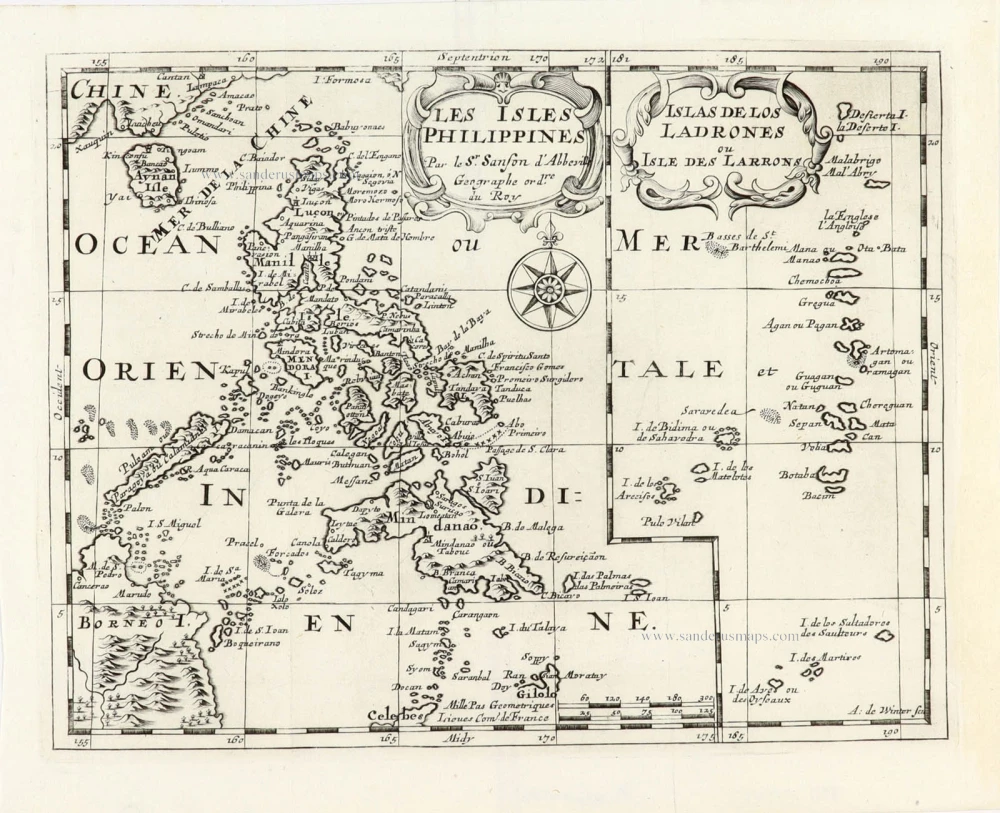
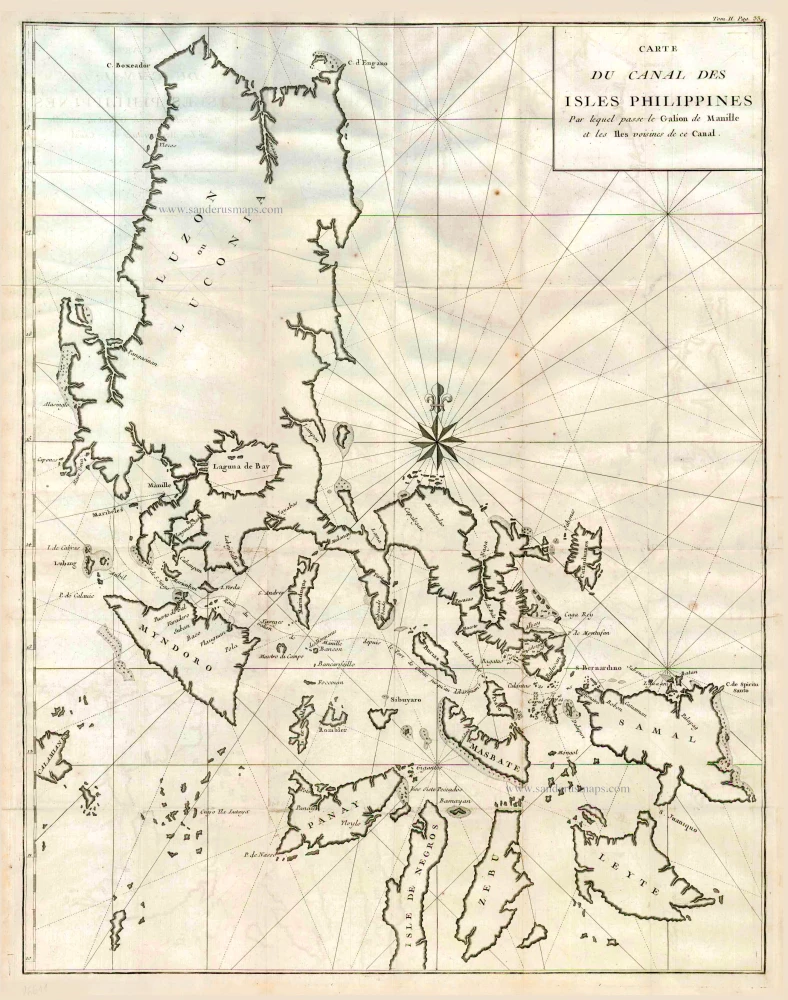
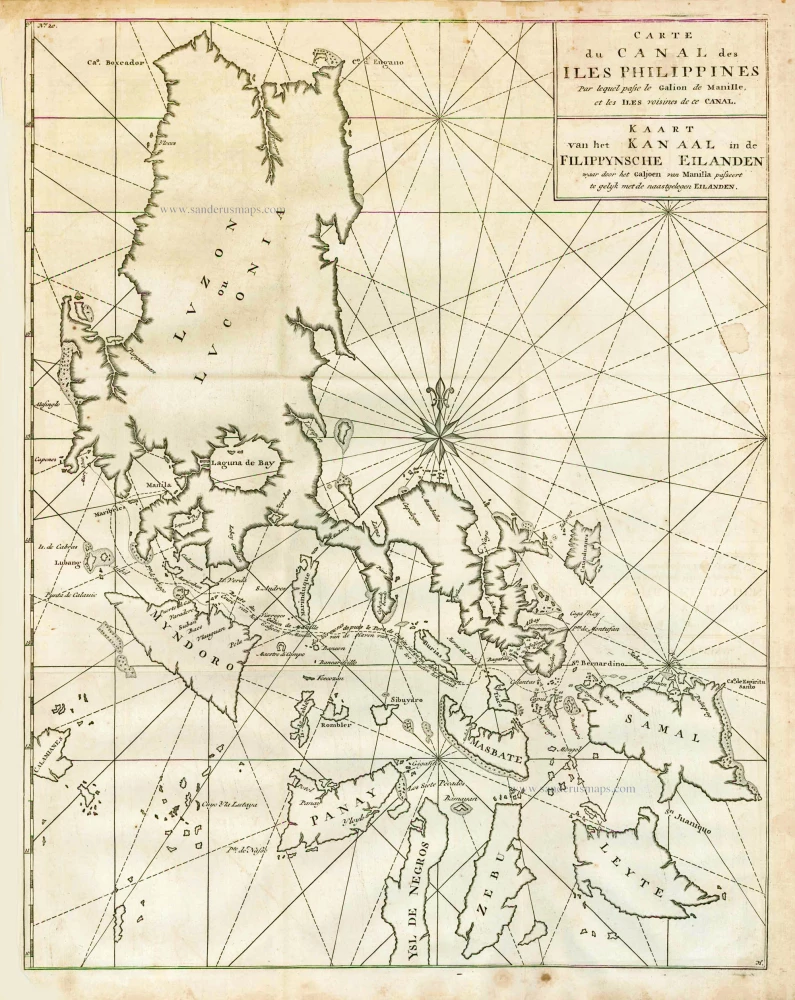
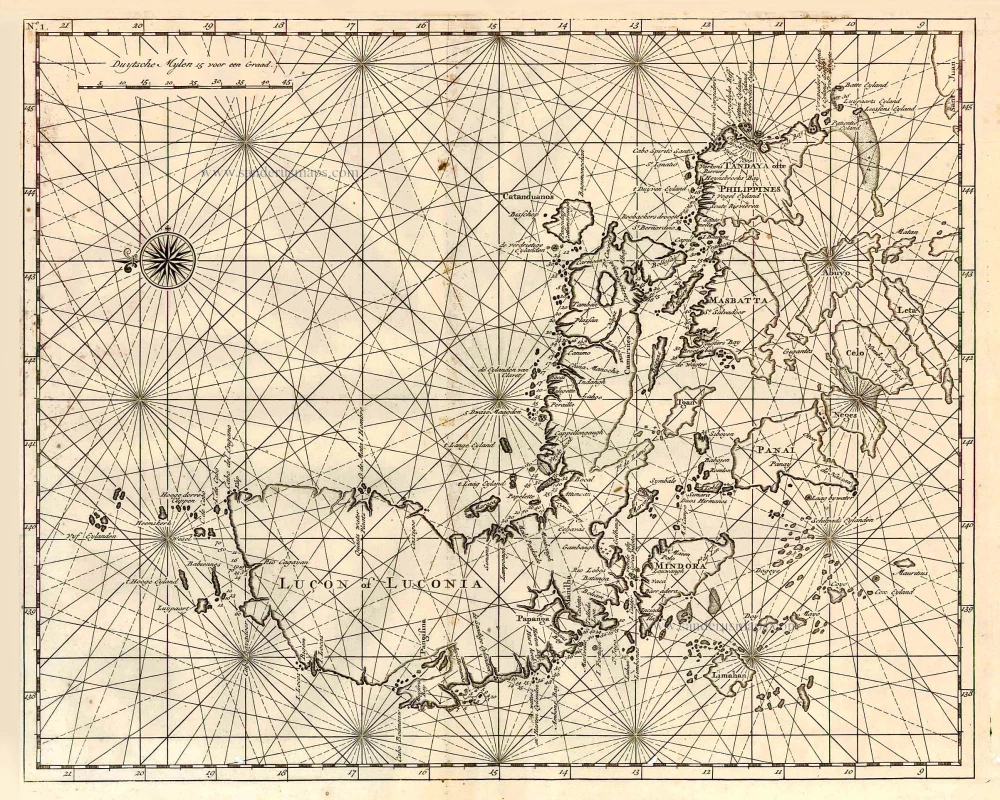
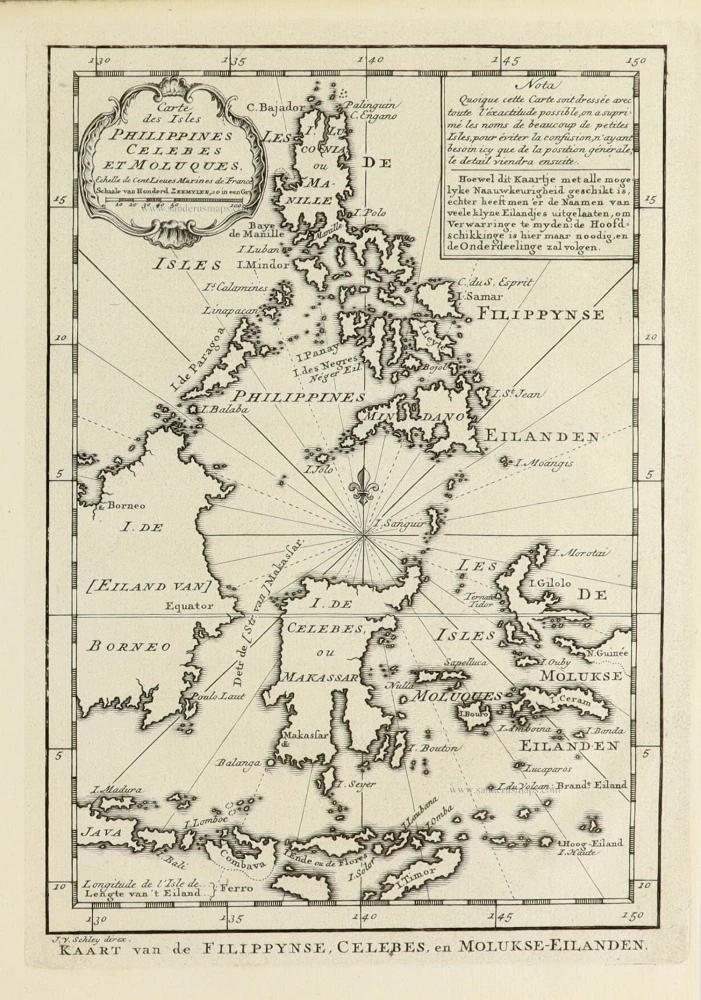
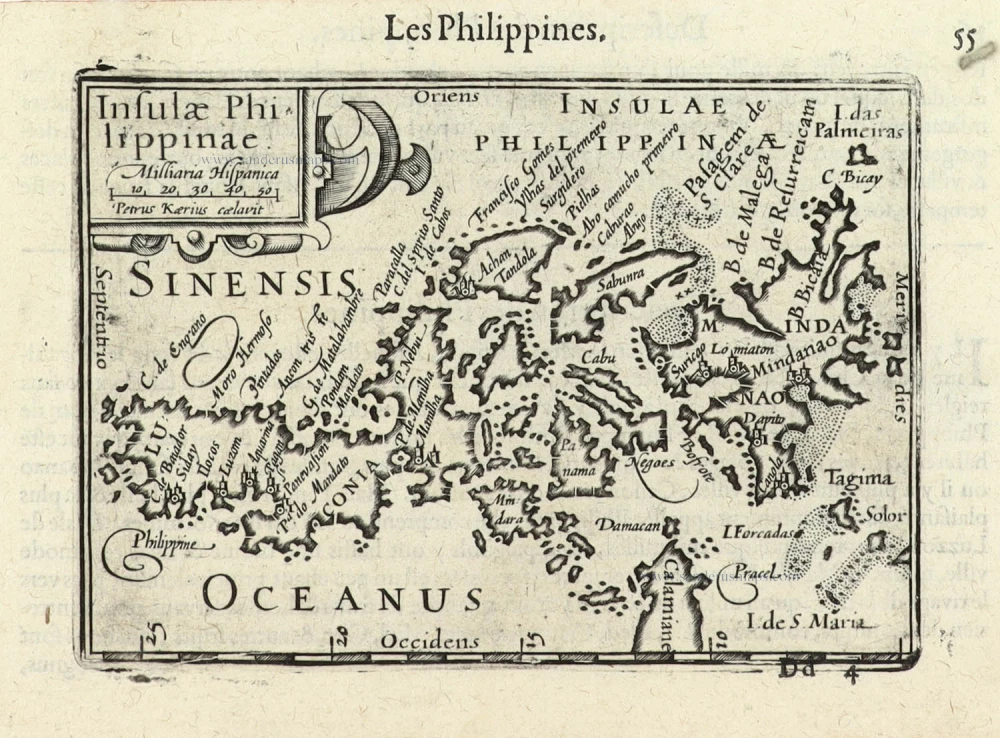
Philippines, by Nicolas Sanson, published by Prevost d'Exiles. 1747-74
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. Still very young, he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette for the publishing of atlases. From then on, certain maps bore his name, and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. From then on, there