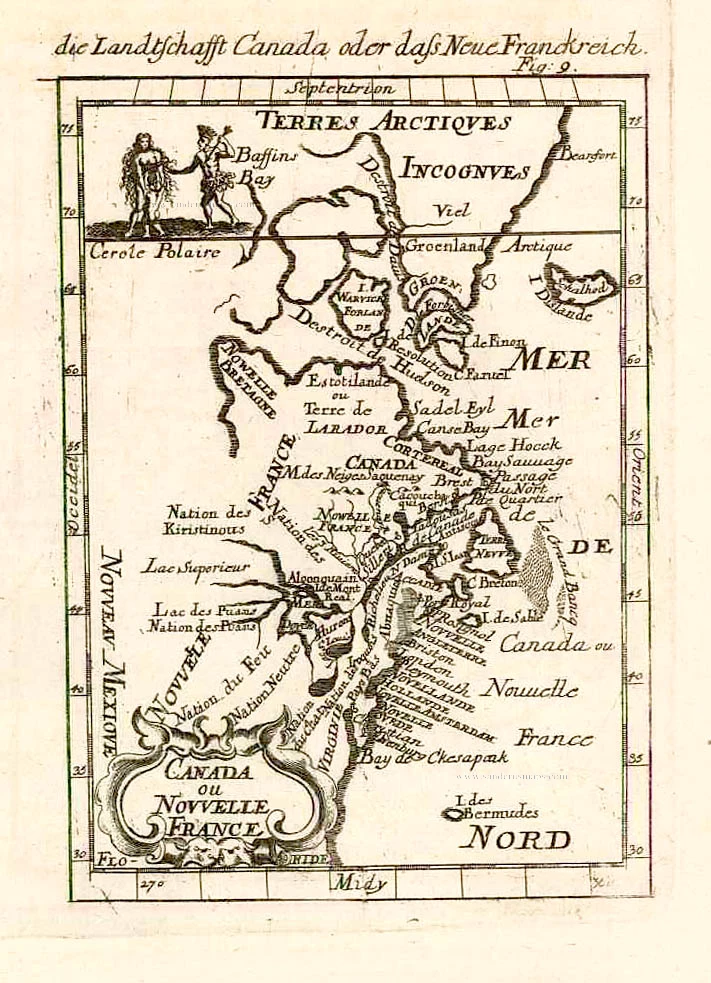
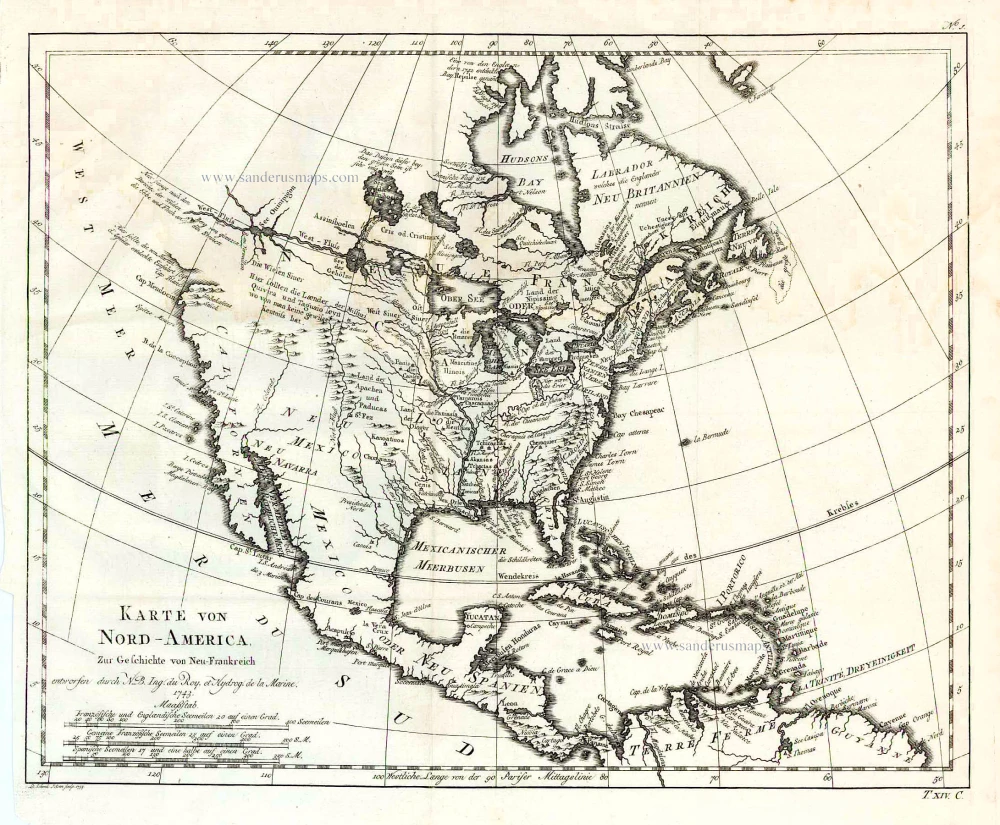
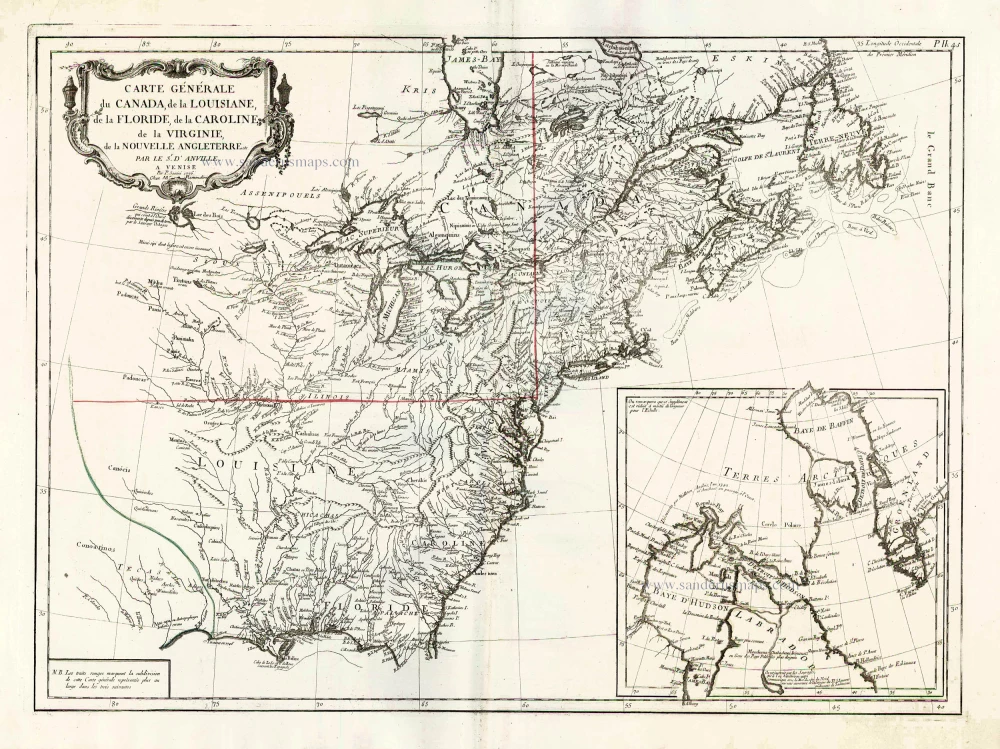
