Tricarico by Braun G. & Hogenberg F. c. 1625
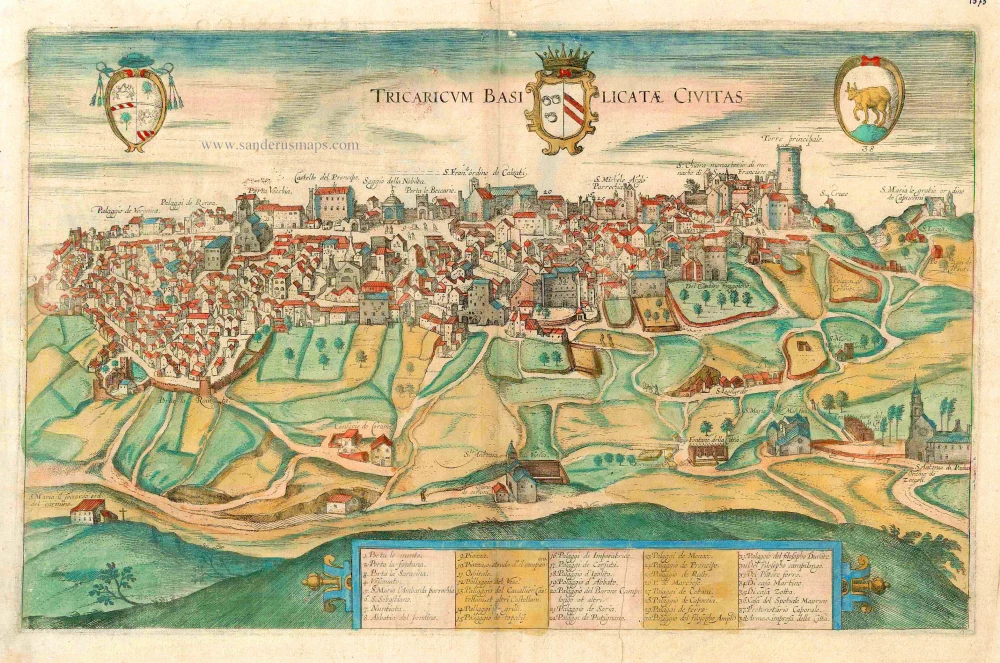
CAPTION: Tricarico, a city in the Basilicata.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The city of Tricaricolies in a territory of the Neapolitan Kingdom, which was formerly called Luciania but today Basilicata. Many say it was built out of two ruined towns, one formerly called Tricae and the other Aegie (for which reason it has kept both names). There is a bishopric here, and besides the bishop's church many splendid monasteries and churches, in which precious relics and sacred objects are kept, such as the bones of the holy Abbot Antonius, which give out a powerful light and are kept in the main church with proper reverence and respect."
This is a view from the west of the town of Tricarico, situated on the ridge of a hill. The most prominent feature is the Norman tower to the south, which today is the town's landmark. Alongside it are many noble palaces, churches and monasteries. On the left is the cathedral of Santa Maria Assunta (4), which goes back to Robert Guiscard, next to the Norman castle (Castello del Prencipe). Here, Louis I of Anjou was crowned king of Naples in 1383. There is archaeological evidence of settlements here in prehistorical and Roman times. The town was fortified in the Lombardian period, alternately a Saracen and Byzantine fortress, and in the 11th/12th centuries, it was the centre of a critical Norman county. The bishopric's founding goes back to AD 968, first as a suffragan of the Orthodox city of Hydrus (Otranto). (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.
Tricaricum Basilicatae Civitas.
Item Number: 16652 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Europe > Italy - Cities
Tricarico by Braun G. & Hogenberg F.
Title: Tricaricum Basilicatae Civitas.
Date of the first edition: 1617.
Date of this map: c. 1625.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 320 x 532mm (12.6 x 20.94 inches).
Sheet size: 410 x 540mm (16.14 x 21.26 inches).
Verso: French text.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Théatre des Principales Villes de tout l'Univers Vol. VI. c. 1625. (Van der Krogt 4, 41:3.6)
CAPTION: Tricarico, a city in the Basilicata.