was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Moullart-Sanson restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.
Antoine François Prévost (l'abbé)
Antoine François Prévost (1697–1763), also known as Abbé Prévost, was a French writer, historian, and traveller, best remembered for his literary works, particularly Manon Lescaut. However, beyond his contributions to literature, Prévost also played a notable role in disseminating geographical and cartographical knowledge during the 18th century.
Prévost demonstrated a keen interest in geography and exploration, which was reflected in his ambitious historical and travel writings. One of his most significant contributions to the field of cartography came through his monumental work "Histoire générale des voyages", published between 1746 and 1759. This multi-volume series compiled detailed narratives of travels and discoveries from various parts of the world, accompanied by maps and illustrations.
Though Prévost was not a cartographer by profession, his work was instrumental in popularising geographical knowledge in Enlightenment Europe. The maps included in Histoire générale des voyages were often created by prominent contemporary cartographers and engravers, providing readers with visual representations of remote and little-known regions. Through these collaborations, Prévost helped disseminate some of the era’s most critical cartographical works to a broader, non-specialist audience.
His writings, along with the associated maps, made a significant contribution to the European understanding of global geography, colonial territories, and navigation routes during a period of rapid maritime exploration and expansion. Prévost's work stands as a testament to the interconnection between literature, travel writing, and cartography in the Enlightenment period.
