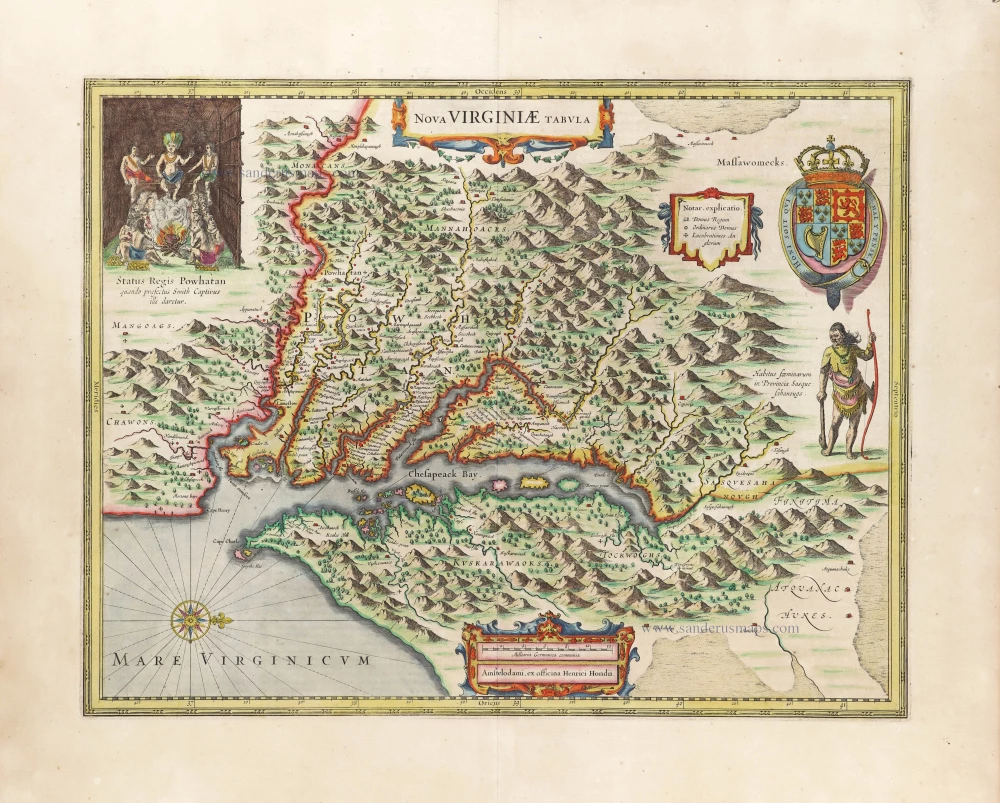
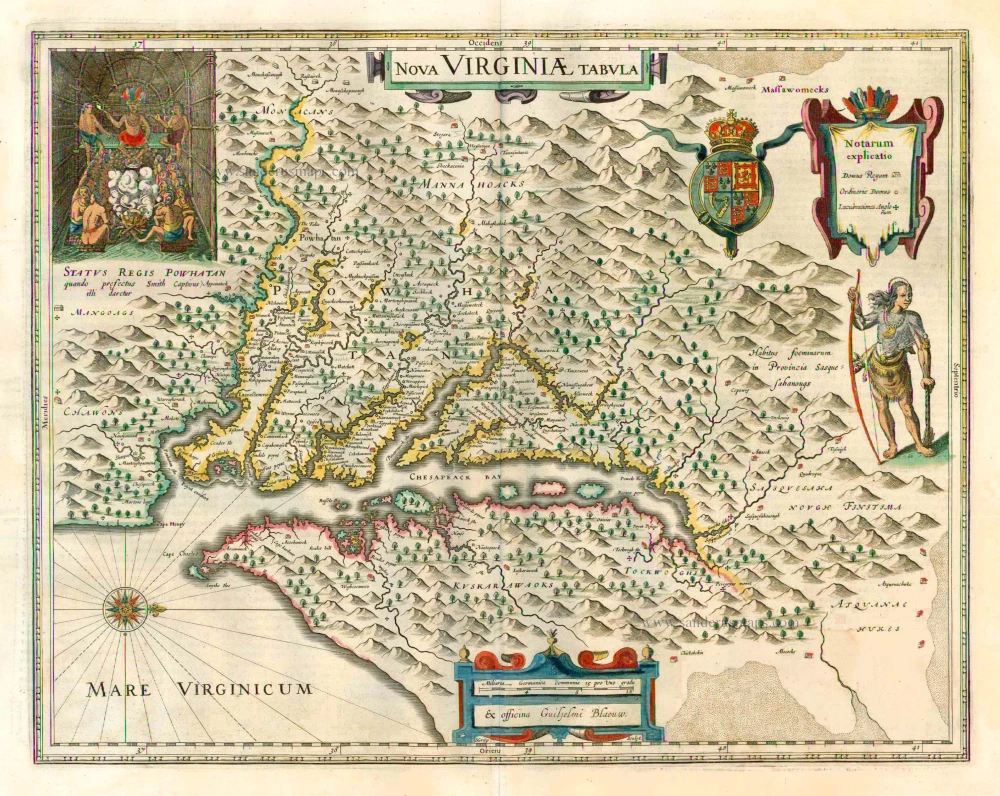
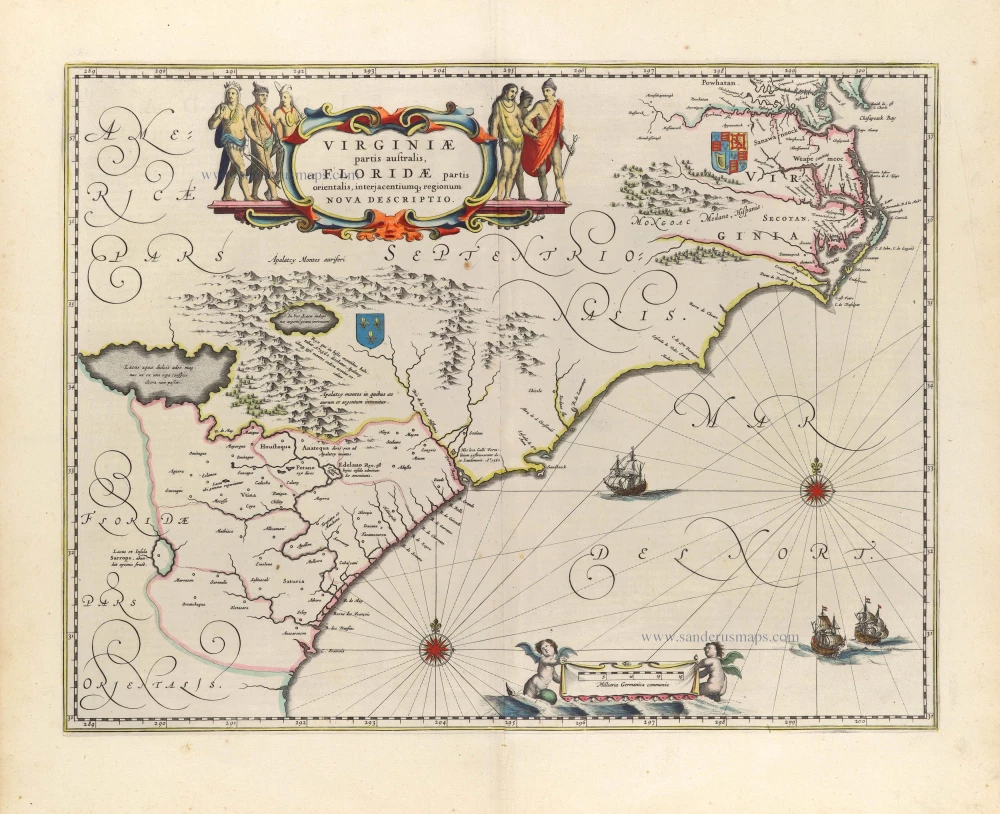
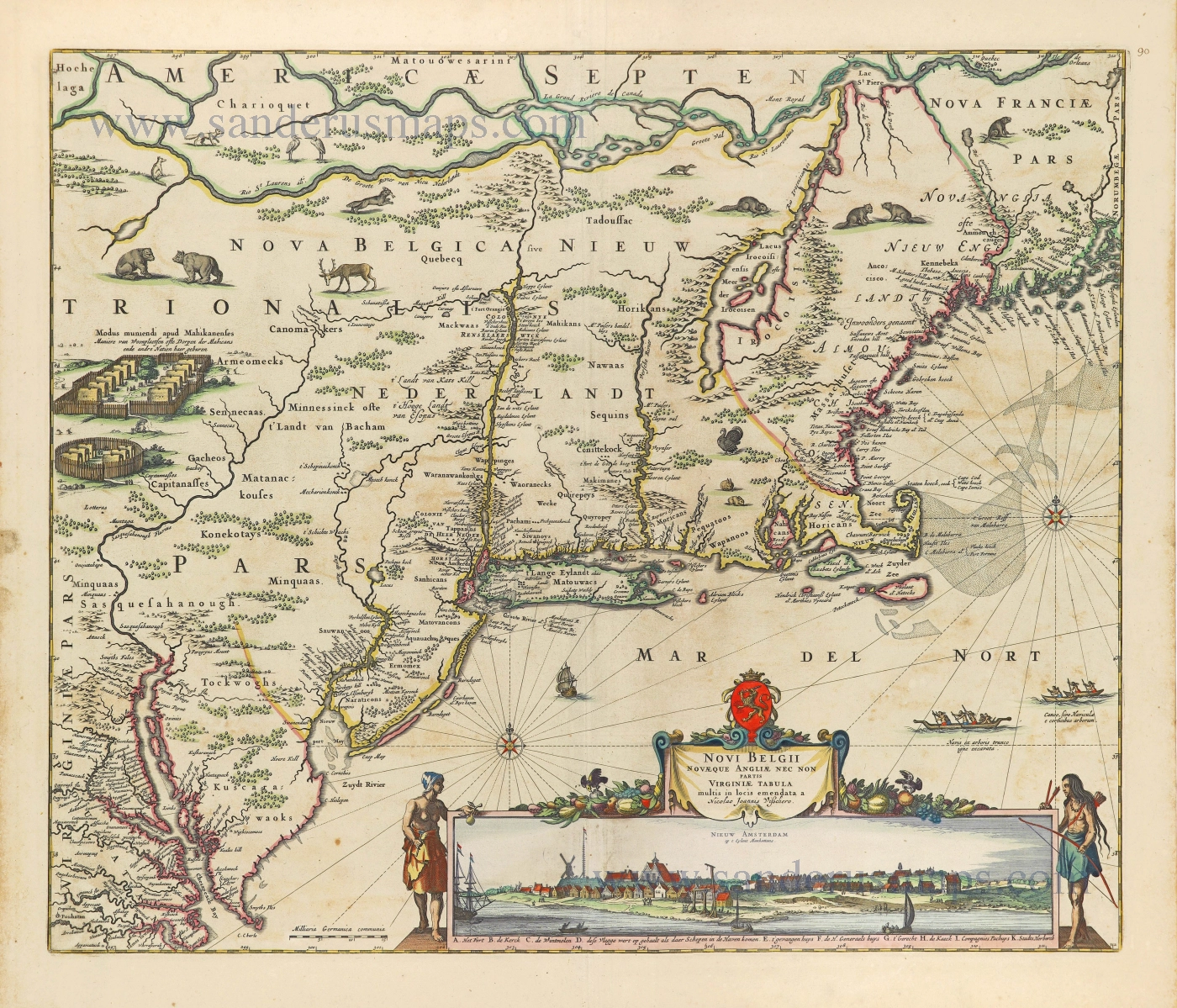
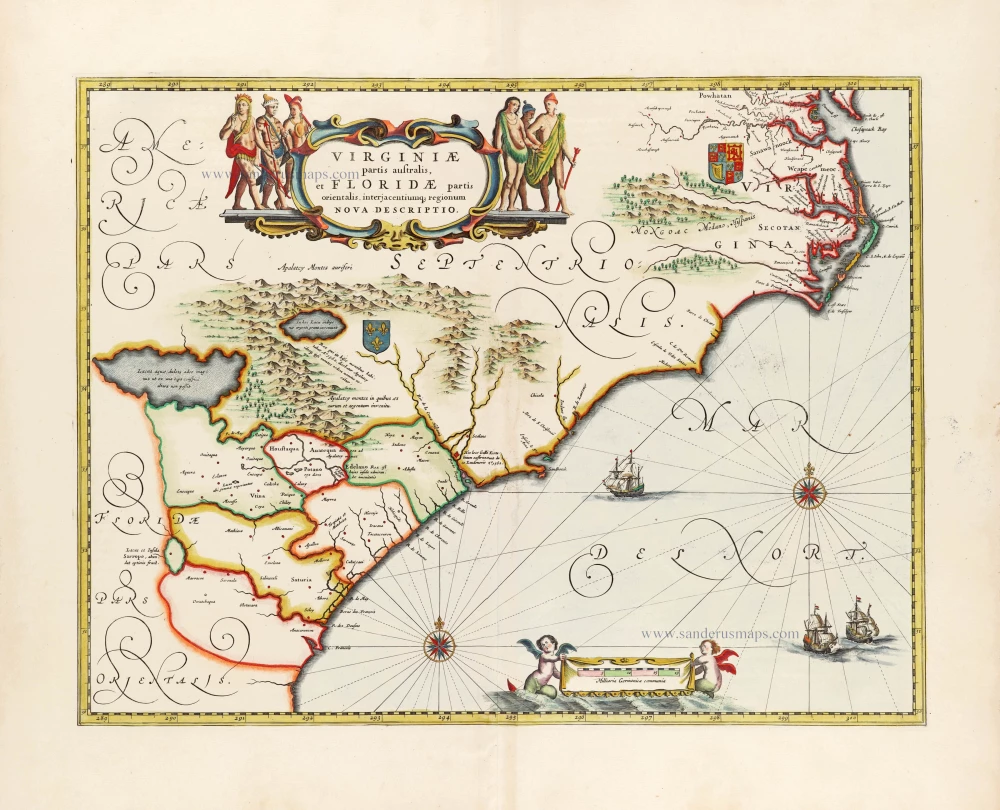
Virginia by Henricus Hondius. 1666
This is Henricus Hondius' derivative of John Smith's crucial map of Virginia, 1612. It is, however, drawn from his deceased brother Jodocus' version of 1618. The two have led separate careers for at least ten years, and in 1629, upon the death of Jodocus, Willem Blaeu acquired several plates from the estate. About thirty formed the nucleus of Blaeu's Atlantis Appendix of 1630. This challenge to the atlas of Henricus, which was by now quite dated, stimulated fierce competition between the two