COMMENTARY BY BRAUN: "The city of Tricaricolies in a territory of the Neapolitan Kingdom, which was formerly called Luciania but today Basilicata. Many say it was built out of two ruined towns, one formerly called Tricae and the other Aegie (for which reason it has kept both names). There is a bishopric here, and besides the bishop's church many splendid monasteries and churches, in which precious relics and sacred objects are kept, such as the bones of the holy Abbot Antonius, which give out a powerful light and are kept in the main church with proper reverence and respect."
This is a view from the west of the town of Tricarico, situated on the ridge of a hill. The most prominent feature is the Norman tower to the south, which today is the town's landmark. Alongside it are many noble palaces, churches and monasteries. On the left is the cathedral of Santa Maria Assunta (4), which goes back to Robert Guiscard, next to the Norman castle (Castello del Prencipe). Here, Louis I of Anjou was crowned king of Naples in 1383. There is archaeological evidence of settlements here in prehistorical and Roman times. The town was fortified in the Lombardian period, alternately a Saracen and Byzantine fortress, and in the 11th/12th centuries, it was the centre of a critical Norman county. The bishopric's founding goes back to AD 968, first as a suffragan of the Orthodox city of Hydrus (Otranto). (Taschen)
Braun G. & Hogenberg F. and the Civitates Orbis Terrarum.
The Civitates Orbis Terrarum, also known as the 'Braun & Hogenberg', is a six-volume town atlas and the most excellent book of town views and plans ever published: 363 engravings, sometimes beautifully coloured. It was one of the best-selling works in the last quarter of the 16th century. Georg Braun, a skilled writer, wrote the text accompanying the plans and views on the verso. Many plates were engraved after the original drawings of a professional artist, Joris Hoefnagel (1542-1600). The first volume was published in Latin in 1572 and the sixth in 1617. Frans Hogenberg, a talented engraver, created the tables for volumes I through IV, and Simon van den Neuwel made those for volumes V and VI. Other contributors were cartographers Daniel Freese and Heinrich Rantzau, who provided valuable geographical information. Works by Jacob van Deventer, Sebastian Münster, and Johannes Stumpf were also used as references. Translations appeared in German and French, making the atlas accessible to a wider audience.
Since its original publication of volume 1 in 1572, the Civitates Orbis Terrarum has left an indelible mark on the history of cartography. The first volume was followed by seven more editions in 1575, 1577, 1582, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1612. Vol.2, initially released in 1575, saw subsequent editions in 1597 and 1612. The subsequent volumes, each a treasure trove of historical insights, graced the world in 1581, 1588, 1593, 1599, and 1606. The German translation of the first volume, a testament to its widespread appeal, debuted in 1574, followed by the French edition in 1575.
Several printers were involved: Theodor Graminaeus, Heinrich von Aich, Gottfried von Kempen, Johannis Sinniger, Bertram Buchholtz, and Peter von Brachel, all of whom worked in Cologne.
Georg Braun (1541-1622)
Georg Braun, the author of the text accompanying the plans and views in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, was born in Cologne in 1541. After his studies in Cologne, he entered the Jesuit Order as a novice, indicating his commitment to learning and intellectual pursuits. In 1561, he obtained his bachelor's degree; in 1562, he received his Magister Artium, further demonstrating his academic achievements. Although he left the Jesuit Order, he continued his studies in theology, gaining a licentiate in theology. His theological background likely influenced the content and tone of the text in the Civitates Orbis Terrarum, adding a unique perspective to the work.
Frans Hogenberg (1535-1590)
Frans Hogenberg was a Flemish and German painter, engraver, and mapmaker. He was born in Mechelen as the son of Nicolaas Hogenberg.
By the end of the 1560s, Frans Hogenberg was employed upon Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, published in 1570; he is named an engraver of numerous maps. In 1568, he was banned from Antwerp by the Duke of Alva and travelled to London, where he stayed a few years before emigrating to Cologne. He immediately embarked on his two most important works, the Civitates, published in 1572 and the Geschichtsblätter, which appeared in several series from 1569 until about 1587.
Thanks to large-scale projects like the Geschichtsblätter and the Civitates, Hogenberg's social circumstances improved with each passing year. He died as a wealthy man in Cologne in 1590.