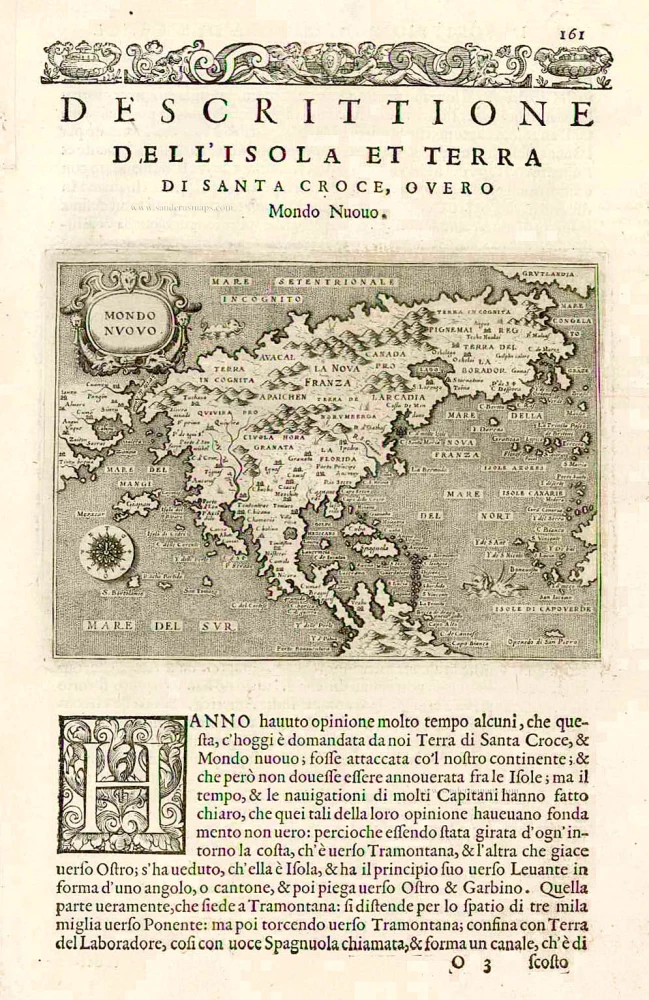
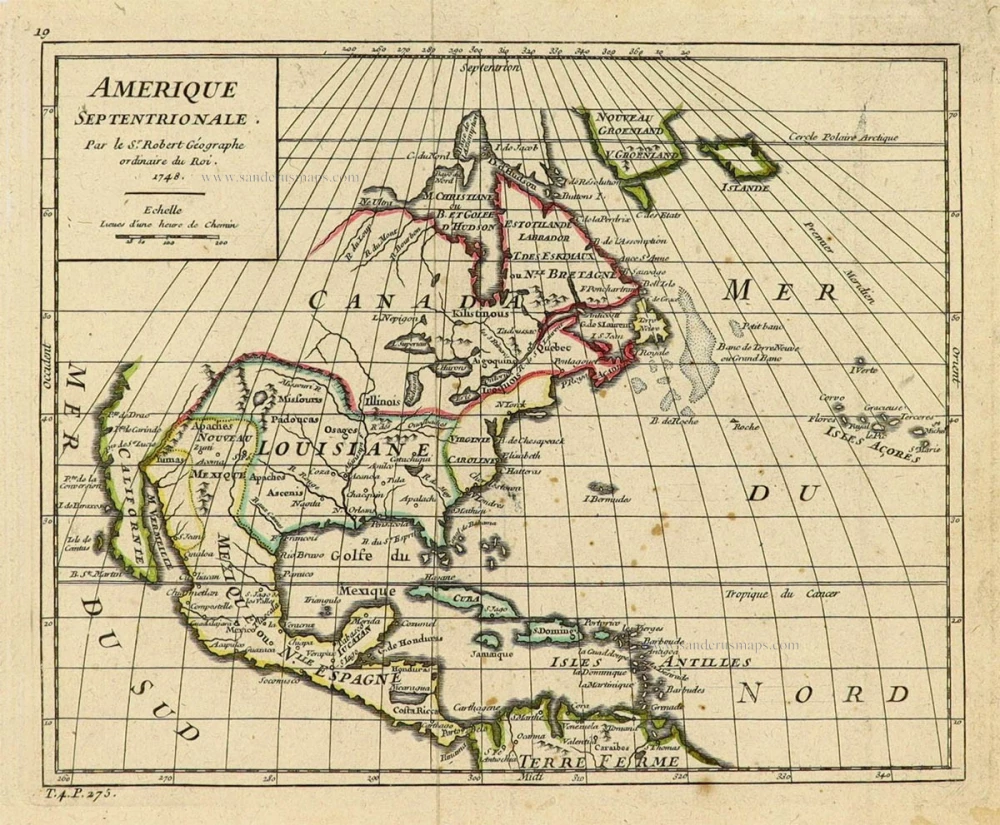
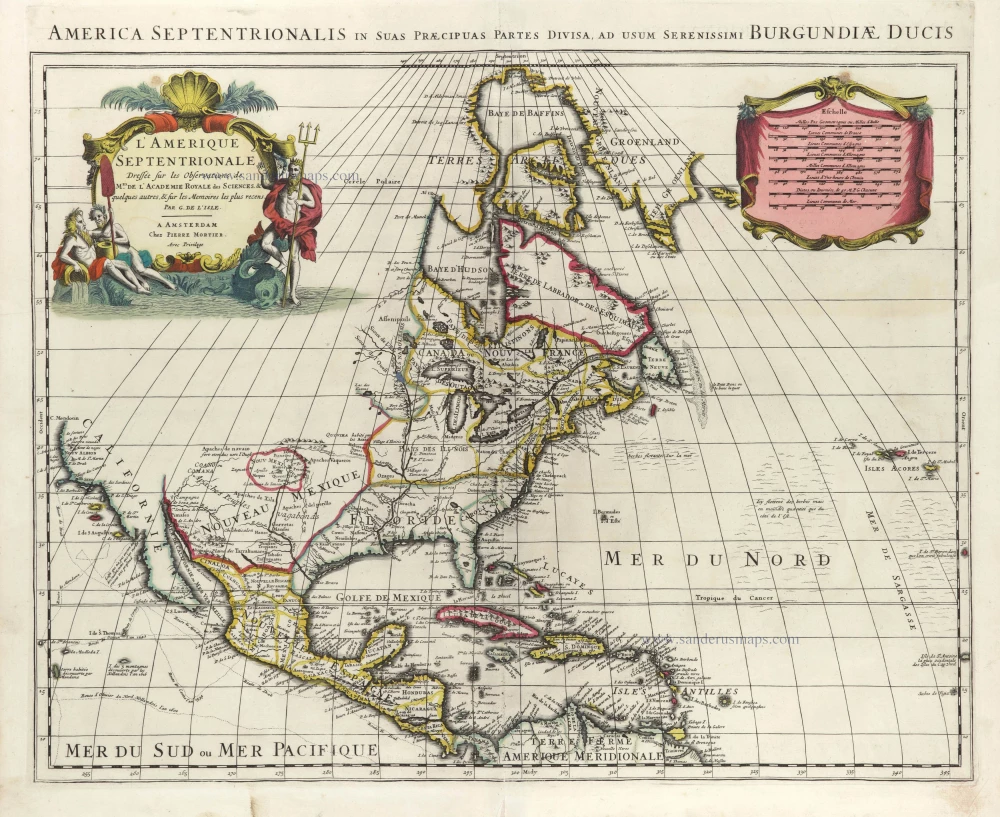
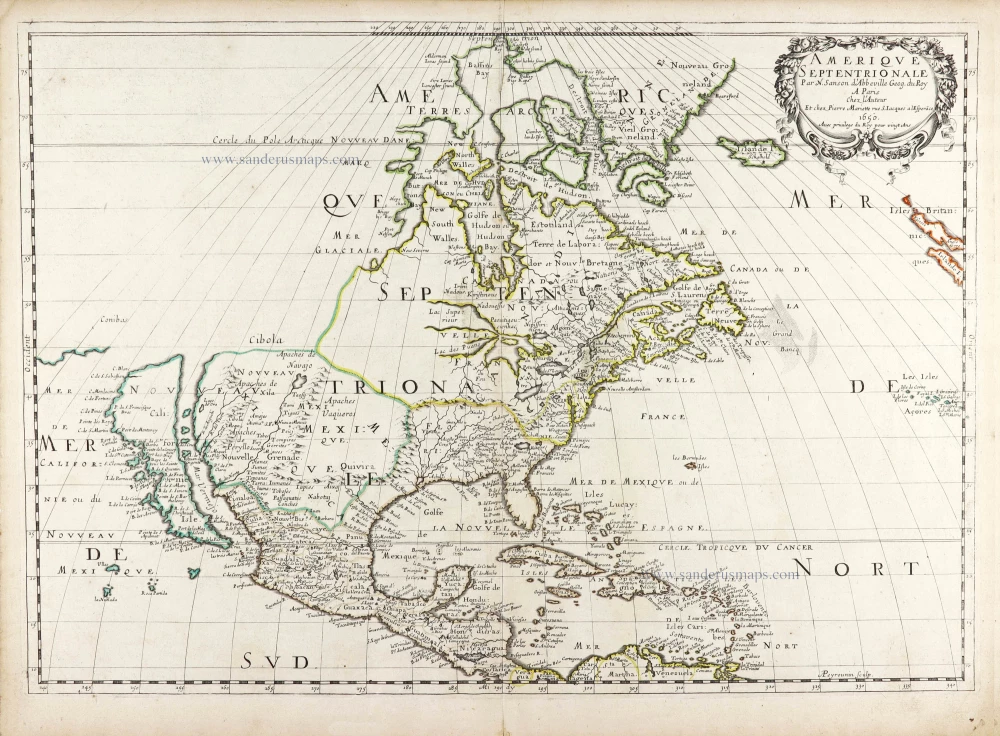