houses. The sale of plates must have occurred by 2 March 1630 as a contract of that date survives where Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius, angry at the sale of plates to their competitor, engaged engravers to cut some new plates after those of Jodocus within eighteen months so that they could advance their own atlas.
The Virginia was one of the first engraved as it appears in Janssonius' Atlantis Appendix of 1630. Attractively engraved, it is the only Smith derivative to bear an Indian facing the Chesapeake Bay. After the death of Janssonius in 1664, the business was left to different parties. It could not be divided in such a way that ensured the continued production of the various atlases. In 1694 Petrus Schenk acquired all of the Atlas Major plates at public auction from the heirs of Jansson van Waesberge and began issuing the maps with his own imprint. (Burden)
The Hondius Family
Jodocus Hondius the Elder (1563-1612)
Joost d’Hondt was born at Wakken (Flanders) in 1563. Two years later, his family settled in Ghent, where young Joost displayed an excellent gift for drawing and calligraphy. Through study and lessons, he developed his talents and became an engraver with a good reputation.
Due to the circumstances of the war, he moved to London in 1584, where he settled down as an engraver, instrument-maker, and map-maker. In 1587, he married Coletta van den Keere, sister of the well-known engraver Pieter van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius); some years earlier, his sister, Jacomina, had married Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus). Joost, who had Latinized his name to Jodocus Hondius, closely co-operated with his two brothers-in-law.
The political situation in the Northern Netherlands in 1593 was such that Jodocus seemed justified in establishing himself in Amsterdam, where many Antwerp printers, publishers, and engravers had gone. In this new centre of cartography, Jodocus Hondius set up his business “In de Wackere Hondt” (in the vigilant dog), this name being an allusion to his birthplace and name. He engraved many maps and published atlases and many other works, such as his continuation of Gerard Mercator’s Atlas.
