was born in Ghent in 1571 as the son of the type-founder, Hendrik van den Keere. In 1584, he moved with his family to London for religious reasons. There, Van den Keere received training as an engraver from Jodocus Hondius, his brother-in-law. Not only the companionship with Jodocus Hondius but also the acquaintanceship with Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus), author of the text of the Germania Inferior, originates from the years of refuge in London.
Upon their settlement in Amsterdam in 1593, both Keere and Hondius embarked on a monumental project. Their collaboration resulted in the creation of a large wall map of Europe, a masterpiece that still stands as a testament to their skill and vision, dated 1595: Nova totius Europae descriptio.
In 1610, he set up a workshop in the Kalverstraat that he called ‘In den onseeckeren tijd’ (In the uncertain time). During this period, he made numerous copperplates, including maps for his Atlas of the Netherlands and the Atlas Minor published by Jodocus Hondius.
The Germania Inferior (1617) is the first original atlas of the Netherlands published in folio size. The text for the atlas, both in Dutch and in French, was written by Petrus Montanus. After 1623, Claes Jansz. Visscher bought the plates and substituted his name for Kaerius’s. In 1634, Visscher included many of these maps in his Germana Inferior.
Kaerius's fame is not only based on his atlas of the Netherlands. He is even better known as an engraver of many loose-leaf maps and as a collaborator of book publishers. His maps are found, i.e., in the Caert thresoor (Barent Langenes, 1598), Licht der Zeevaert (Blaeu, 1608), Atlas Minor (Hondius, 1628), and Caertboeck vande Midellandsche Zee (Barents, 1595).
The Visscher Family
For nearly a century, the members of the Visscher family were essential art dealers and map publishers in Amsterdam.
Claes Jansz. Visscher, or N.J. Piscator (1587-1652)
Claes Jansz. Vischer bought a house in Amsterdam, 'de gulden Bors', on the crucial Kalverstraat and changed the name into "In de Visscher"; under this title, the shop was to flourish for many years.
He was famous for his engravings and etchings of Dutch landscapes and 'historical scenes', such as sieges, battles, etc. These 'historical scenes' were considered contemporary illustrated news items, especially e.g. that of 'the Eighty Years' War'.
For the publication of his first atlas, he bought copperplates of the atlas Germania Inferior by Pieter van den Keere (1623).
In 1649, he published an atlas entitled Tabularum Geographicarum Contractarum, containing the same maps as Langenes' Caert Thresoor, for which Visscher had only new title pages engraved.
Claes Jansz. Visscher died in 1652. His wife, Neeltjen Florisdr., had already died in 1640. They had seven children, four of whom were still alive at Claes Jansz.'s death. One was Nicolaes Visscher I, who was to continue his father's business.
Nicolaes Visscher I (1618-1679)
Nicolaes Visscher I partnered with his father, continued the business, and stayed on the Kalverstraat 'in de Visscher' till his death.
In about 1657, the first edition of his Atlas Contractus Orbis Terrarum appeared.
Between 1664 and 1677, several editions of his Atlas Contractus appeared without a printed index, for these atlases had no fixed contents but were composed according to the buyer's financial leaping pole.
In May 1664, Nicolaes Visscher was admitted as a member of the Booksellers' Guild of his town. In July 1677, he was granted a patent of the States of Holland and West-Friesland for printing and publishing maps and atlases for 15 years.
After this, he again published an Atlas Contractus with a printed index. At about the same time, he also brought out an Atlas Minor.
Nicolaes Visscher II (1649-1702)
Nicolaes Visscher II inherited the 'shop' from his father. To obtain a new privilege, he applied to the States of Holland and West-Friesland in 1682 for a patent for printing and publishing maps. This patent was granted to him the same year. He moved the firm to the Dam, but it kept the same signboard: "In de Visscher".
Around 1683, he published his first Atlas Minor with a printed index of 91 maps. In 1684, an atlas Germania Inferior appeared. Till 1697, he published another number of atlases. He used his grandfather's (Claes Jansz.) maps less often now and relied more and more on his own.
The wars waged at this time initiated the compilation of maps of the countries where the armies operated. Many war maps were included in the various editions of his Atlas Minor.
After Nicolaes's death, his wife, Elizabeth Verseyl, published all the war maps as an atlas under the title De Stoel des Oorlogs in de Wereld (The seat of war in the world).
The widow of Nicolaes Visscher II (?-1726)
His widow continued the business energetically, and by her hand, under the name of her deceased husband, numerous atlases appeared, e.g., several editions of the Atlas Minor, an Atlas Maior and De Stoel des Oorlogs. The shop enjoyed a high reputation due to the assortment's incredible variety. Not only 'Visscher' maps but also maps of other publishers were obtainable. With the death of Elizabeth Verseyl in 1726, the last descendant died of a great map- and atlas-publishing firm in Amsterdam.
Ultraiectum Dominium.
Item Number: 28220 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > The Netherlands
Utrecht by Petrus Kaerius (Pieter Van den Keere), published by Claes Jansz. Visscher.
With an inset view of the town of Utrecht.
Title: Ultraiectum Dominium.
CJVisscher excudebat, 1624.
Engraver: Petrus Kaerius (Pieter Van den Keere).
Date of the first edition: 1617 (by Petrus Kaerius).
Date of this map: 1624.
Date on map: 1624.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 370 x 480mm (14.57 x 18.9 inches).
Sheet size: 425 x 535mm (16.73 x 21.06 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original coloured, two additional vertical folds (reinforced), reinforcements at some small marginal tears.
Condition Rating: B.
Separate publication.