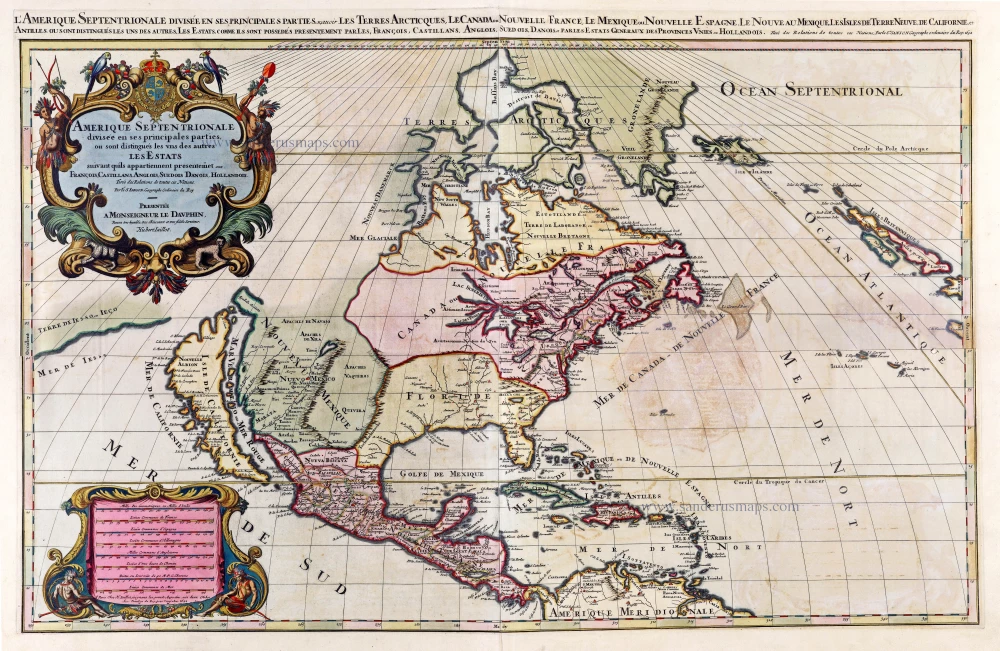
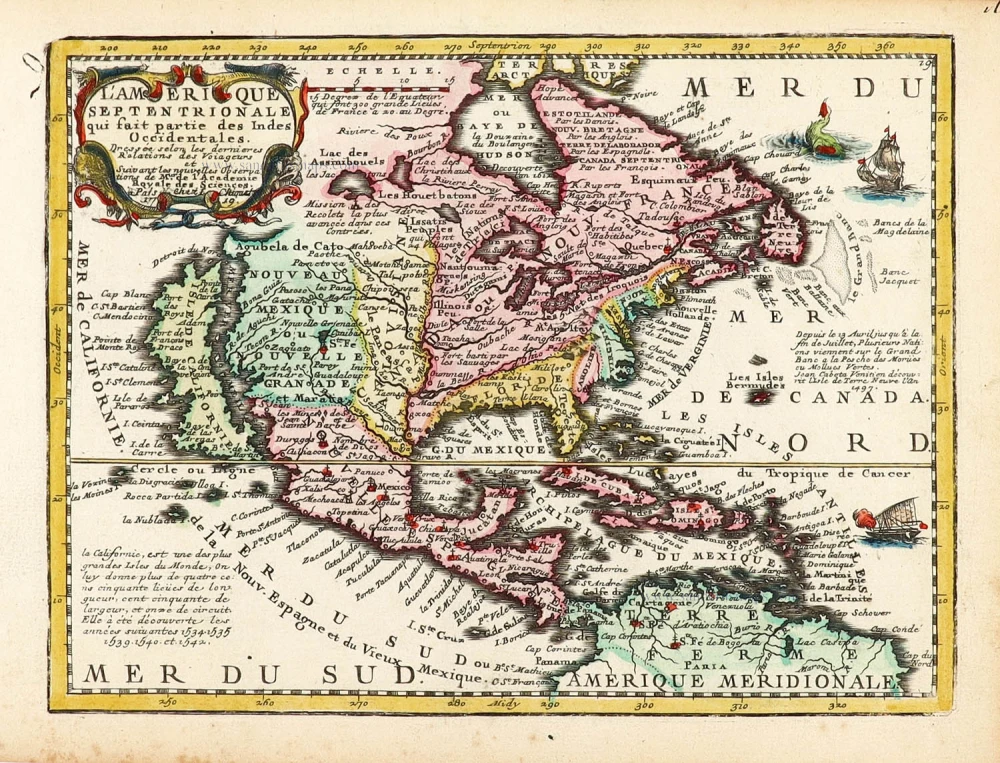
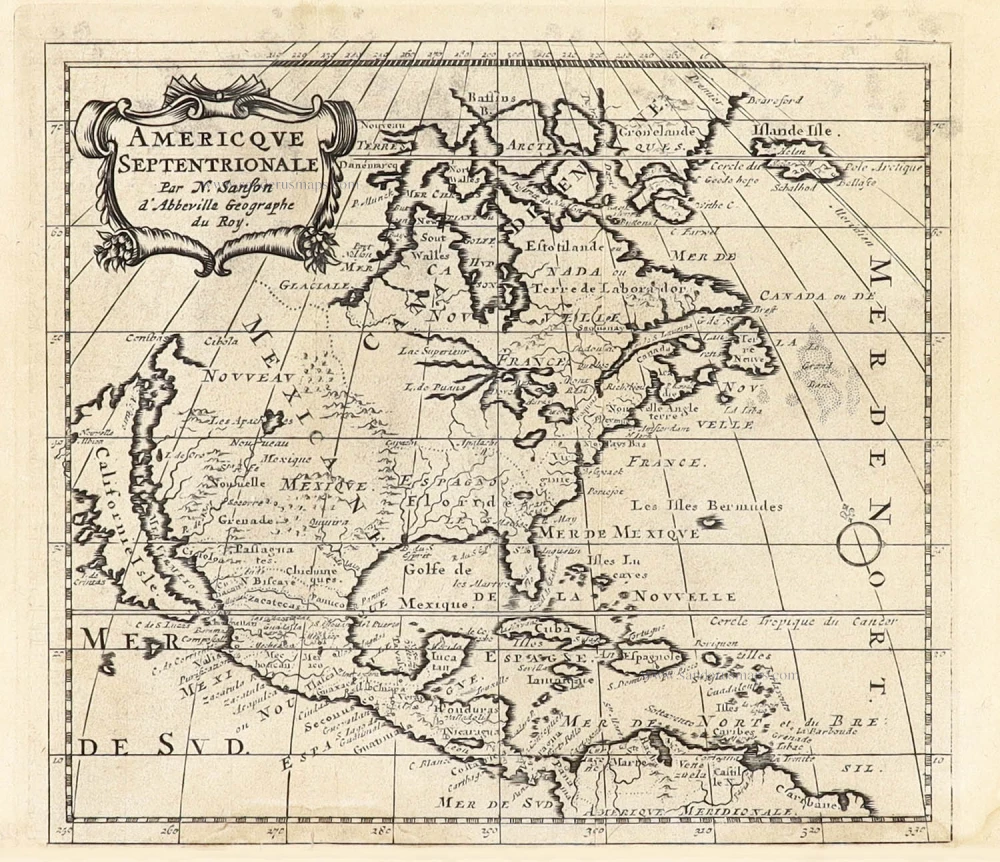