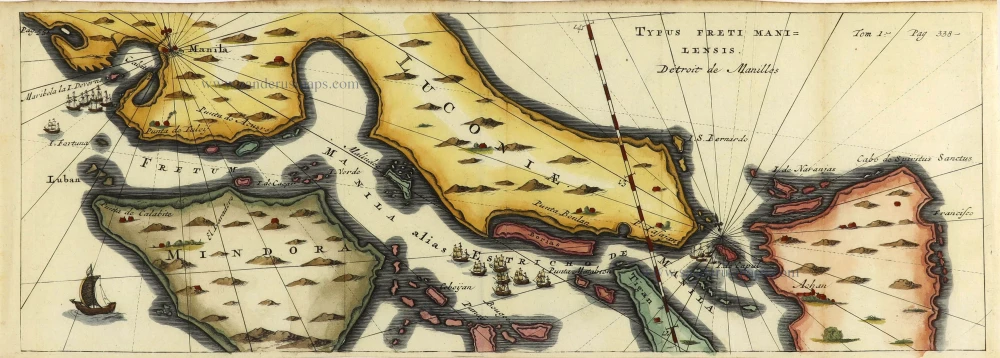
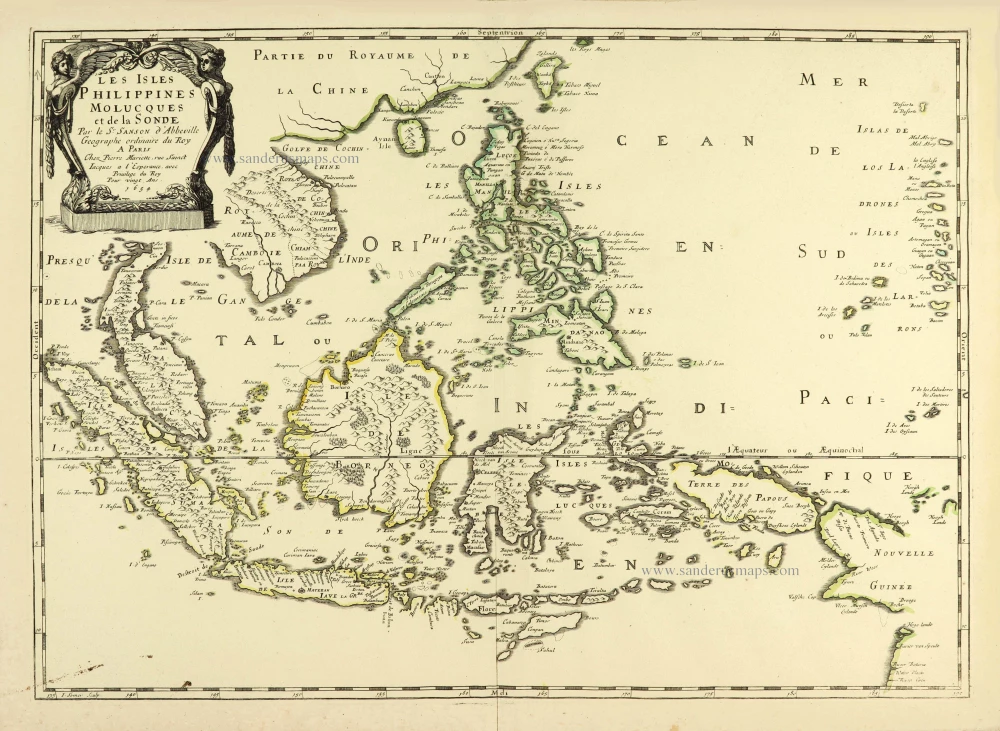
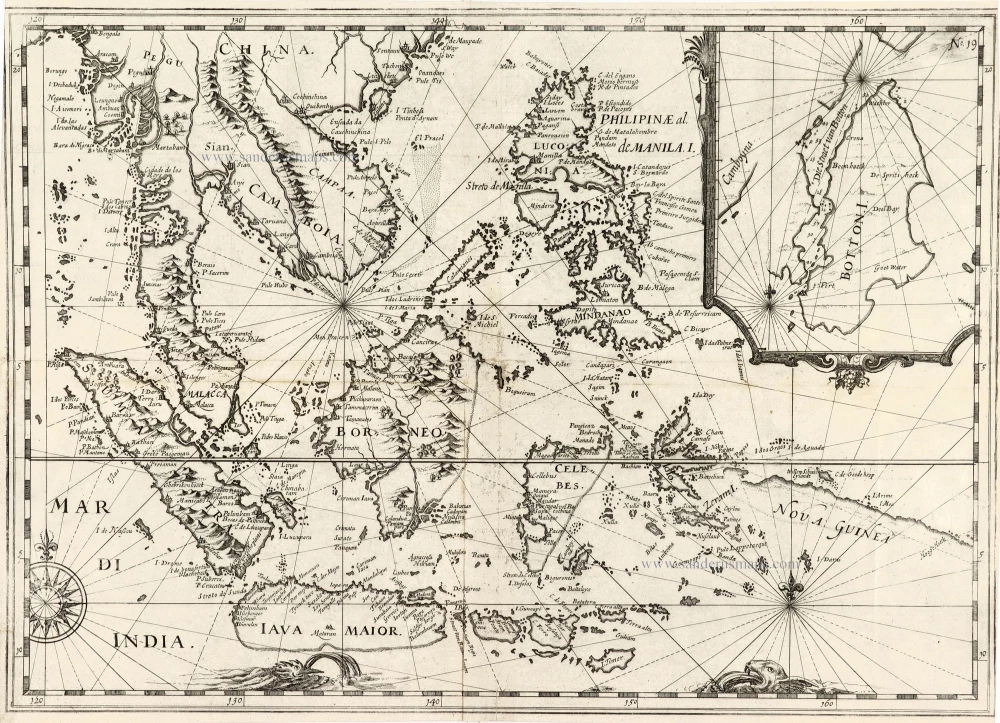
