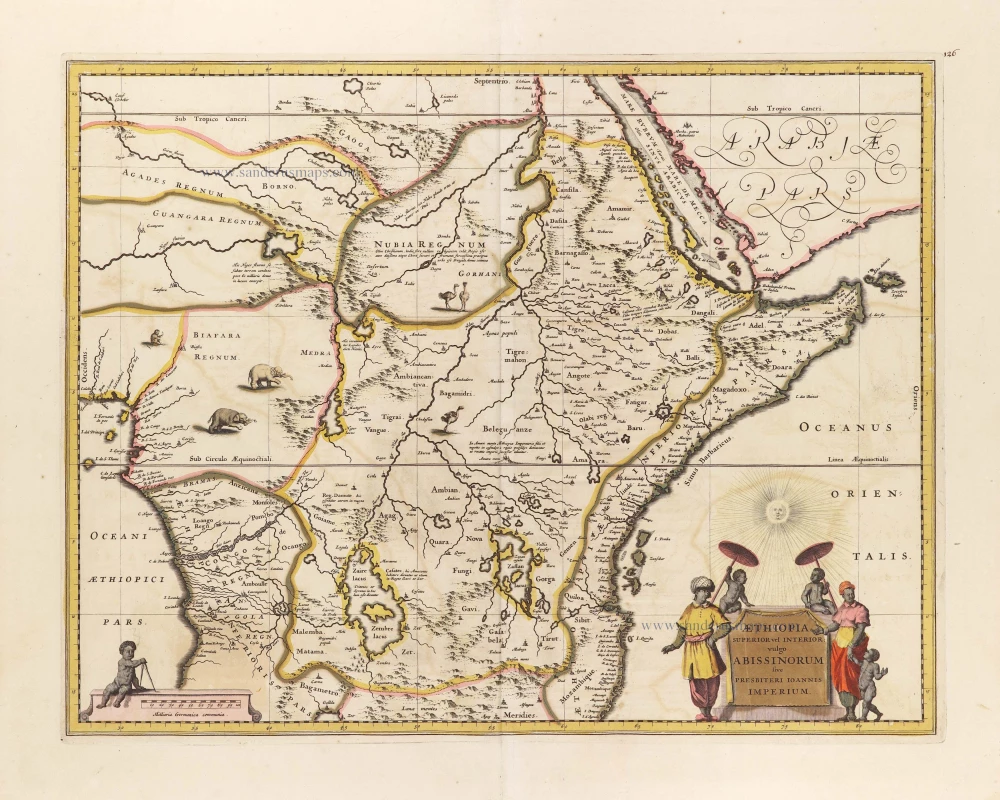
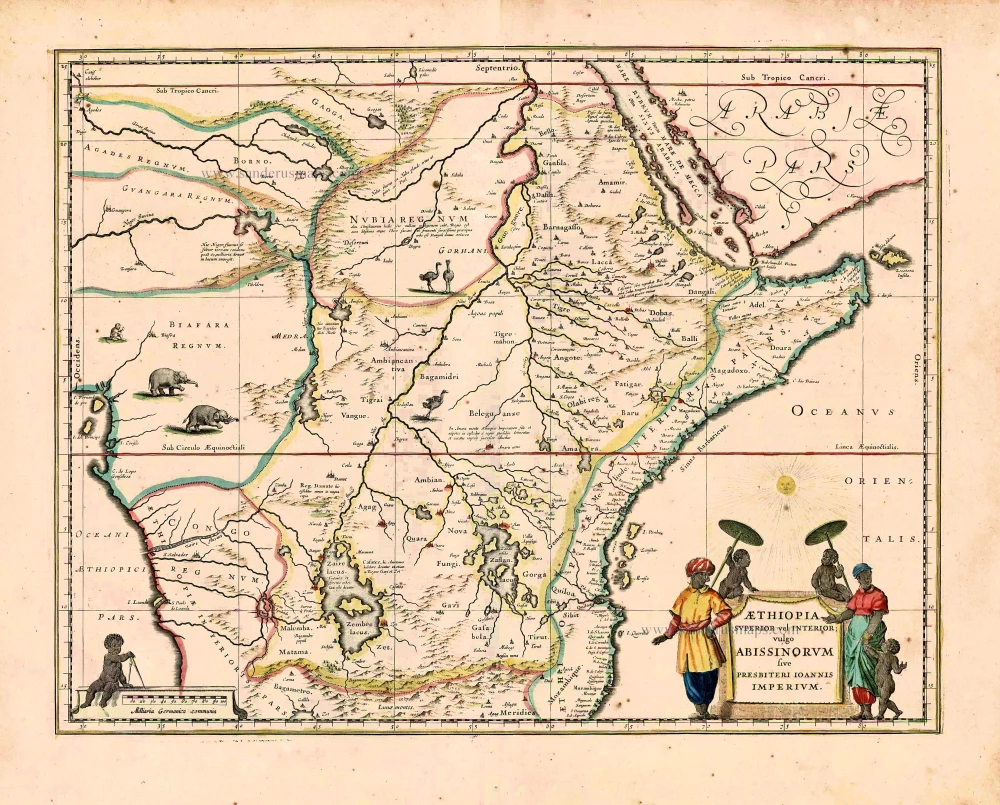
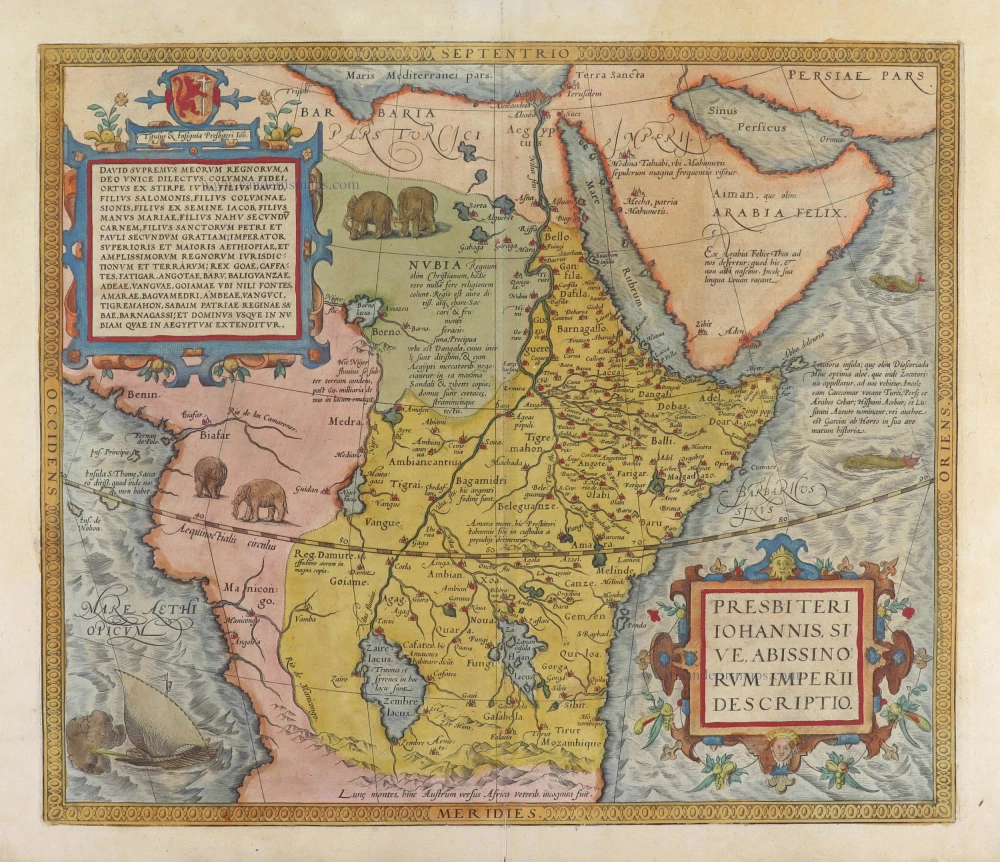
Kingdom of Prester John (Central & East Africa), by Frederick de Wit. c. 1705
Translation of cartouche text: Upper or Central Ethiopia, in the vernacular "The Empire of the Abyssinians or Prester John".