Rare second edition by Claes Jansz. Visscher of this highly decorative map of the Province of Utrecht.
In the Zuiderzee, a cartouche is located with a view of Utrecht (Traiectum). A shield with the coat of arms of the province of Utrecht is shown in the upper right. Below it, two upright-standing costumed figures (TRAIECTINI) are depicted. Along the bottom border are two rows of coats of arms. The left one shows the arms of the towns in the bishopric Utrecht (Utrecht, Amersfoort, Rhenen, Wijk and Montfort), and the right one shows the coats of arms of the principal vassals and allies of the bishopric Utrecht.
The map content is a reduction of the map of Utrecht by Cornelius Anthonisz. Hornhovius of 1599, now only known from a later edition by Clement de Jonghe. (Schilder)
Pieter Van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius) (1571-c.1650)
Pieter van den Keere was born in Ghent in 1571 as the son of the type-founder, Hendrik van den Keere. In 1584, he moved with his family to London for religious reasons. There, Van den Keere received training as an engraver from Jodocus Hondius, his brother-in-law. Not only the companionship with Jodocus Hondius but also the acquaintanceship with Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus), author of the text of the Germania Inferior, originates from the years of refuge in London.
Upon their settlement in Amsterdam in 1593, both Keere and Hondius embarked on a monumental project. Their collaboration resulted in the creation of a large wall map of Europe, a masterpiece that still stands as a testament to their skill and vision, dated 1595: Nova totius Europae descriptio.
In 1610, he set up a workshop in the Kalverstraat that he called ‘In den onseeckeren tijd’ (In the uncertain time). During this period, he made numerous copperplates, including maps for his Atlas of the Netherlands and the Atlas Minor published by Jodocus Hondius.
The Germania Inferior (1617) is the first original atlas of the Netherlands published in folio size. The text for the atlas, both in Dutch and in French, was written by Petrus Montanus. After 1623, Claes Jansz. Visscher bought the plates and substituted his name for Kaerius’s. In 1634, Visscher included many of these maps in his Germana Inferior.
Kaerius's fame is not only based on his atlas of the Netherlands. He is even better known as an engraver of many loose-leaf maps and as a collaborator of book publishers. His maps are found, i.e., in the Caert thresoor (Barent Langenes, 1598), Licht der Zeevaert (Blaeu, 1608), Atlas Minor (Hondius, 1628), and Caertboeck vande Midellandsche Zee (Barents, 1595).
The Visscher Family
For nearly a century, the members of the Visscher family were essential art dealers and map publishers in Amsterdam.
Claes Jansz. Visscher, or N.J. Piscator (1587-1652)
Claes Jansz. Vischer bought a house in Amsterdam, 'de gulden Bors', on the crucial Kalverstraat and changed the name into "In de Visscher"; under this title, the shop was to flourish for many years.
He was famous for his engravings and etchings of Dutch landscapes and 'historical scenes', such as sieges, battles, etc. These 'historical scenes' were considered contemporary illustrated news items, especially e.g. that of 'the Eighty Years' War'.
For the publication of his first atlas, he bought copperplates of the atlas Germania Inferior by Pieter van den Keere (1623).
In 1649, he published an atlas entitled Tabularum Geographicarum Contractarum, containing the same maps as Langenes' Caert Thresoor, for which Visscher had only new title pages engraved.
Claes Jansz. Visscher died in 1652. His wife, Neeltjen Florisdr., had already died in 1640. They had seven children, four of whom were still alive at Claes Jansz.'s death. One was Nicolaes Visscher I, who was to continue his father's business.
Nicolaes Visscher I (1618-1679)
Nicolaes Visscher I partnered with his father, continued the business, and stayed on the Kalverstraat 'in de Visscher' till his death.
In about 1657, the first edition of his Atlas Contractus Orbis Terrarum appeared.
Between 1664 and 1677, several editions of his Atlas Contractus appeared without a printed index, for these atlases had no fixed contents but were composed according to the buyer's financial leaping pole.
In May 1664, Nicolaes Visscher was admitted as a member of the Booksellers' Guild of his town. In July 1677, he was granted a patent of the States of Holland and West-Friesland for printing and publishing maps and atlases for 15 years.
After this, he again published an Atlas Contractus with a printed index. At about the same time, he also brought out an Atlas Minor.
Nicolaes Visscher II (1649-1702)
Nicolaes Visscher II inherited the 'shop' from his father. To obtain a new privilege, he applied to the States of Holland and West-Friesland in 1682 for a patent for printing and publishing maps. This patent was granted to him the same year. He moved the firm to the Dam, but it kept the same signboard: "In de Visscher".
Around 1683, he published his first Atlas Minor with a printed index of 91 maps. In 1684, an atlas Germania Inferior appeared. Till 1697, he published another number of atlases. He used his grandfather's (Claes Jansz.) maps less often now and relied more and more on his own.
The wars waged at this time initiated the compilation of maps of the countries where the armies operated. Many war maps were included in the various editions of his Atlas Minor.
After Nicolaes's death, his wife, Elizabeth Verseyl, published all the war maps as an atlas under the title De Stoel des Oorlogs in de Wereld (The seat of war in the world).
The widow of Nicolaes Visscher II (?-1726)
His widow continued the business energetically, and by her hand, under the name of her deceased husband, numerous atlases appeared, e.g., several editions of the Atlas Minor, an Atlas Maior and De Stoel des Oorlogs. The shop enjoyed a high reputation due to the assortment's incredible variety. Not only 'Visscher' maps but also maps of other publishers were obtainable. With the death of Elizabeth Verseyl in 1726, the last descendant died of a great map- and atlas-publishing firm in Amsterdam.