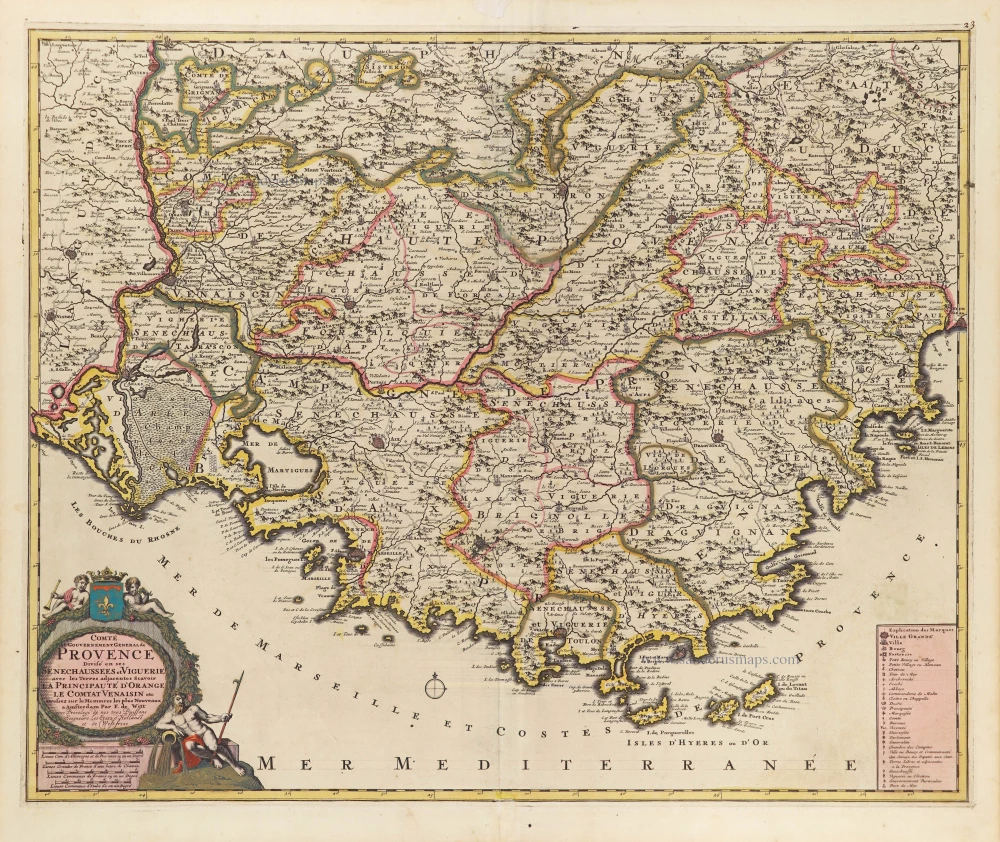
The Provence by Hubert Jaillot, after Nicolas Sanson. 1692
Alexis-Hubert JAILLOT (1632-1712)
A.-H. Jaillot first started as a sculptor. In 1664 he married Jeanne Berey, daughter of the publisher and dealer of prints Nicolas I Berey. Jaillot soon rushed into the print business due to his father-in-law's deaths in 1665 and his brother-in-law in 1667. In 1668, A.-H. Jaillot and his wife acquire the Berey fund's geographical part, which consists of globes, maps, city views and atlases. He becomes the tenant of his father-in-law's shop, Aux Deux Globes, which he buys two years later.
Jaillot enters into an agreement with Guillaume Sanson to publish his maps that will form his Atlas Nouveau's embryo. Sanson undertakes to obtain the privilege for his maps for twenty years and to cede it to Jaillot, as is the custom. Jaillot, for its part, takes care of the engraving, printing and sale of the maps. He engages engravers, François Caumartin and Louis Cordier, to engrave his maps.
A conflict arises between Jaillot and Sanson, and in 1674 it comes to a lawsuit. In 1677 they came back to an agreement.
The Atlas Nouveau first appeared in 1681 and brought great prosperity to his publisher. Jaillot owes him his title of the geographer to the king, awarded on July 20, 1686. He continues to issue maps and signs more and more himself. In 1695, he published the Atlas Français, two-thirds of which are his maps and only one third by Sanson.
A.H. Jaillot dies in 1712 and leaves a vast trading fund.
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. Still very young, he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette for the publishing of atlases. From then on, certain maps bore his name, and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. From then on, there was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Moullart-Sanson restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.