Prester John is a mythical Christian king thought to have lived in East Africa. In 1520, a sizable Portuguese expedition under Francisco Alvares travelled to East Africa, where they were received hospitably by the Coptic Christian king David II. David was considered to be Prester John's successor. Alvares described his journey after his return to Portugal. His book was the most important source of information on Ethiopia for more than a century.
Frederick de Wit (1630-1706)
The engraver and map-seller, Frederick de Wit, was born in Gouda (Netherlands) in 1630 as a son of Hendrick Fredericksz de Wit. Through his marriage with Maria van der Waag of Amsterdam in 1661, he obtained citizenship of the city where he had been working since 1648 and where he became one of the most famous engravers of maps of the second half of the 17th century. Although De Wit was a Catholic, which meant that he was not favoured at the time by the city council, he was awarded the honour of being listed as one of the "excellent citizens" on the roll of the city council in the years 1694-1704. However, his name was not written in the Guild of St. Luke book before 1664. At that time, he lived on the Kalverstraat "in de Witte Pascaert", where he stayed until his death in 1706. His earliest dates on maps engraved are 1659 (Regni Daniae) and 1660 (World map).
Frederick de Wit published several world atlases, a sea atlas, and an atlas of the Netherlands.
The dating of the maps is difficult. However, as a privilege was granted in 1689, the annotation 'cum privilegio' marks an edition after 1688.
Around 1700, Frederick de Wit entered the market with a town atlas. He produced two volumes with a total of 260 plans and views. Most were printed from plates used for Janssonius and Blaeu town atlases.
After he died in 1706, his widow continued the shop until 1709. The plates and stock of De Wit's atlas were sold to Covens & Mortier in 1710, who sold the atlas for an extended period.
Aethiopia Superior vel Interior; vulgo Abissinorum sive Presbiteri Ioannis Imperium.
Item Number: 29162 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Africa
Kingdom of Prester John (Central & East Africa), by Frederick de Wit.
Title: Aethiopia Superior vel Interior; vulgo Abissinorum sive Presbiteri Ioannis Imperium.
Date of the first edition: 1634.
Date of this map: c. 1705.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 385 x 498mm (15.16 x 19.61 inches).
Sheet size: 540 x 630mm (21.26 x 24.8 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original coloured, green colour (verdigris) turned brown.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Atlas. Amsterdam, Frederick de Wit, after 1705. (Koeman, III p. 202, Wit16; Carhart p. 159 A157)
The map is copied from Blaeu but slightly extended to the left and north, and the geography of the Congo region was changed.
Translation of cartouche text: Upper or Central Ethiopia, in the vernacular "The Empire of the Abyssinians or Prester John".
Prester John is a mythical Christian king thought to have lived in East Africa. In 1520, a sizable Portuguese expedition under Francisco Alvares travelled to East Africa, where they were received hospitably by the Coptic Christian king David II. David was considered to be Prester John's successor. Alvares described his journey after his return to Portugal. His book was the most important source of information on Ethiopia for more than a century.
Frederick de Wit (1630-1706)
The engraver and map-seller, Frederick de Wit, was born in Gouda (Netherlands) in 1630 as a son of Hendrick Fredericksz de Wit. Through his marriage with Maria van der Waag of Amsterdam in 1661, he obtained citizenship of the city where he had been working since 1648 and where he became one of the most famous engravers of maps of the second half of the 17th century. Although De Wit was a Catholic, which meant that he was not favoured at the time by the city council, he was awarded the honour of being listed as one of the "excellent citizens" on the roll of the city council in the years 1694-1704. However, his name was not written in the Guild of St. Luke book before 1664. At that time, he lived on the Kalverstraat "in de Witte Pascaert", where he stayed until his death in 1706. His earliest dates on maps engraved are 1659 (Regni Daniae) and 1660 (World map).
Frederick de Wit published several world atlases, a sea atlas, and an atlas of the Netherlands.
The dating of the maps is difficult. However, as a privilege was granted in 1689, the annotation 'cum privilegio' marks an edition after 1688.
Around 1700, Frederick de Wit entered the market with a town atlas. He produced two volumes with a total of 260 plans and views. Most were printed from plates used for Janssonius and Blaeu town atlases.
After he died in 1706, his widow continued the shop until 1709. The plates and stock of De Wit's atlas were sold to Covens & Mortier in 1710, who sold the atlas for an extended period.