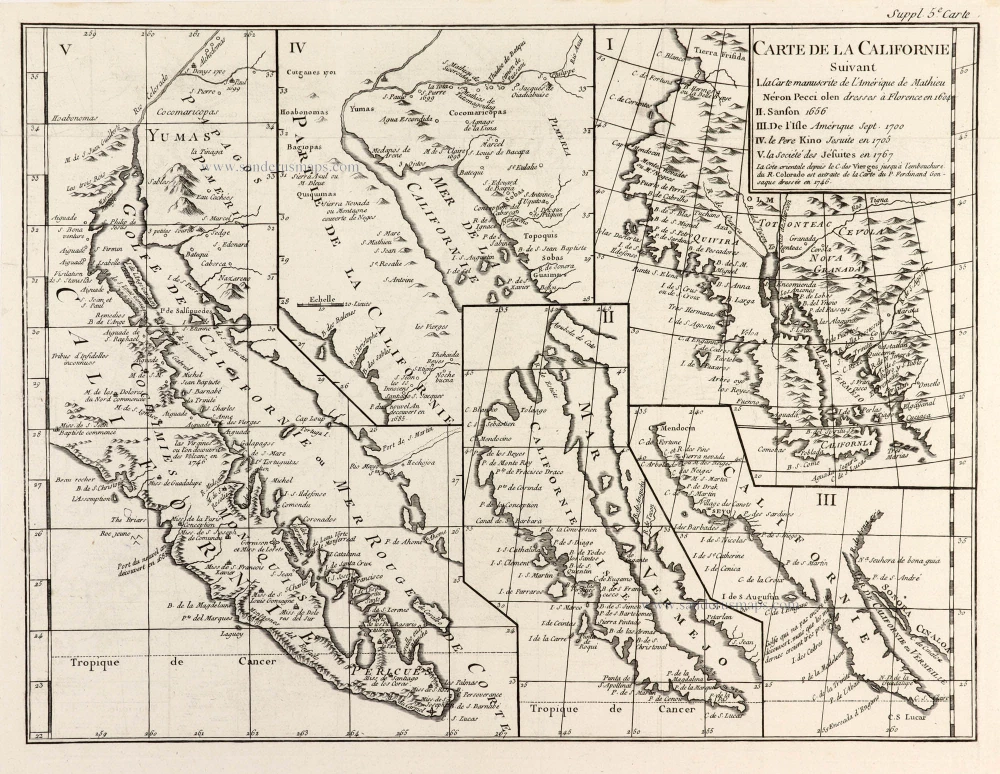
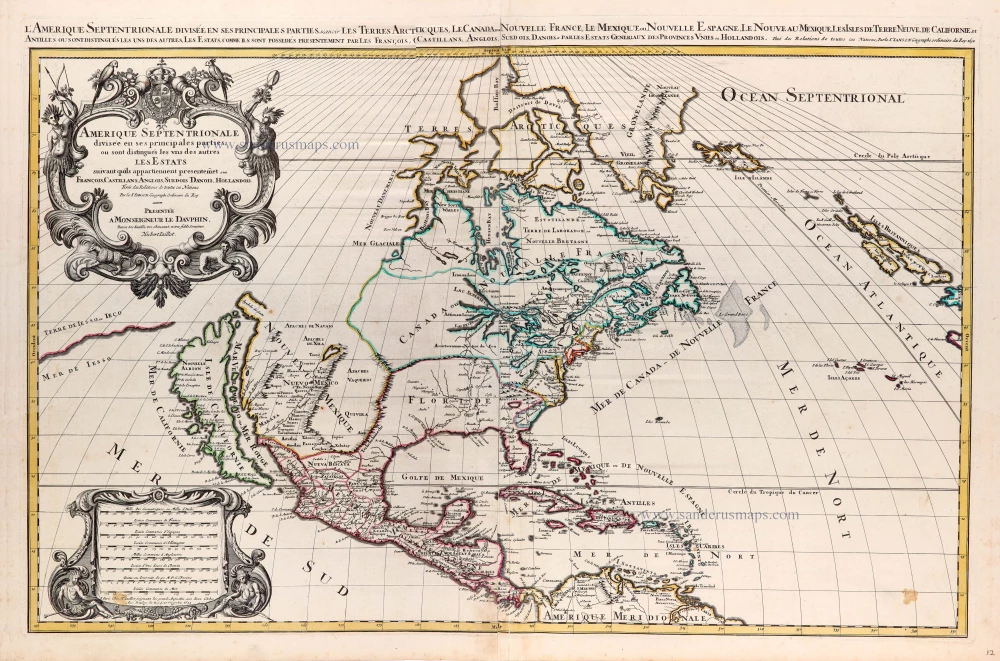
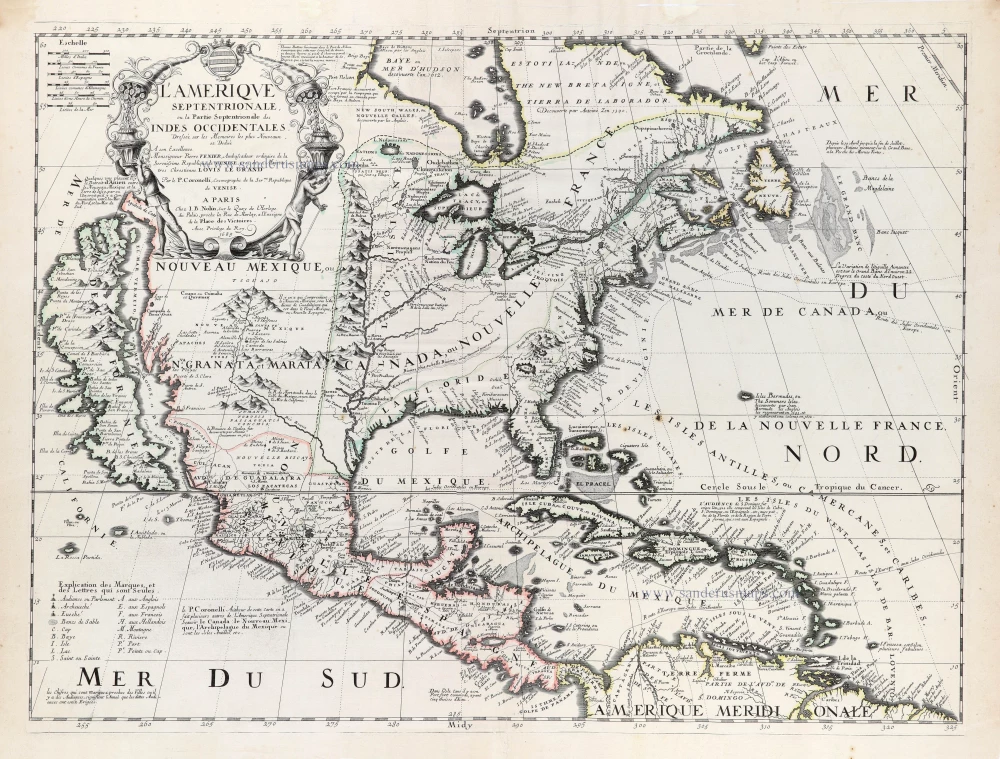
North America, by Nicolas Sanson, published by Pierre Mortier after A.H. Jaillot. 1694
The map is derived from Jaillot's large map of 1674, but most probably through Mortier's large version of it published in 1692. Jaillot published his similar-sized version, 1695, in the Atlas François.