He suddenly passed away in February 1612. The publishing firm of Jodocus Hondius was continued by his widow, later on, by his two sons, Jodocus Jr. and Henricus, and by his son-in-law, J. Janssonius.
Jodocus Hondius II (1594-1629) & Henricus Hondius (1597-1651)
After the father’s death, the widow and her seven children continued publishing the atlases under the name of Jodocus Hondius till 1620. The firm was reinforced by the very welcome help of Joannes Janssonius (1588-1664), who married 24-year-old Elisabeth Hondius in 1612. After 1619, Mercator’s Atlas was published under the name of Henricus Hondius.
One of the most dramatic events in the early history of commercial cartography in Amsterdam was the sale of Jodocus Hondius Jr.’s copper plates to Willem Jansz. Blaeu in 1629, the year of his death. At least 34 plates, from which Jodocus II had printed single-sheet maps for his benefit, passed into the hands of his great competitor. Immediately after that, his brother, Henricus, and Joannes Janssonius ordered the engraving of identical plates.
Henricus devoted all his energy to publishing the Atlas for an extended period. He saw its growth up to and including the fourth part in 1646; after that, his name no longer figures on the title pages. After 1638, the title of the Atlas was changed to Atlas Novus; Joannes Janssonius mainly carried it on.
The competition with the Blaeu's dates from 1630. In 1630, Willem Janszoon (=Blaeu) first attacked with his Atlantis Appendix. In 1635, Blaeu completed his Theatrum Orbis Terrarum in two volumes with French, Latin, Dutch, and German texts, prompting Henricus Hondius to speed up the enlargement of his Atlas.
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.
Nova Virginiae Tabula.
Item Number: 29956 Authenticity Guarantee
Category: Antique maps > America > North America
Old, antique map of Virginia, by Henricus Hondius, published by Joannes Janssonius.
Title: Nova Virginiae Tabula.
Amstelodami, ex officina Henrici Hondii.
Oriented to the West.
Cartographer: John Smith.
Date of the first edition: 1630.
Date of this map: 1666.
Copper engraving, printed on paper.
Image size: 380 x 500mm (14.96 x 19.69 inches).
Sheet size: 520 x 600mm (20.47 x 23.62 inches).
Verso: Latin text.
Condition: Original coloured, excellent.
Condition Rating: A+.
From: Joannis Janssonii Atlas Contractus, sive Atlantis Majoris Compendium, . . . Amsterdam, Janssonius Heirs, 1666. (Van der Krogt, 1:407)
This is Henricus Hondius' derivative of John Smith's crucial map of Virginia, 1612. It is, however, drawn from his deceased brother Jodocus' version of 1618. The two have led separate careers for at least ten years, and in 1629, upon the death of Jodocus, Willem Blaeu acquired several plates from the estate. About thirty formed the nucleus of Blaeu's Atlantis Appendix of 1630. This challenge to the atlas of Henricus, which was by now quite dated, stimulated fierce competition between the two houses. The sale of plates must have occurred by 2 March 1630 as a contract of that date survives where Henricus Hondius and his partner Joannes Janssonius, angry at the sale of plates to their competitor, engaged engravers to cut some new plates after those of Jodocus within eighteen months so that they could advance their own atlas.
The Virginia was one of the first engraved as it appears in Janssonius' Atlantis Appendix of 1630. Attractively engraved, it is the only Smith derivative to bear an Indian facing the Chesapeake Bay. After the death of Janssonius in 1664, the business was left to different parties. It could not be divided in such a way that ensured the continued production of the various atlases. In 1694 Petrus Schenk acquired all of the Atlas Major plates at public auction from the heirs of Jansson van Waesberge and began issuing the maps with his own imprint. (Burden)
The Hondius Family
Jodocus Hondius the Elder (1563-1612)
Joost d’Hondt was born at Wakken (Flanders) in 1563. Two years later, his family settled in Ghent, where young Joost displayed an excellent gift for drawing and calligraphy. Through study and lessons, he developed his talents and became an engraver with a good reputation.