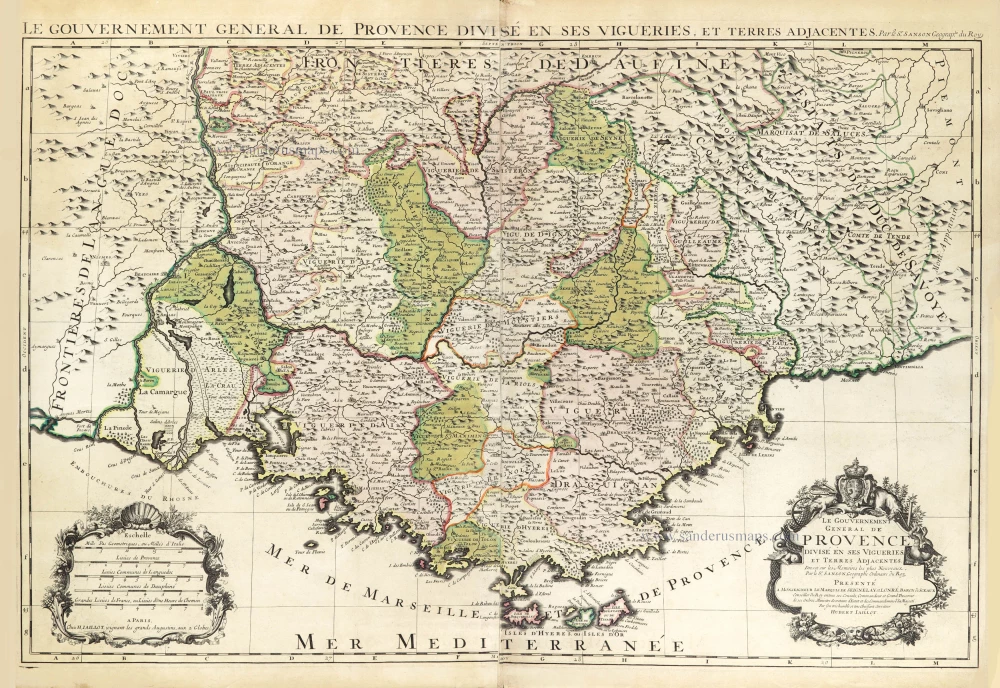
Le Gouvernement General de Provence divisé en ses Vigueries, et Terres Adjacentes.
Item Number: 30407 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > France
The Provence by Hubert Jaillot, after Nicolas Sanson.
Title: Le Gouvernement General de Provence divisé en ses Vigueries, et Terres Adjacentes.
Dressé sur les Memoires les plus Nouveaux.
Par le Sr. Sanson, Geographe Ordinaire du Roy.
A Paris, Chez H. Jaillot, joignant les grands Augustins, aux 2 Globes.
Dedicated to the Marquis de Seignelay et Lonré par Hubert Jaillot.
Cartographer: Nicolas Sanson.
Date of the first edition: 1692.
Date of this map: 1692.
Copper engraving, printed on paper from two plates, joined.
Image size: 565 x 845mm (22.24 x 33.27 inches).
Sheet size: 620 x 915mm (24.41 x 36.02 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original-coloured, age-toned.
Condition Rating: B.
From: Atlas nouveau contenant toutes les parties du monde ... Paris, 1692 (Pastoureau, Jaillot I-D) = Dutch pirated edition.
Alexis-Hubert JAILLOT (1632-1712)
A.-H. Jaillot first started as a sculptor. In 1664 he married Jeanne Berey, daughter of the publisher and dealer of prints Nicolas I Berey. Jaillot soon rushed into the print business due to his father-in-law's deaths in 1665 and his brother-in-law in 1667. In 1668, A.-H. Jaillot and his wife acquire the Berey fund's geographical part, which consists of globes, maps, city views and atlases. He becomes the tenant of his father-in-law's shop, Aux Deux Globes, which he buys two years later.
Jaillot enters into an agreement with Guillaume Sanson to publish his maps that will form his Atlas Nouveau's embryo. Sanson undertakes to obtain the privilege for his maps for twenty years and to cede it to Jaillot, as is the custom. Jaillot, for its part, takes care of the engraving, printing and sale of the maps. He engages engravers, François Caumartin and Louis Cordier, to engrave his maps.
A conflict arises between Jaillot and Sanson, and in 1674 it comes to a lawsuit. In 1677 they came back to an agreement.
The Atlas Nouveau first appeared in 1681 and brought great prosperity to his publisher. Jaillot owes him his title of the geographer to the king, awarded on July 20, 1686. He continues to issue maps and signs more and more himself. In 1695, he published the Atlas Français, two-thirds of which are his maps and only one third by Sanson.
A.H. Jaillot dies in 1712 and leaves a vast trading fund.
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. Still very young, he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette for the publishing of atlases. From then on, certain maps bore his name, and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. From then on, there was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Moullart-Sanson restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.