Alexis-Hubert JAILLOT (1632-1712)
A.-H. Jaillot first started as a sculptor. In 1664 he married Jeanne Berey, daughter of the publisher and dealer of prints Nicolas I Berey. Jaillot soon rushed into the print business due to his father-in-law's deaths in 1665 and his brother-in-law in 1667. In 1668, A.-H. Jaillot and his wife acquire the Berey fund's geographical part, which consists of globes, maps, city views and atlases. He becomes the tenant of his father-in-law's shop, Aux Deux Globes, which he buys two years later.
Jaillot enters into an agreement with Guillaume Sanson to publish his maps that will form his Atlas Nouveau's embryo. Sanson undertakes to obtain the privilege for his maps for twenty years and to cede it to Jaillot, as is the custom. Jaillot, for its part, takes care of the engraving, printing and sale of the maps. He engages engravers, François Caumartin and Louis Cordier, to engrave his maps.
A conflict arises between Jaillot and Sanson, and in 1674 it comes to a lawsuit. In 1677 they came back to an agreement.
The Atlas Nouveau first appeared in 1681 and brought great prosperity to his publisher. Jaillot owes him his title of the geographer to the king, awarded on July 20, 1686. He continues to issue maps and signs more and more himself. In 1695, he published the Atlas Français, two-thirds of which are his maps and only one third by Sanson.
A.H. Jaillot dies in 1712 and leaves a vast trading fund.
SANSON FAMILY
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703) - Pierre Moullart-Sanson (? -1730)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. He was still very young; he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier, who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette to publish atlases. From then on, specific maps bore his name and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. There was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Pierre Moullart-Sanson was the son of Françoise Sanson (third child of Nicolas) and Pierre Moullart. He restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.
Covens & Mortier. A Map Publishing House in Amsterdam. 1721-1866.
During almost two centuries, the largest and most important Dutch publishing house in commercial cartography was the Amsterdam firm of Covens & Mortier. Concerning quantity, it was possibly even the biggest contemporary map-trading house worldwide. They distributed innumerable maps, atlases, globes, and books.
Pieter (Pierre) Mortier (Leiden, 1661 – Amsterdam, 1711)
Nothing is known about the youth of Pieter Mortier. He studied in Paris from 1681 to approximately 1685. There he must have come into contact with French 'libraires' and learned the bookselling trade. Beginning 1685 he returned to Amsterdam where he opened a small bookshop. In the same year, he became a member of the Book, Art Sellers' and Printers' guild.
Pieter sold books in Dutch and foreign languages, but he also published books on his own, usually in the French language. His business flourished such that in 1688 he was already forced to rent another house on the Vijgendam.
Pieter Mortier's first privilege for maps was granted by the States of Holland and West Friesland on September 15 1690. It refers to the maps of Sanson that he 'is printing and correcting with great pains and care'.
Pieter began the large scale publication of maps and atlases. By the beginning of the 18th century, Pieter had become so wealthy that he could purchase three houses in Amsterdam: on the Beurssluis, on the Vijgendam, and the Heremietensteeg. He rebuilt the house on the Vijgendam into a large prestigious house that would serve for over a century as a shop, business, and residential structure for Covens & Mortier's publishing house.
He died on February 13, 1711, after a brief illness. The company continued to exist under Pieter's widow's management, Amelia' s-Gravesande.
After she died in 1719, her son Cornelis, took over the management for a few years.
On November 20, 1721, a company was founded by Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I. The latter was married the same year with Cornelis's sister. From that year on, the name of :
Covens & Mortier.
Their firm would see a massive expansion in the next 140 years. In 1732 the heirs sold the property to their brother Cornelis and his partner Covens. Their main competitors were Reinier & Josua Ottens and Gerard Valck & Petrus Schenck. After the death of Johannes Covens I (1774), his son Johannes Covens II (1722-1794) entered the business. From 1778, Johannes added a new company name :
J. Covens & Son.
Johannes Covens II was succeeded by his son Cornelis Covens (1764-1825), who, in turn, brought Peter Mortier IV, the great-grandson of Petrus Mortier I, into the business. The name was from 1794 to 1866:
Mortier, Covens & Son.
The last Covens in the series was Cornelis Johannes Covens (1806-1880).
Covens & Mortier had a large stock of atlases and maps, including those of: Delisle, Jaillot, Johannes Janssonius, Sanson, Claes Jansz. Visscher, Nicolaas Visscher, and Frederik de Wit. For decades, an impressive number of atlases came from the press.
Amerique Septentrionale, Divisee en ses Principales Parties.
Item Number: 29125 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > America > North America
Old, antique map of North America, by Nicolas Sanson, published by Pierre Mortier after A.H. Jaillot.
Title: Amerique Septentrionale, Divisee en ses Principales Parties.