Due to the circumstances of the war, he moved to London in 1584, where he settled down as an engraver, instrument-maker, and map-maker. In 1587, he married Coletta van den Keere, sister of the well-known engraver Pieter van den Keere (Petrus Kaerius); some years earlier, his sister, Jacomina, had married Pieter van den Berghe (Petrus Montanus). Joost, who had Latinized his name to Jodocus Hondius, closely co-operated with his two brothers-in-law.
The political situation in the Northern Netherlands in 1593 was such that Jodocus seemed justified in establishing himself in Amsterdam, where many Antwerp printers, publishers, and engravers had gone. In this new centre of cartography, Jodocus Hondius set up his business “In de Wackere Hondt” (in the vigilant dog), this name being an allusion to his birthplace and name. He engraved many maps and published atlases and many other works, such as his continuation of Gerard Mercator’s Atlas.
He suddenly passed away in February 1612. The publishing firm of Jodocus Hondius was continued by his widow, later on, by his two sons, Jodocus Jr. and Henricus, and by his son-in-law, J. Janssonius.
Jodocus Hondius II (1594-1629) & Henricus Hondius (1597-1651)
After the father’s death, the widow and her seven children continued publishing the atlases under the name of Jodocus Hondius till 1620. The firm was reinforced by the very welcome help of Joannes Janssonius (1588-1664), who married 24-year-old Elisabeth Hondius in 1612. After 1619, Mercator’s Atlas was published under the name of Henricus Hondius.
One of the most dramatic events in the early history of commercial cartography in Amsterdam was the sale of Jodocus Hondius Jr.’s copper plates to Willem Jansz. Blaeu in 1629, the year of his death. At least 34 plates, from which Jodocus II had printed single-sheet maps for his benefit, passed into the hands of his great competitor. Immediately after that, his brother, Henricus, and Joannes Janssonius ordered the engraving of identical plates.
Henricus devoted all his energy to publishing the Atlas for an extended period. He saw its growth up to and including the fourth part in 1646; after that, his name no longer figures on the title pages. After 1638, the title of the Atlas was changed to Atlas Novus; Joannes Janssonius mainly carried it on.
The competition with the Blaeu's dates from 1630. In 1630, Willem Janszoon (=Blaeu) first attacked with his Atlantis Appendix. In 1635, Blaeu completed his Theatrum Orbis Terrarum in two volumes with French, Latin, Dutch, and German texts, prompting Henricus Hondius to speed up the enlargement of his Atlas.
The Janssonius Family
Joannes Janssonius (Arnhem, 1588-1664), son of the Arnhem publisher Jan Janssen, married Elisabeth Hondius, daughter of Jodocus Hondius, in Amsterdam in 1612. After his marriage, he settled down in this town as a bookseller and publisher of cartographic material. In 1618, he established himself in Amsterdam next door to Blaeu’s bookshop. He entered into serious competition with Willem Jansz. Blaeu when copying Blaeu’s Licht der Zeevaert after the expiration of the privilege in 1620. His activities concerned the publication of atlases, books, single maps, and an extensive book trade with branches in Frankfurt, Danzig, Stockholm, Copenhagen, Berlin, Koningsbergen, Geneva, and Lyon. In 1631, he began publishing atlases together with Henricus Hondius.
In the early 1640s, Henricus Hondius left the atlas publishing business to Janssonius. Competition with Joan Blaeu, Willem’s son and successor, in atlas production, prompted Janssonius to enlarge his Atlas Novus finally into a work of six volumes, into which a sea atlas and an atlas of the Old World were inserted. Other atlases published by Janssonius are Mercator’s Atlas Minor, Hornius’s historical atlas (1652), the townbooks in eight volumes (1657), Cellarius’s Atlas Coelestis and several sea atlases and pilot guides.
After the death of Joannes Janssonius, the shop and publishing firm were continued by the heirs under the direction of Johannes van Waesbergen (c. 1616-1681), son-in-law of Joannes Janssonius. Van Waesbergen added Janssonius's name to his own.
In 1676, Joannes Janssonius’s heirs sold by auction “all the remaining Atlases in Latin, French, High and Low German, as well as the Stedeboecken in Latin, in 8 volumes, bound and unbound, maps, plates belonging to the Atlas and Stedeboecken.” The copperplates from Janssonius’s atlases were afterwards sold to Schenk and Valck.