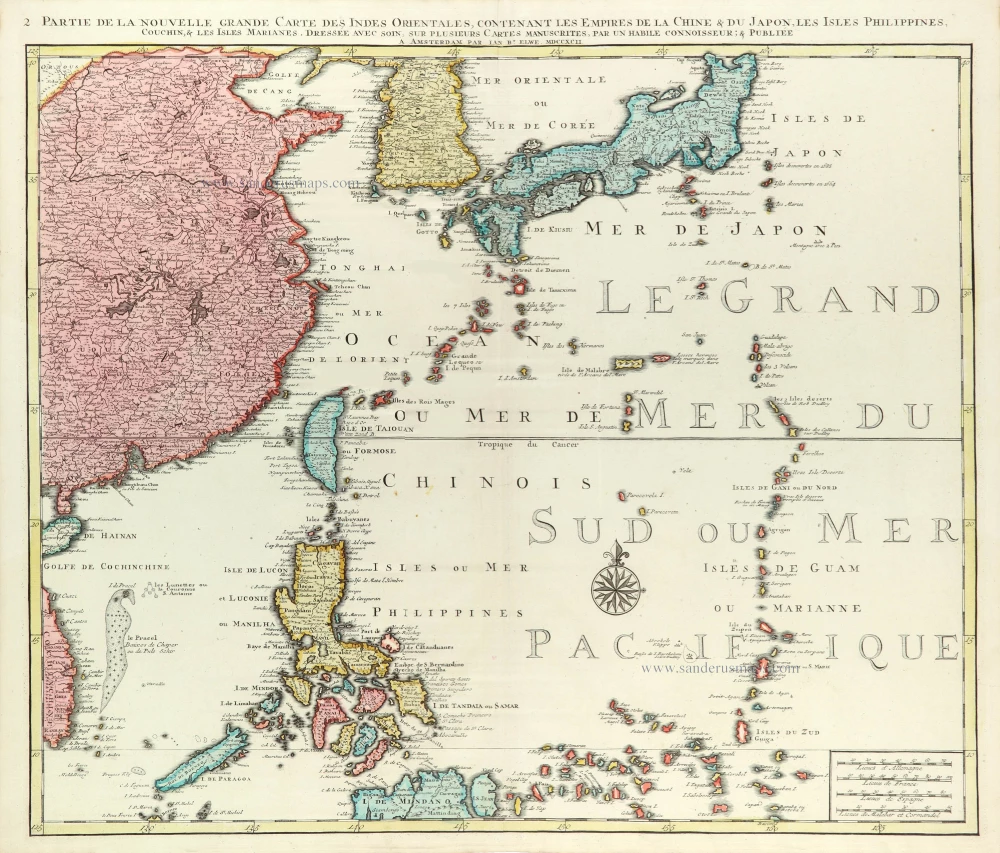
Les Isles Philippines [on sheet with] Islas de los Ladrones ou Isle des Larrons.