Présenté à Monseigneur le Duc de Bourgogne,
Pars Son Tres humbl: et tres obeissa: Serviteur H. Iaillot.
A Paris 1694.
Added title along map top: America Septentrionalis is suas praecipuas partes divisa, ad usum Serenissima Burgundiae Ducis.
First state (of 5).
Date of the first edition: 1694.
Date of this map: 1694.
Date on map: 1694.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Map size: 480 x 585mm (18.9 x 23.03 inches).
Sheet size: 540 x 630mm (21.26 x 24.8 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Original coloured, green colour (verdigris) turned brown.
Condition Rating: A.
From: Atlas Royal, Amsterdam, 1694.
This copy comes from a de Wit composite atlas, ca. 1705.
The map is derived from Jaillot's large map of 1674, but most probably through Mortier's large version of it published in 1692. Jaillot published his similar-sized version, 1695, in the Atlas François.
Alexis-Hubert JAILLOT (1632-1712)
A.-H. Jaillot first started as a sculptor. In 1664 he married Jeanne Berey, daughter of the publisher and dealer of prints Nicolas I Berey. Jaillot soon rushed into the print business due to his father-in-law's deaths in 1665 and his brother-in-law in 1667. In 1668, A.-H. Jaillot and his wife acquire the Berey fund's geographical part, which consists of globes, maps, city views and atlases. He becomes the tenant of his father-in-law's shop, Aux Deux Globes, which he buys two years later.
Jaillot enters into an agreement with Guillaume Sanson to publish his maps that will form his Atlas Nouveau's embryo. Sanson undertakes to obtain the privilege for his maps for twenty years and to cede it to Jaillot, as is the custom. Jaillot, for its part, takes care of the engraving, printing and sale of the maps. He engages engravers, François Caumartin and Louis Cordier, to engrave his maps.
A conflict arises between Jaillot and Sanson, and in 1674 it comes to a lawsuit. In 1677 they came back to an agreement.
The Atlas Nouveau first appeared in 1681 and brought great prosperity to his publisher. Jaillot owes him his title of the geographer to the king, awarded on July 20, 1686. He continues to issue maps and signs more and more himself. In 1695, he published the Atlas Français, two-thirds of which are his maps and only one third by Sanson.
A.H. Jaillot dies in 1712 and leaves a vast trading fund.
SANSON FAMILY
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703) - Pierre Moullart-Sanson (? -1730)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. He was still very young; he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier, who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette to publish atlases. From then on, specific maps bore his name and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. There was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Pierre Moullart-Sanson was the son of Françoise Sanson (third child of Nicolas) and Pierre Moullart. He restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.
Covens & Mortier. A Map Publishing House in Amsterdam. 1721-1866.
During almost two centuries, the largest and most important Dutch publishing house in commercial cartography was the Amsterdam firm of Covens & Mortier. Concerning quantity, it was possibly even the biggest contemporary map-trading house worldwide. They distributed innumerable maps, atlases, globes, and books.
Pieter (Pierre) Mortier (Leiden, 1661 – Amsterdam, 1711)
Nothing is known about the youth of Pieter Mortier. He studied in Paris from 1681 to approximately 1685. There he must have come into contact with French 'libraires' and learned the bookselling trade. Beginning 1685 he returned to Amsterdam where he opened a small bookshop. In the same year, he became a member of the Book, Art Sellers' and Printers' guild.
Pieter sold books in Dutch and foreign languages, but he also published books on his own, usually in the French language. His business flourished such that in 1688 he was already forced to rent another house on the Vijgendam.
Pieter Mortier's first privilege for maps was granted by the States of Holland and West Friesland on September 15 1690. It refers to the maps of Sanson that he 'is printing and correcting with great pains and care'.
Pieter began the large scale publication of maps and atlases. By the beginning of the 18th century, Pieter had become so wealthy that he could purchase three houses in Amsterdam: on the Beurssluis, on the Vijgendam, and the Heremietensteeg. He rebuilt the house on the Vijgendam into a large prestigious house that would serve for over a century as a shop, business, and residential structure for Covens & Mortier's publishing house.
He died on February 13, 1711, after a brief illness. The company continued to exist under Pieter's widow's management, Amelia' s-Gravesande.
After she died in 1719, her son Cornelis, took over the management for a few years.
On November 20, 1721, a company was founded by Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I. The latter was married the same year with Cornelis's sister. From that year on, the name of :
Covens & Mortier.
Their firm would see a massive expansion in the next 140 years. In 1732 the heirs sold the property to their brother Cornelis and his partner Covens. Their main competitors were Reinier & Josua Ottens and Gerard Valck & Petrus Schenck. After the death of Johannes Covens I (1774), his son Johannes Covens II (1722-1794) entered the business. From 1778, Johannes added a new company name :
J. Covens & Son.
Johannes Covens II was succeeded by his son Cornelis Covens (1764-1825), who, in turn, brought Peter Mortier IV, the great-grandson of Petrus Mortier I, into the business. The name was from 1794 to 1866:
Mortier, Covens & Son.
The last Covens in the series was Cornelis Johannes Covens (1806-1880).
Covens & Mortier had a large stock of atlases and maps, including those of: Delisle, Jaillot, Johannes Janssonius, Sanson, Claes Jansz. Visscher, Nicolaas Visscher, and Frederik de Wit. For decades, an impressive number of atlases came from the press.