Item Number: 30304 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > Asia > Southeast Asia
Philippines, by Nicolas Sanson, published by Prevost d'Exiles.
Title: Les Isles Philippines [on sheet with] Islas de los Ladrones ou Isle des Larrons.
Par le Sr. Sanson d'Abbeville Geographe ord.re du Roy.
A. de Winter scu.
Cartographer: Nicolas Sanson.
Engraver: Anthoine de Winter.
Date of the first edition: 1652.
Date of this map: 1747-74.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 190 x 245mm (7.48 x 9.65 inches).
Sheet size: 220 x 270mm (8.66 x 10.63 inches).
Verso: Blank.
Condition: Excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Prevost d'Exiles. Allgemeine Historie der Reisen zu Wasser und Lande; oder Sammlung aller Reisebeschreibungen, welche bis itzo in verschiedene Sprachen von allen Völkern herausgegeben worden, ... Leipzig, Arkstee und Merkus, 1747-74.
Nicolas Sanson (1600-1667) - Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703)
Originally from Abbeville, Nicolas I Sanson showed a keen interest in historical geography. Still very young, he published a map of ancient Gaul and two treatises, Britannia and Portus Itius on Abbeville and Boulogne's origins. His meeting with Melchior Tavernier was decisive: it prompted him to give up his duties as a military engineer in Picardy and devote himself to engraved cartography.
At the same time, Sanson had drawn up the outline of modern France. He got the help of Tavernier who encouraged him to compete with the Dutch map publishers. Tavernier contacted other French cartographers whose works he published.
From 1643, N. Sanson obtained a privilege to publish a work personally, the Princes souverains de l'Italie. Then, in 1644 and 1645, he had his famous geographical tables printed, which significantly contributed to his fame. He also published a series of atlases in quarto of the four continents.
In 1648, N. Sanson associated himself with Mariette for the publishing of atlases. From then on, certain maps bore his name, and others Mariette's. N. Sanson and Mariette worked together for more than 20 years. After the death of N. Sanson, Mariette acquired the entire fund. Since Mariette only wanted to publish complete atlases, individual maps were no longer sold, and some army generals complained to the king.
The disagreement between the Sanson family and Pierre II Mariette culminated in 1671 when Guillaume Sanson took the case to court. From then on, there was no longer any question of collaboration: Guillaume Sanson started working for another publisher, Alexis-Hubert Jaillot.
The Sanson family faced financial difficulties, and in 1692, their cousin, Pierre Moullart-Sanson, bought the entire geographic fund from his uncles and aunt. Moullart-Sanson restarted the publishing of Sanson's world atlas, and in 1704 he acquired a privilege for publishing all the works of Nicolas and Guillaume Sanson, which continued to be published until 1730.
Antoine François Prévost (l'abbé)
Antoine François Prévost (1697–1763), also known as Abbé Prévost, was a French writer, historian, and traveller, best remembered for his literary works, particularly Manon Lescaut. However, beyond his contributions to literature, Prévost also played a notable role in disseminating geographical and cartographical knowledge during the 18th century.
Prévost demonstrated a keen interest in geography and exploration, which was reflected in his ambitious historical and travel writings. One of his most significant contributions to the field of cartography came through his monumental work "Histoire générale des voyages", published between 1746 and 1759. This multi-volume series compiled detailed narratives of travels and discoveries from various parts of the world, accompanied by maps and illustrations.
Though Prévost was not a cartographer by profession, his work was instrumental in popularising geographical knowledge in Enlightenment Europe. The maps included in Histoire générale des voyages were often created by prominent contemporary cartographers and engravers, providing readers with visual representations of remote and little-known regions. Through these collaborations, Prévost helped disseminate some of the era’s most critical cartographical works to a broader, non-specialist audience.
His writings, along with the associated maps, made a significant contribution to the European understanding of global geography, colonial territories, and navigation routes during a period of rapid maritime exploration and expansion. Prévost's work stands as a testament to the interconnection between literature, travel writing, and cartography in the Enlightenment period.